Symphony No. 104 (Haydn)
The Symphony No. 104 in D major (H. 1/104) is Joseph Haydn's final symphony. It is the last of the twelve London symphonies, and is known (somewhat arbitrarily, given the existence of eleven others) as the London Symphony. In Germany it is commonly known as the Salomon Symphony after Johann Peter Salomon, who arranged Haydn's two tours of London, even though it is one of three of the last twelve symphonies written for Viotti's Opera Concerts, rather than for Salomon.[1]
The work was composed in 1795 while Haydn was living in London, and premiered there at the King's Theatre on 4 May 1795, in a concert featuring exclusively Haydn's own compositions and directed by the composer.[2] The premiere was a success; Haydn wrote in his diary "The whole company was thoroughly pleased and so was I. I made 4000 gulden on this evening: such a thing is possible only in England."[3]
Scoring
The work is scored for two flutes, two oboes, two clarinets in A, two bassoons, two horns in D and G, two trumpets in D, timpani and strings.[4]
Movements
First movement
The symphony opens with a slow and grand introduction in D minor, whose first two bars are as follows:
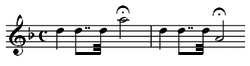
This leads to the main body of the sonata form movement, in D major. Its opening theme is as follows:

The movement is monothematic: the second theme is simply the first theme transposed to A major. The exposition is in D major, with the strings playing the first theme. The theme goes straight into A major with the woodwinds to form a second theme. The exposition closes with a codetta and is followed by the development which begins in B minor, using the rhythmic pattern of the second half of the theme. The development ends with the full orchestra. In the recapitulation, the first theme is heard again in D Major. It uses imitative patterns of the woodwinds in the second theme. The movement closes with a coda, also in D major.
Second movement
This movement, in G major, opens with the main theme in the strings. After this, a brief episode highlighting A minor and D minor leads to a modified repeat of the main theme in both strings and bassoon. From here, a second section begins which modulates to various other keys, including G minor and B♭ major, but continues to feature the melody of the main theme. After arriving on the dominant of G major, the music of the first section returns. The rest of the movement consists of a modification of the first section of music, with several changes in rhythm and more prominence to the winds, especially the flute.
Third movement
The third movement is a minuet and trio in D major. The minuet section consists of a rounded binary (A,B,A') form with an opening section emphasizing the tonic, while the second section visits the relative minor (B minor) and the dominant (A major). The trio is in B♭ major, and uses the oboe and bassoon extensively. Like in the minuet, this trio's B section emphasizes the relative minor (in this case, G minor). The trio ends with a transition back to dominant of the main key in preparation for the return to the minuet.
Fourth movement

The exuberant finale, in fast tempo and in sonata form, opens in the mode of folk music using a drone bass and a theme often claimed to have originated as a Croatian folk song; for details see Haydn and folk music. The development section settles on the dominant of the main key, as is typical, but the recapitulation does not occur immediately. Instead, the development is extended with a section in F♯ minor, after which the recapitulation in D major follows immediately.
See also
- List of symphonies by name
References
- Steinberg, Michael. "The Symphony: a listeners guide". p. 245. Oxford University Press, 1995.
- Michael Steinberg, "The Symphony: A Listeners Guide" (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 1995), p. 246.
- Steinberg, Michael. "The Symphony: a listeners guide". pp. 245–47. Oxford University Press, 1995.
- Hoboken, Anthony van (1957). Joseph Haydn: Thematisch-bibliographisches Werkverzeichnis. Main: B. Schott's Söhne. p. 221.
External links
- The Finale can be found on http://www.pointclassics.com/dl/2650902.4.Finale-%20spirituoso.48k.mp3 to listen to.
- Piano reduction (pdf)
- Symphony No. 104 is available in PDF format created from MuseData.
- Symphony No. 104: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)