Taylor series
In mathematics, the Taylor series of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor's series are named after Brook Taylor who introduced them in 1715.
| Part of a series of articles about | ||||||
| Calculus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
||||||
|
Specialized |
||||||
If zero is the point where the derivatives are considered, a Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the 18th century.
The partial sum formed by the n first terms of a Taylor series is a polynomial of degree n that is called the nth Taylor polynomial of the function. Taylor polynomials are approximations of a function, which become generally better when n increases. Taylor's theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error introduced by the use of such approximations. If the Taylor series of a function is convergent, its sum is the limit of the infinite sequence of the Taylor polynomials. A function may be not equal to the sum of its Taylor series, even if its Taylor series is convergent. A function is analytic at a point x if it is equal to the sum of its Taylor series in some open interval (or open disk in the complex plane) containing x. This implies that the function is analytic at every point of the interval (or disk).
Definition
The Taylor series of a real or complex-valued function f (x) that is infinitely differentiable at a real or complex number a is the power series
where n! denotes the factorial of n. In the more compact sigma notation, this can be written as
where f(n)(a) denotes the nth derivative of f evaluated at the point a. (The derivative of order zero of f is defined to be f itself and (x − a)0 and 0! are both defined to be 1.)
When a = 0, the series is also called a Maclaurin series.[1]
Examples
The Taylor series for any polynomial is the polynomial itself.
The Maclaurin series for 1/1 − x is the geometric series
so the Taylor series for 1/x at a = 1 is
By integrating the above Maclaurin series, we find the Maclaurin series for ln(1 − x), where ln denotes the natural logarithm:
The corresponding Taylor series for ln x at a = 1 is
and more generally, the corresponding Taylor series for ln x at an arbitrary nonzero point a is:
The Taylor series for the exponential function ex at a = 0 is
The above expansion holds because the derivative of ex with respect to x is also ex, and e0 equals 1. This leaves the terms (x − 0)n in the numerator and n! in the denominator for each term in the infinite sum.
History
The Greek philosopher Zeno considered the problem of summing an infinite series to achieve a finite result, but rejected it as an impossibility;[2] the result was Zeno's paradox. Later, Aristotle proposed a philosophical resolution of the paradox, but the mathematical content was apparently unresolved until taken up by Archimedes, as it had been prior to Aristotle by the Presocratic Atomist Democritus. It was through Archimedes's method of exhaustion that an infinite number of progressive subdivisions could be performed to achieve a finite result.[3] Liu Hui independently employed a similar method a few centuries later.[4]
In the 14th century, the earliest examples of the use of Taylor series and closely related methods were given by Madhava of Sangamagrama.[5][6] Though no record of his work survives, writings of later Indian mathematicians suggest that he found a number of special cases of the Taylor series, including those for the trigonometric functions of sine, cosine, tangent, and arctangent. The Kerala School of Astronomy and Mathematics further expanded his works with various series expansions and rational approximations until the 16th century.
In the 17th century, James Gregory also worked in this area and published several Maclaurin series. It was not until 1715 however that a general method for constructing these series for all functions for which they exist was finally provided by Brook Taylor,[7] after whom the series are now named.
The Maclaurin series was named after Colin Maclaurin, a professor in Edinburgh, who published the special case of the Taylor result in the 18th century.
Analytic functions
If f (x) is given by a convergent power series in an open disk (or interval in the real line) centred at b in the complex plane, it is said to be analytic in this disk. Thus for x in this disk, f is given by a convergent power series
Differentiating by x the above formula n times, then setting x = b gives:
and so the power series expansion agrees with the Taylor series. Thus a function is analytic in an open disk centred at b if and only if its Taylor series converges to the value of the function at each point of the disk.
If f (x) is equal to its Taylor series for all x in the complex plane, it is called entire. The polynomials, exponential function ex, and the trigonometric functions sine and cosine, are examples of entire functions. Examples of functions that are not entire include the square root, the logarithm, the trigonometric function tangent, and its inverse, arctan. For these functions the Taylor series do not converge if x is far from b. That is, the Taylor series diverges at x if the distance between x and b is larger than the radius of convergence. The Taylor series can be used to calculate the value of an entire function at every point, if the value of the function, and of all of its derivatives, are known at a single point.
