Stepper Point
Stepper Point (Cornish: Penn Stuppert)[1] is a headland on the Atlantic coast in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is at grid reference SW911781.




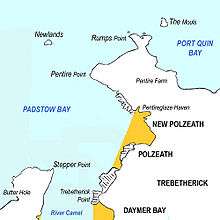
Stepper Point and Pentire Point stand at either side of the mouth of the River Camel; Stepper to the south-west, Pentire to the north-east.
The headland above Stepper Point is topped by a stone tower, built as a 'day mark' to serve as a navigation beacon for seafarers during daylight. It is referred to locally as the Daymark. There is also a coastguard lookout building on the headland. This is reached by a metalled road from the tiny hamlet of Crugmeer but vehicle access is restricted.
The South West Coast Path closely follows the coastline of the headland. The three-mile (5 km) stretch of coast path from Padstow to Stepper Point has fairly easy gradients and is well-surfaced; beyond Stepper towards Trevone, the path becomes rougher and more sharply graded.
Sightseeing boat tours regularly travel along the coast from the nearby port of Padstow.
Geography
The headland rises to 242 feet (74 m) at its highest point. The land is used for farming and the remains of several defunct stone quarries can be seen.
The coast to the east of Stepper Point is on the estuary of the River Camel. This side of the headland boasts the sandhills of Tregirls beach and St George's cove (which is easily accessed from the coast path). A little further north, Harbour Cove and Hawker's Cove (where the Padstow lifeboat was stationed until 1967) are connected at low water by an extensive sandy beach which forms part of a sandbank at the mouth of the estuary known as Doom Bar.
To the south-west of the headland, the coastal scenery is more rugged with cliffs rising above a rocky foreshore. A mile south of Stepper point is another small headland called Gunver Head and a further mile on is the small sandy beach at Trevone.
Due to its important geological features Stepper Point was designated a Site of Special Scientific Interest in 1990.[2]
References
- Place-names in the Standard Written Form (SWF) Archived 2013-05-15 at the Wayback Machine : List of place-names agreed by the MAGA Signage Panel Archived 2013-05-15 at the Wayback Machine. Cornish Language Partnership.
- "Stepper Point" (PDF). Natural England. 1990. Retrieved 28 October 2011.
- Duxbury, Brenda; Williams, Michael (1987). The River Camel. St Teath: Bossiney Books. ISBN 0-948158-26-3.