Sinohelicoprion
Sinohelicoprion ("Chinese spiral jaw") is an extinct genus of helicoprinid eugeneodontid fish that lived during the late Permian 254 to 252 million years ago and became extinct during the Permian-Triassic extinction event.[1]
| Sinohelicoprion | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Tooth whorl (IVPP V4752.2) of S. qomolangma, Paleozoological Museum of China | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Order: | †Eugeneodontida |
| Family: | †Helicoprionidae |
| Genus: | †Sinohelicoprion Liu & Chang, 1963 |
| Species | |
| |
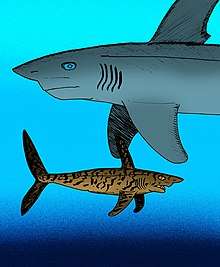
Comparison of S. changhsingensis and Helicoprion sp.
It was first named and classified by H. T. Liu and M. N. Chang in 1963.[2][3]
Gallery
 Information board about Sinohelicoprion in Paleozoological Museum of China.
Information board about Sinohelicoprion in Paleozoological Museum of China.
gollark: Anarchocommunism or whatever seems like wishy-washy impossible stuff.
gollark: It's not, really. Central planning is just *not* tractable.
gollark: Oh, you mean *I'm* "spy"? Right.
gollark: Still, stuff *mostly* works currently.
gollark: Status quo problematic, some thing or other probably better, ☭ bad.
References
- "Sinohelicoprion". Fossilworks. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- "The Paleobiology Database". Retrieved 14 December 2015.
- H. T. Liu; M. N. Chang (1963). "First discovery of helicoprionid in China". Vertebrata PalAsiatica (in Chinese). 7 (2): 123–129.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.