Uses of the Taylor series for analytic functions include:
- The partial sums (the Taylor polynomials) of the series can be used as approximations of the function. These approximations are good if sufficiently many terms are included.
- Differentiation and integration of power series can be performed term by term and is hence particularly easy.
- An analytic function is uniquely extended to a holomorphic function on an open disk in the complex plane. This makes the machinery of complex analysis available.
- The (truncated) series can be used to compute function values numerically, (often by recasting the polynomial into the Chebyshev form and evaluating it with the Clenshaw algorithm).
- Algebraic operations can be done readily on the power series representation; for instance, Euler's formula follows from Taylor series expansions for trigonometric and exponential functions. This result is of fundamental importance in such fields as harmonic analysis.
- Approximations using the first few terms of a Taylor series can make otherwise unsolvable problems possible for a restricted domain; this approach is often used in physics.
Approximation error and convergence

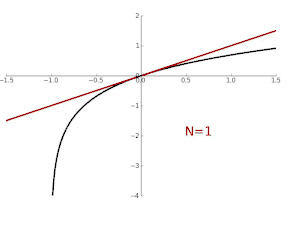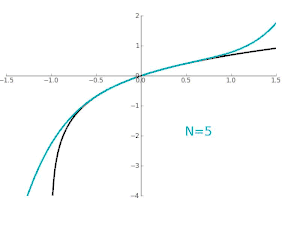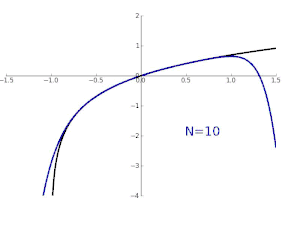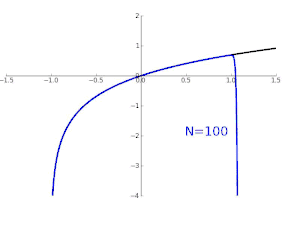
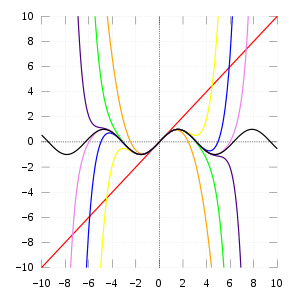
Pictured on the right is an accurate approximation of sin x around the point x = 0. The pink curve is a polynomial of degree seven:
The error in this approximation is no more than |x|9/9!. In particular, for −1 < x < 1, the error is less than 0.000003.
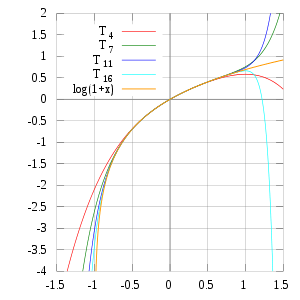
In contrast, also shown is a picture of the natural logarithm function ln(1 + x) and some of its Taylor polynomials around a = 0. These approximations converge to the function only in the region −1 < x ≤ 1; outside of this region the higher-degree Taylor polynomials are worse approximations for the function. This is similar to Runge's phenomenon.
The error incurred in approximating a function by its nth-degree Taylor polynomial is called the remainder or residual and is denoted by the function Rn(x). Taylor's theorem can be used to obtain a bound on the size of the remainder.
In general, Taylor series need not be convergent at all. And in fact the set of functions with a convergent Taylor series is a meager set in the Fréchet space of smooth functions. And even if the Taylor series of a function f does converge, its limit need not in general be equal to the value of the function f (x). For example, the function
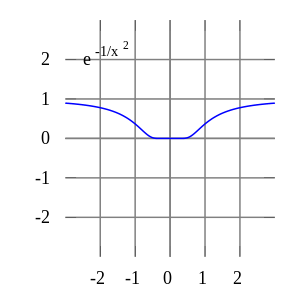
is infinitely differentiable at x = 0, and has all derivatives zero there. Consequently, the Taylor series of f (x) about x = 0 is identically zero. However, f (x) is not the zero function, so does not equal its Taylor series around the origin. Thus, f (x) is an example of a non-analytic smooth function.
