Limit of a sequence
In mathematics, the limit of a sequence is the value that the terms of a sequence "tend to".[1] If such a limit exists, the sequence is called convergent. A sequence that does not converge is said to be divergent.[2] The limit of a sequence is said to be the fundamental notion on which the whole of analysis ultimately rests.[1]

| n | n sin(1/n) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.841471 |
| 2 | 0.958851 |
| ... | |
| 10 | 0.998334 |
| ... | |
| 100 | 0.999983 |
As the positive integer becomes larger and larger, the value becomes arbitrarily close to . We say that "the limit of the sequence equals ."
Limits can be defined in any metric or topological space, but are usually first encountered in the real numbers.
History
The Greek philosopher Zeno of Elea is famous for formulating paradoxes that involve limiting processes.
Leucippus, Democritus, Antiphon, Eudoxus, and Archimedes developed the method of exhaustion, which uses an infinite sequence of approximations to determine an area or a volume. Archimedes succeeded in summing what is now called a geometric series.
Newton dealt with series in his works on Analysis with infinite series (written in 1669, circulated in manuscript, published in 1711), Method of fluxions and infinite series (written in 1671, published in English translation in 1736, Latin original published much later) and Tractatus de Quadratura Curvarum (written in 1693, published in 1704 as an Appendix to his Optiks). In the latter work, Newton considers the binomial expansion of (x + o)n which he then linearizes by taking limits (letting o → 0).
In the 18th century, mathematicians such as Euler succeeded in summing some divergent series by stopping at the right moment; they did not much care whether a limit existed, as long as it could be calculated. At the end of the century, Lagrange in his Théorie des fonctions analytiques (1797) opined that the lack of rigour precluded further development in calculus. Gauss in his etude of hypergeometric series (1813) for the first time rigorously investigated under which conditions a series converged to a limit.
The modern definition of a limit (for any ε there exists an index N so that ...) was given by Bernhard Bolzano (Der binomische Lehrsatz, Prague 1816, little noticed at the time) and by Karl Weierstrass in the 1870s.
Real numbers
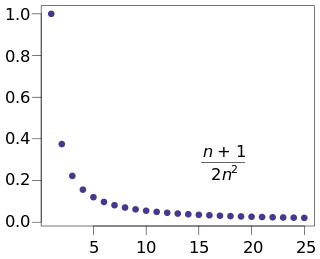
In the real numbers, a number is the limit of the sequence if the numbers in the sequence become closer and closer to and not to any other number.
Examples
- If for constant c, then .[proof 1]
- If , then .[proof 2]
- If when is even, and when is odd, then . (The fact that whenever is odd is irrelevant.)
- Given any real number, one may easily construct a sequence that converges to that number by taking decimal approximations. For example, the sequence converges to . Note that the decimal representation is the limit of the previous sequence, defined by
- .
- Finding the limit of a sequence is not always obvious. Two examples are (the limit of which is the number e) and the Arithmetic–geometric mean. The squeeze theorem is often useful in such cases.
Formal definition
We call the limit of the sequence if the following condition holds:
- For each real number , there exists a natural number such that, for every natural number , we have .
In other words, for every measure of closeness , the sequence's terms are eventually that close to the limit. The sequence is said to converge to or tend to the limit , written or .
Symbolically, this is:
If a sequence converges to some limit, then it is convergent; otherwise it is divergent.
Illustration
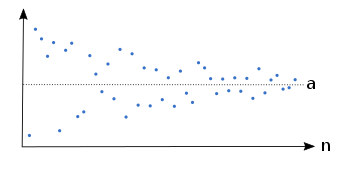 Example of a sequence which converges to the limit .
Example of a sequence which converges to the limit .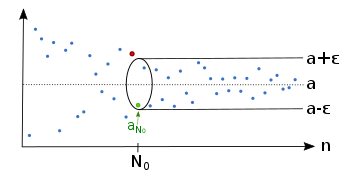 Regardless which we have, there is an index , so that the sequence lies afterwards completely in the epsilon tube .
Regardless which we have, there is an index , so that the sequence lies afterwards completely in the epsilon tube .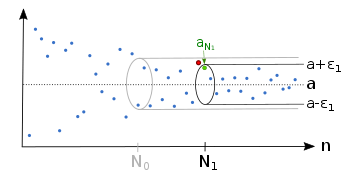 There is also for a smaller an index , so that the sequence is afterwards inside the epsilon tube .
