Soju
Soju (/ˈsoʊdʒuː/; from Korean: 소주; 燒酒 [so.dʑu]) is a clear, colorless distilled beverage of Korean origin.[1][2][3] It is usually consumed neat, and its alcohol content varies from about 16.8% to 53% alcohol by volume (ABV).[4][5] Most brands of soju are made in South Korea. While soju is traditionally made from rice, wheat, or barley, modern producers often replace rice with other starches such as potatoes and sweet potatoes.
 Pouring soju into a soju glass | |
| Type | Spirit |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Korea |
| Region of origin | Andong |
| Alcohol by volume | 16.8–53% |
| Colour | Clear |
| Ingredients | Rice |
| Related products | baijiu, shochu |
Etymology
Soju (소주; 燒酒) means "burned liquor", with the first syllable so (소; 燒; "burn") referring to the heat of distillation, and the second syllable ju (주; 酒) referring to "alcoholic drink".[6] In 2008, "soju" was included in the Merriam-Webster Dictionary.[7] Merriam-Webster dated the word's appearance in the American English lexicon at 1951.[2] In 2016, the word was included in the Oxford Dictionary of English.[8] Chinese shāojiǔ (烧酒), more commonly known as báijiǔ (白酒), and Japanese shōchū (焼酎), with the altered second character, are the words with the same origin with soju.
Another name for soju is noju (노주; 露酒; "dew liquor"), with its first letter ro (로; 露; "dew") likening the droplets of the collected alcohol during the distilling process to dew-drops.[9][10] Some soju brand names include iseul (이슬), the native-Korean word for "dew", or ro (로; 露), the Sino-Korean word for "dew".
History and production

.jpg)
The origin of soju dates back to the 13th century Goryeo, when the Levantine distilling technique was introduced to the Korean Peninsula during the Mongol invasions of Korea (1231–1259), by the Yuan Mongols who had acquired the technique of distilling arak from the Persians during their invasions of the Levant, Anatolia, and Persia.[11] The distilleries were set up around the city of Gaegyeong, the then capital (current Kaesong). In the surrounding areas of Kaesong, soju is still called arak-ju (아락주).[12] Andong soju, the direct root of modern South Korean soju varieties, started as the home-brewed liquor developed in the city of Andong, where the Yuan Mongol's logistics base was located during this era.[13]
Soju is traditionally made by distilling alcohol from fermented grains.[14] The rice wine for distilled soju is usually fermented for about 15 days, and the distillation process involves boiling the filtered, mature rice wine in a sot (cauldron) topped with soju gori (two-storied distilling appliance with a pipe). In the 1920s, over 3,200 soju breweries existed throughout the Korean Peninsula.[15]
Soju referred to a distilled beverage with 35% ABV until 1965, when diluted soju with 30% ABV appeared with South Korean government's prohibition of the traditional distillation of soju from rice, in order to alleviate rice shortages.[5][15] Instead, soju was created using highly distilled ethanol (95% ABV) from sweet potatoes and tapioca, which was mixed with flavorings, and sweeteners, and water.[11][16] The end products are marketed under a variety of soju brand names. A single supplier (Korea Ethanol Supplies Company) sells ethanol to all soju producers in South Korea. Until the late 1980s, saccharin was the most popular sweetener used by the industry, but it has since been replaced by stevioside.[17]
Although the prohibition was lifted in 1999, cheap soju continues to be made this way. Diluted soju has showed a trend towards lower alcohol content. The ABV of 30% fell to 25% by 1973, and 23% by 1998.[15] Currently, soju with less than 17% ABV are widely available.[4] In 2017, a typical 375 millilitres (13.2 imp fl oz; 12.7 US fl oz) bottle of diluted soju retails at ₩1,700 (approximately $1.69) in supermarkets and convenience stores, and for ₩4,000–5,000 (approximately $3.99–4.98) in restaurants.[18][19]
Several regions have resumed distilling soju from grains since 1999. Traditional hand-crafted Andong soju has about 45% ABV. Hwayo (화요) is a brand with five different mixes constituting an ABV range from 17% to 53%.[5]
In 2000s, soju started to dominate the world's spirit market. Jinro soju has been the largest selling spirit in the world for more than a decade.[20][21] Two other soju brands, Chum Churum and Good Day, featured in the top 10, and three other soju brands are present in the top 100 global spirits brands of 2016.[20]
Fruit sojus have been produced since 2015. When cocktail was first introduced into Korea, it was first made to taste the fruit extract or juice by adding soju. As it was for the first time, soju, which is not even soju, began to be a big trend. [22]
Etiquette
Soju outside Korea
Korea
There are a number of soju brands directly outside the Korean Peninsula for the ethnic Korean population, and most use rice as the foundation since the price is significantly cheaper than in South Korea. Soju from North and South Korea, from firms like Jinro,[23] is also imported.