In real analysis, this example shows that there are infinitely differentiable functions f (x) whose Taylor series are not equal to f (x) even if they converge. By contrast, the holomorphic functions studied in complex analysis always possess a convergent Taylor series, and even the Taylor series of meromorphic functions, which might have singularities, never converge to a value different from the function itself. The complex function e−1/z2, however, does not approach 0 when z approaches 0 along the imaginary axis, so it is not continuous in the complex plane and its Taylor series is undefined at 0.
More generally, every sequence of real or complex numbers can appear as coefficients in the Taylor series of an infinitely differentiable function defined on the real line, a consequence of Borel's lemma. As a result, the radius of convergence of a Taylor series can be zero. There are even infinitely differentiable functions defined on the real line whose Taylor series have a radius of convergence 0 everywhere.[8]
A function cannot be written as a Taylor series centred at a singularity; in these cases, one can often still achieve a series expansion if one allows also negative powers of the variable x; see Laurent series. For example, f (x) = e−1/x2 can be written as a Laurent series.
Generalization
There is, however, a generalization[9][10] of the Taylor series that does converge to the value of the function itself for any bounded continuous function on (0,∞), using the calculus of finite differences. Specifically, one has the following theorem, due to Einar Hille, that for any t > 0,
Here Δn
h is the nth finite difference operator with step size h. The series is precisely the Taylor series, except that divided differences appear in place of differentiation: the series is formally similar to the Newton series. When the function f is analytic at a, the terms in the series converge to the terms of the Taylor series, and in this sense generalizes the usual Taylor series.
In general, for any infinite sequence ai, the following power series identity holds:
So in particular,
The series on the right is the expectation value of f (a + X), where X is a Poisson-distributed random variable that takes the value jh with probability e−t/h·(t/h)j/j!. Hence,
The law of large numbers implies that the identity holds.[11]
List of Maclaurin series of some common functions
Several important Maclaurin series expansions follow.[12] All these expansions are valid for complex arguments x.
Exponential function
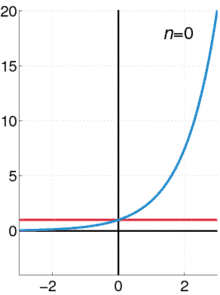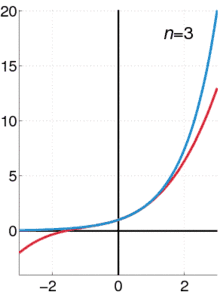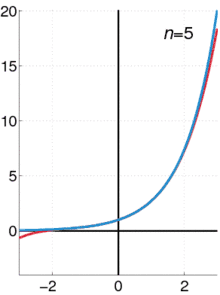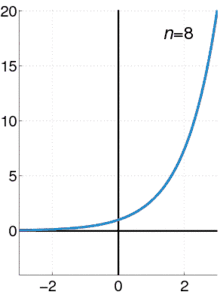
The exponential function (with base e) has Maclaurin series
- .
It converges for all x.
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm (with base e) has Maclaurin series
They converge for . (In addition, the series for ln(1 − x) converges for x = −1, and the series for ln(1 + x) converges for x = 1.)
Geometric series
The geometric series and its derivatives have Maclaurin series
All are convergent for . These are special cases of the binomial series given in the next section.
Binomial series
The binomial series is the power series
whose coefficients are the generalized binomial coefficients
(If n = 0, this product is an empty product and has value 1.) It converges for for any real or complex number α.
When α = −1, this is essentially the infinite geometric series mentioned in the previous section. The special cases α = 1/2 and α = −1/2 give the square root function and its inverse:
When only the linear term is retained, this simplifies to the binomial approximation.
Trigonometric functions
The usual trigonometric functions and their inverses have the following Maclaurin series:
All angles are expressed in radians. The numbers Bk appearing in the expansions of tan x are the Bernoulli numbers. The Ek in the expansion of sec x are Euler numbers.
