Tharawal language
The Tharawal language (Thurawal, Dharawal, Wodiwodi) is an Australian Aboriginal language of New South Wales.
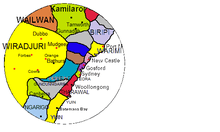
Traditional lands of Australian Aboriginal tribes around Sydney, New South Wales.[4]
| Tharawal | |
|---|---|
| Dharawal | |
| Region | New South Wales, Australia |
| Ethnicity | Tharawal, Wodiwodi, Gweagal |
| Revival | 27 self-identified speakers (2016 census)[1] |
Pama–Nyungan
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | tbh |
| Glottolog | thur1254[2] |
| AIATSIS[3] | S59 |
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Velar | Alveolar | Dental | Palatal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | b | ɡ | d | d̪ | ɟ |
| Nasal | m | ŋ | n | n̪ | ɲ |
| Lateral | l | ||||
| Rhotic | r | ||||
| Approximant | w | j |
Vowels
Vowels are phonemically /a i u/.[5]
gollark: If I say [REDACTED] it should pick a random thing without telling me.
gollark: Where are my recreational nuclear weapons?
gollark: BEES
gollark: WHY CAN I NOT COMBINE SMOKE WITH HOURGLASS
gollark: Technically, I can just read them out of the apiodatabasees.
References
- "Census 2016, Language spoken at home by Sex (SA2+)". stat.data.abs.gov.au. ABS. Retrieved 30 October 2017.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Thurawal". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- S59 Tharawal at the Australian Indigenous Languages Database, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies
- This map is indicative only.
- Eades, Diana K. (1976). The Dharawal and Dhurga Languages of the New South Wales South Coast.
External links
- Bibliography of Tharawal people and language resources, at the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.