Canada
Liquors in Canada are subject to regulations that vary from province to province. In Ontario, the provincially run Liquor Control Board of Ontario (LCBO) sells soju, but not all outlets carry it. The LCBO sells a variable number of different kinds of soju, there are usually three or four different brands carried in the system at all times. Not all LCBO locations have soju, since the LCBO introduced online ordering it can be ordered for home delivery anywhere in the province. Almost all Korean restaurants with an AGCO liquor license sell it.
In British Columbia, the BC Liquor Store sells over a dozen types of soju.[24]
In other Canadian provinces liquor sales may be privatized or semi-privatized. In Alberta, for example, a liquor store may carry dozens of brands of Soju.[25]
United States
The liquor licensing laws in the states of California and New York specifically exempt the sale of soju from regulation relating to the sale of other distilled spirits, allowing businesses with a beer/wine license to sell it without requiring the more expensive license required for other distilled spirits.[26] The only stipulation is that the soju must be clearly labeled as such and contain less than 25% alcohol.[27]
This has led to the appearance in the United States of many soju-based equivalents of traditional Western mixed drinks normally based on vodka or similar spirits, such as the soju martini and the soju cosmopolitan. Another consequence is that the manufacturers of similar distilled spirits from other parts of Asia, such as Japanese shōchū, have begun to re-label their products as soju for sale in those regions.[28]
Jinro's American division has partnered with Korean pop star PSY to promote Soju in the U.S., and in 2013 partnered with the Los Angeles Dodgers to sell Soju at its games.[29]
Brands

Jinro is the largest manufacturer of soju accounting for half of all white spirits sold in South Korea.[30] Soju accounts for 97% of the category. Global sales in 2013 were 750 million bottles.[31] The most popular variety of soju is currently Chamisul[30] (참이슬 - literally meaning "real dew"), a quadruple-filtered soju produced by Jinro, but recently Cheoeum-Cheoreom (처음처럼, lit. "like the first time") of Lotte Chilsung (롯데칠성) and Good Day (좋은데이) of Muhak (무학) are increasing their market share. However, the popularity of brands varies by region. In Busan, C1 Soju (시원 소주) is the local and most popular brand. Ipsaeju (잎새주 - "leaf alcohol") is popular in the Jeollanam-do region.[32] The Daegu Metropolitan Area has its own soju manufacturer, Kumbokju, with the popular brand Cham (참).[33][34] Further north in the same province, Andong Soju is one of Korea's few remaining traditionally distilled brands of soju.[35] On the Special Self-Governing Province of Jeju-do, Hallasan Soju is the most common brand, being named after the island's main mountain Mt. Halla.[32] Also, there is pureun-bam[36](푸른 밤/meaning: blue night) made by Jeju-soju.[37] In Gyeongsangnam-do and Ulsan, the most popular is Good Day (Hangul: 좋은데이), produced by Muhak in Changwon.[32] However, as soon as one crosses the border from Ulsan north to Gyeongju in Gyeongsangbuk-do, it is almost impossible to buy White Soju, and the most popular brands are Chamisul and Cham. Since 2015, the new trends of soju include fruit soju and sparkling soju, which have become increasingly popular in Korea.[38]
New American producers are entering the market. Some, like West 32 Soju, with initial market penetration in major markets like New York, are finding critical success, with West 32 Soju winning a gold medal at the 2017 New York International Spirits Competition.[39][40]