Hyperbolic functions
The hyperbolic functions have Maclaurin series closely related to the series for the corresponding trigonometric functions:
The numbers Bk appearing in the series for tanh x are the Bernoulli numbers.
Calculation of Taylor series
Several methods exist for the calculation of Taylor series of a large number of functions. One can attempt to use the definition of the Taylor series, though this often requires generalizing the form of the coefficients according to a readily apparent pattern. Alternatively, one can use manipulations such as substitution, multiplication or division, addition or subtraction of standard Taylor series to construct the Taylor series of a function, by virtue of Taylor series being power series. In some cases, one can also derive the Taylor series by repeatedly applying integration by parts. Particularly convenient is the use of computer algebra systems to calculate Taylor series.
First example
In order to compute the 7th degree Maclaurin polynomial for the function
- ,
one may first rewrite the function as
- .
The Taylor series for the natural logarithm is (using the big O notation)
and for the cosine function
- .
The latter series expansion has a zero constant term, which enables us to substitute the second series into the first one and to easily omit terms of higher order than the 7th degree by using the big O notation:
Since the cosine is an even function, the coefficients for all the odd powers x, x3, x5, x7, ... have to be zero.
Second example
Suppose we want the Taylor series at 0 of the function
We have for the exponential function
and, as in the first example,
Assume the power series is
Then multiplication with the denominator and substitution of the series of the cosine yields
Collecting the terms up to fourth order yields
The values of can be found by comparison of coefficients with the top expression for , yielding:
Third example
Here we employ a method called "indirect expansion" to expand the given function. This method uses the known Taylor expansion of the exponential function. In order to expand (1 + x)ex as a Taylor series in x, we use the known Taylor series of function ex:
Thus,
Taylor series as definitions
Classically, algebraic functions are defined by an algebraic equation, and transcendental functions (including those discussed above) are defined by some property that holds for them, such as a differential equation. For example, the exponential function is the function which is equal to its own derivative everywhere, and assumes the value 1 at the origin. However, one may equally well define an analytic function by its Taylor series.
Taylor series are used to define functions and "operators" in diverse areas of mathematics. In particular, this is true in areas where the classical definitions of functions break down. For example, using Taylor series, one may extend analytic functions to sets of matrices and operators, such as the matrix exponential or matrix logarithm.
In other areas, such as formal analysis, it is more convenient to work directly with the power series themselves. Thus one may define a solution of a differential equation as a power series which, one hopes to prove, is the Taylor series of the desired solution.
Taylor series in several variables
The Taylor series may also be generalized to functions of more than one variable with[13][14]
For example, for a function that depends on two variables, x and y, the Taylor series to second order about the point (a, b) is
where the subscripts denote the respective partial derivatives.
A second-order Taylor series expansion of a scalar-valued function of more than one variable can be written compactly as
where D f (a) is the gradient of f evaluated at x = a and D2 f (a) is the Hessian matrix. Applying the multi-index notation the Taylor series for several variables becomes
which is to be understood as a still more abbreviated multi-index version of the first equation of this paragraph, with a full analogy to the single variable case.
Example

In order to compute a second-order Taylor series expansion around point (a, b) = (0, 0) of the function
one first computes all the necessary partial derivatives:
Evaluating these derivatives at the origin gives the Taylor coefficients
Substituting these values in to the general formula
produces
Since ln(1 + y) is analytic in |y| < 1, we have
Comparison with Fourier series
The trigonometric Fourier series enables one to express a periodic function (or a function defined on a closed interval [a,b]) as an infinite sum of trigonometric functions (sines and cosines). In this sense, the Fourier series is analogous to Taylor series, since the latter allows one to express a function as an infinite sum of powers. Nevertheless, the two series differ from each other in several relevant issues:
- The finite truncations of the Taylor series of f (x) about the point x = a are all exactly equal to f at a. In contrast, the Fourier series is computed by integrating over an entire interval, so there is generally no such point where all the finite truncations of the series are exact.
- The computation of Taylor series requires the knowledge of the function on an arbitrary small neighbourhood of a point, whereas the computation of the Fourier series requires knowing the function on its whole domain interval. In a certain sense one could say that the Taylor series is "local" and the Fourier series is "global".