There is also for a smaller an index , so that the sequence is afterwards inside the epsilon tube .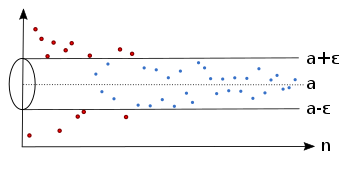 For each there are only finitely many sequence members outside the epsilon tube.
For each there are only finitely many sequence members outside the epsilon tube.
Properties
Limits of sequences behave well with respect to the usual arithmetic operations. If and , then , and, if neither b nor any is zero, .
For any continuous function f, if then . In fact, any real-valued function f is continuous if and only if it preserves the limits of sequences (though this is not necessarily true when using more general notions of continuity).
Some other important properties of limits of real sequences include the following (provided, in each equation below, that the limits on the right exist).
- The limit of a sequence is unique.
- provided
- If for all greater than some , then
- (Squeeze theorem) If for all , and , then .
- If a sequence is bounded and monotonic then it is convergent.
- A sequence is convergent if and only if every subsequence is convergent.
- If every subsequence of a sequence has its own subsequence which converges to the same point, then the original sequence converges to that point.
These properties are extensively used to prove limits without the need to directly use the cumbersome formal definition. Once proven that it becomes easy to show that , (), using the properties above.
Infinite limits
A sequence is said to tend to infinity, written or if, for every K, there is an N such that, for every , ; that is, the sequence terms are eventually larger than any fixed K. Similarly, if, for every K, there is an N such that, for every , . If a sequence tends to infinity, or to minus infinity, then it is divergent (however, a divergent sequence need not tend to plus or minus infinity: take for example ).
Metric spaces
Definition
A point of the metric space is the limit of the sequence if, for all , there is an such that, for every , . This coincides with the definition given for real numbers when and .
Properties
For any continuous function f, if then . In fact, a function f is continuous if and only if it preserves the limits of sequences.
Limits of sequences are unique when they exist, as distinct points are separated by some positive distance, so for less than half this distance, sequence terms cannot be within a distance of both points.
Topological spaces
Definition
A point x of the topological space (X, τ) is a limit of the sequence (xn) if, for every neighbourhood U of x, there is an N such that, for every , . This coincides with the definition given for metric spaces if (X, d) is a metric space and is the topology generated by d.
A limit of a sequence of points in a topological space T is a special case of a limit of a function: the domain is in the space with the induced topology of the affinely extended real number system, the range is T, and the function argument n tends to +∞, which in this space is a limit point of .
Properties
If X is a Hausdorff space then limits of sequences are unique where they exist. Note that this need not be the case in general; in particular, if two points x and y are topologically indistinguishable, any sequence that converges to x must converge to y and vice versa.
Cauchy sequences
A Cauchy sequence is a sequence whose terms ultimately become arbitrarily close together, after sufficiently many initial terms have been discarded. The notion of a Cauchy sequence is important in the study of sequences in metric spaces, and, in particular, in real analysis. One particularly important result in real analysis is the Cauchy criterion for convergence of sequences: A sequence of real numbers is convergent if and only if it is a Cauchy sequence. This remains true in other complete metric spaces.
Definition in hyperreal numbers
The definition of the limit using the hyperreal numbers formalizes the intuition that for a "very large" value of the index, the corresponding term is "very close" to the limit. More precisely, a real sequence tends to L if for every infinite hypernatural H, the term xH is infinitely close to L, i.e., the difference xH − L is infinitesimal. Equivalently, L is the standard part of xH
Thus, the limit can be defined by the formula
where the limit exists if and only if the righthand side is independent of the choice of an infinite H.
See also
- Limit of a net — A net is a topological generalization of a sequence.
- Modes of convergence
- Shift rule
Notes
- Courant (1961), p. 29.
- Courant (1961), p. 39.
Proofs
- Proof: choose . For every ,
- Proof: choose + 1 (the floor function). For every , .
References
- Courant, Richard (1961). "Differential and Integral Calculus Volume I", Blackie & Son, Ltd., Glasgow.
- Frank Morley and James Harkness A treatise on the theory of functions (New York: Macmillan, 1893)