A new all natural soju distilled in Germany called ISAE is also entering the premium soju market. It is distilled according to the German Purity Law (Reinheitsgebot) for grain spirits of 1789 and uses 100% regional winter wheat and organic rice. [41]
Consumption
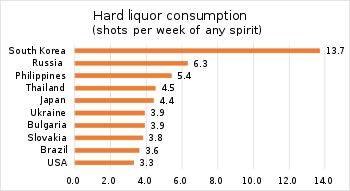
Although beer, whiskey, and wine have been gaining popularity in recent years, soju remains one of the most popular alcoholic beverages in Korea because of its ready availability and relatively low price. More than 3 billion bottles were consumed in South Korea in 2004.[42] In 2006, it was estimated that the average adult Korean (older than 20) had consumed 90 bottles of soju during that year.[43] In 2014, it was reported that South Koreans of drinking age consumed an average of 13.7 shots of spirit per week; the figure for Russia, in second place, was 6.3. By contrast consumption in the U.S. was 3.3 shots, Canada was 2.5, and the U.K. 2.3 shots.[44]
Cocktails

While soju is traditionally consumed straight, a few cocktails and mixed drinks use soju as a base spirit. Beer and soju can be mixed to create somaek (소맥), a portmanteau of the words soju and maekju (맥주 beer).[45] Flavored soju is also available. It is also popular to blend fruits with soju and to drink it in "slushy" form.[46] Another very popular flavored soju is yogurt soju (요구르트 소주), which is a combination of soju, yogurt, and lemon lime soda.[47]
A poktan-ju (폭탄주) ("bomb drink") consists of a shot glass of soju dropped into a pint of beer (similar to a boilermaker); it is drunk quickly.[48] This is similar to the Japanese sake bomb.[49]
Soju is sometimes mistakenly referred to as cheongju (청주), a Korean rice wine. Mass-produced soju is also mistaken for Chinese baijiu, a grain liquor, and shōchū, a Japanese liquor.
See also
- Andong soju
- Korean alcoholic beverages
- Rice wine
- Korean cuisine
- Korean beer
- Baijiu
- Shōchū
- Awamori
References
- "soju". Oxford Dictionary of English. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- "soju". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- Miller, Norman (2 December 2013). "Soju: the most popular booze in the world". The Guardian. Retrieved 13 April 2017.
- Park, Eun-jee (19 November 2014). "Koreans looking for weaker soju". Korea JoongAng Daily. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- Hall, Joshua (17 October 2014). "Soju Makers Aim to Turn Fire Water Into Liquid Gold". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- "soju" 소주. Standard Korean Language Dictionary (in Korean). National Institute of Korean Language. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- Boutin, Paul (8 July 2008). "Merriam-Webster's new dictionary words for 2008". Gawker. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- "New words list June 2016". Oxford English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 14 April 2017. Retrieved 14 April 2017. Lay summary.
- "noju" 노주. Standard Korean Language Dictionary (in Korean). National Institute of Korean Language. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- Pettid, Michael J. (2008). Korean Cuisine: An Illustrated History. London: Reaktion Books. p. 118. ISBN 978-1-86189-348-2.
- Cho, Ines (20 October 2005). "Moving beyond the green blur: a history of soju". Korea JoongAng Daily. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- "soju" 소주. Doopedia. Doosan Corporation. Retrieved 7 December 2008.
- 도, 현신 (2011). Jeonjaengi yorihan eumsigui yeoksa 전쟁이 요리한 음식의 역사. Seoul: Sidae Books. pp. 213–224. ISBN 978-89-5940-200-7.
- Jang, Gyehyang (1670). Eumsik dimibang 음식디미방 [Guidebook of Homemade Food and Drinks] (in Middle Korean). Andong, Joseon Korea.