- The Taylor series is defined for a function which has infinitely many derivatives at a single point, whereas the Fourier series is defined for any integrable function. In particular, the function could be nowhere differentiable. (For example, f (x) could be a Weierstrass function.)
- The convergence of both series has very different properties. Even if the Taylor series has positive convergence radius, the resulting series may not coincide with the function; but if the function is analytic then the series converges pointwise to the function, and uniformly on every compact subset of the convergence interval. Concerning the Fourier series, if the function is square-integrable then the series converges in quadratic mean, but additional requirements are needed to ensure the pointwise or uniform convergence (for instance, if the function is periodic and of class C1 then the convergence is uniform).
- Finally, in practice one wants to approximate the function with a finite number of terms, say with a Taylor polynomial or a partial sum of the trigonometric series, respectively. In the case of the Taylor series the error is very small in a neighbourhood of the point where it is computed, while it may be very large at a distant point. In the case of the Fourier series the error is distributed along the domain of the function.
See also
Notes
- Thomas & Finney 1996, §8.9
- Lindberg, David (2007). The Beginnings of Western Science (2nd ed.). University of Chicago Press. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-226-48205-7.
- Kline, M. (1990). Mathematical Thought from Ancient to Modern Times. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 35–37. ISBN 0-19-506135-7.
- Boyer, C.; Merzbach, U. (1991). A History of Mathematics (Second revised ed.). John Wiley and Sons. pp. 202–203. ISBN 0-471-09763-2.
- "Neither Newton nor Leibniz – The Pre-History of Calculus and Celestial Mechanics in Medieval Kerala" (PDF). MAT 314. Canisius College. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-02-23. Retrieved 2006-07-09.
- S. G. Dani (2012). "Ancient Indian Mathematics – A Conspectus". Resonance. 17 (3): 236–246. doi:10.1007/s12045-012-0022-y.
- Taylor, Brook (1715). Methodus Incrementorum Directa et Inversa [Direct and Reverse Methods of Incrementation] (in Latin). London. p. 21–23 (Prop. VII, Thm. 3, Cor. 2). Translated into English in Struik, D. J. (1969). A Source Book in Mathematics 1200–1800. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. pp. 329–332.
- Rudin, Walter (1980), Real and Complex Analysis, New Dehli: McGraw-Hill, p. 418, Exercise 13, ISBN 0-07-099557-5
- Feller, William (1971), An introduction to probability theory and its applications, Volume 2 (3rd ed.), Wiley, pp. 230–232.
- Hille, Einar; Phillips, Ralph S. (1957), Functional analysis and semi-groups, AMS Colloquium Publications, 31, American Mathematical Society, pp. 300–327.
- Feller, William (1970). An introduction to probability theory and its applications. 2 (3 ed.). p. 231.
- Most of these can be found in (Abramowitz & Stegun 1970).
- Lars Hörmander (1990), The analysis of partial differential operators, volume 1, Springer, Eqq. 1.1.7 and 1.1.7′
- Duistermaat; Kolk (2010), Distributions: Theory and applications, Birkhauser, ch. 6
References
- Abramowitz, Milton; Stegun, Irene A. (1970), Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, New York: Dover Publications, Ninth printing
- Thomas, George B., Jr.; Finney, Ross L. (1996), Calculus and Analytic Geometry (9th ed.), Addison Wesley, ISBN 0-201-53174-7
- Greenberg, Michael (1998), Advanced Engineering Mathematics (2nd ed.), Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-321431-1
External links
- "Taylor series", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Taylor Series". MathWorld.
- Taylor polynomial - practical introduction
- Madhava of Sangamagramma
- "discussion of the Parker-Sochacki Method"
- Another Taylor visualisation — where you can choose the point of the approximation and the number of derivatives
- Taylor series revisited for numerical methods at Numerical Methods for the STEM Undergraduate
- Cinderella 2: Taylor expansion
- Taylor series
- Inverse trigonometric functions Taylor series
- "Essence of Calculus: Taylor series" – via YouTube.