말을 셰여 장 닉게 글힌 믈 두 말애 가 거든 누록 닷 되 섯거 녀헛다가 닐웨 지내거든 고 믈 두 사발을 몬져 힌 후에 술 세 사발을 그 믈에 부어 고로고로 저으라. 불이 셩면 술이 만이 나 긔운이 구무 가온드로 나 고 불이 면 술이 듯듯고 블이 듕면 노여 긋디 아니면 마시 심히 덜고 우희 믈을 로 라 이 법을 일치 아니면 온 술이 세 병 나니라
CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - Schwartzman, Nathan (25 March 2009). "90 Years of Soju". Asian Correspondent. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- Chosun.com Infographics Team (29 August 2016). "증류식 소주 vs. 희석식 소주의 차이" [Differences between distilled vs. diluted soju]. The Chosun Ilbo (in Korean). Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- Chosun.com Infographics Team (22 August 2016). "이슬과 땀의 술, 소주 한잔 하실래요?" [Liquor of dew and sweat: What about a glass of soju?]. The Chosun Ilbo (in Korean). Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- 권, 영은 (5 January 2017). "소주 한 병 1,700원…편의점ㆍ대형마트, 다음주부터 맥주·소줏값 인상". Hankook Ilbo (in Korean). Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- 박, 찬일 (12 January 2017). "[박찬일 셰프의 맛있는 미학]소주 5000원 시대". Kyunghyang Shinmun (in Korean). Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- "Soju dominates Real 100" (PDF). International Wine and Spirit Research. 13 July 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2017.
- Archibald, Anna (27 August 2015). "Why You Should Be Drinking Korean Soju Right Now". Liquor.com. Retrieved 14 December 2015.
- "Fuit sojus site".
- "Jinro Brings New Soju Brand To China". Drinks Daily. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- http://www.bcliquorstores.com/product-catalogue?search=soju&sort=_score:desc&page=1. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-08. Retrieved 2016-05-22.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Soju Goes Where Vodka Cannot Tread, Los Angeles Times, June 27, 2002. (Accessed February 2011)
- "Ku Soju is under construction". www.kusoju.com.
- "What is Sochu?". Sake World Homepage. Archived from the original on July 22, 2012. Retrieved November 22, 2014.
- "Move Over Vodka; Korean Soju's Taking A Shot At America". NPR. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "It's official: Jinro soju is the world's best-selling liquor". Cable News Network. Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. Retrieved December 15, 2015.
- "Jinro Soju – the world leader". The Whiskey Exchange. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "The Most Popular Soju by Region in South Korea". Viki Inc. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "Charm Soju". EtradeDaegu. Retrieved November 22, 2014.
- "ð -"ִ "". Retrieved November 22, 2014.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-04-02. Retrieved 2011-11-09.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- 방영덕. "신세계, 제주소주 브랜드명은 `푸른밤`…소주 사업 본격화". mk.co.kr (in Korean). Retrieved 2019-03-15.
- 제주소주. "제주소주". 제주소주 (in Korean). Retrieved 2019-03-15.
- kang, pilsung (2016-03-22). "the sparkling soju and fruit soju are new trends".
- "HOME". West 32 Soju. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- "2017 Winners – New York International Spirits Competition". nyispiritscompetition.com. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- "ISAE all natural Soju". ISAE SOJU by KYOPO spirits. Retrieved 2018-07-26.
- "Cigarette Sales Surge to Historic High". Chosun Ilbo. Archived from the original on October 17, 2007. Retrieved June 29, 2005.
- "Let's Have a Soju Tonight". KBS World. Retrieved January 1, 2008.
- "South Koreans drink twice as much liquor as Russians and more than four times as much as Americans". Quartz. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "Korean Drink Soju Cocktail : Socol, Somaek". Foodstoryist. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "Slushie Soju, a new way for Koreans (the #1 alcoholic beverage consumers) in the world to enjoy their favorite beverage". 6Theory Media, LLC. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "koreataste.org". Archived from the original on 2012-06-20.
- "Heavy-Drinking Culture Challenged in S. Korea". The Seoul Times Company. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- "Sake Bomb". Autodesk Inc. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Soju. |
| Look up soju in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |