Sinapinic acid
Sinapinic acid, or sinapic acid (Sinapine - Origin: L. Sinapi, sinapis, mustard, Gr., cf. F. Sinapine.), is a small naturally occurring hydroxycinnamic acid. It is a member of the phenylpropanoid family. It is a commonly used matrix in MALDI mass spectrometry.[1][2] It is a useful matrix for a wide variety of peptides and proteins. It serves well as a matrix for MALDI due to its ability to absorb laser radiation and to also donate protons (H+) to the analyte of interest.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
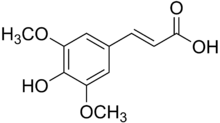
| IUPAC name
3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | |
| Other names
Sinapinic acid Sinapic acid 3,5-Dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid 4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxycinnamic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 224.21 g/mol |
| Melting point | 203 to 205 °C (397 to 401 °F; 476 to 478 K) (decomposes) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Sinapic acid can form dimers with itself (one structure) and ferulic acid (three different structures) in cereal cell walls and therefore may have a similar influence on cell-wall structure to that of the diferulic acids.[3]
Sinapine is an alkaloidal amine found in black mustard seeds. It is considered a choline ester of sinapinic acid.[4]
Metabolism
sinapate 1-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that uses UDP-glucose and sinapate to produce UDP and 1-sinapoyl-D-glucose.
Sinapoylglucose—malate O-sinapoyltransferase is an enzyme that uses 1-O-sinapoyl-beta-D-glucose and (S)-malate to produce D-glucose and sinapoyl-(S)-malate.
Related compounds
Canolol is a phenolic compound found in crude canola oil. It is produced by decarboxylation of sinapic acid during canola seed roasting.[7]
See also
References
- Beavis RC, Chait BT (1989). "Matrix-assisted laser-desorption mass spectrometry using 355 nm radiation". Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 3 (12): 436–9. doi:10.1002/rcm.1290031208. PMID 2520224.
- Beavis RC, Chait BT (1989). "Cinnamic acid derivatives as matrices for ultraviolet laser desorption mass spectrometry of proteins". Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 3 (12): 432–5. doi:10.1002/rcm.1290031207. PMID 2520223.
- Bunzel M, Ralph J, Kim H, Lu F, Ralph SA, Marita JM, Hatfield RD, Steinhart H (2003). "Sinapate dehydrodimers and sinapate-ferulate heterodimers in cereal dietary fibre". J. Agric. Food Chem. 51 (5): 1427–1434. doi:10.1021/jf020910v. PMID 12590493.
- Tzagoloff, A. (1963). "Metabolism of Sinapine in Mustard Plants. I. Degradation of Sinapine into Sinapic Acid & Choline". Plant Physiology. 38 (2): 202–206. doi:10.1104/pp.38.2.202. PMC 549906. PMID 16655775.
- Comparison of Phenolic Acids and Flavan-3-ols During Wine Fermentation of Grapes with Different Harvest Times. Rong-Rong Tian, Qiu-Hong Pan, Ji-Cheng Zhan, Jing-Ming Li, Si-Bao Wan, Qing-Hua Zhang and Wei-Dong Huang, Molecules, 2009, 14, pages 827-838, doi:10.3390/molecules14020827
- Gávez, M. C.; Barroso, C. G. A.; Péez-Bustamante, J. A. (1994). "Analysis of polyphenolic compounds of different vinegar samples". Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und -Forschung. 199: 29–31. doi:10.1007/BF01192948.
- Antioxidant canolol production from a renewable feedstock via an engineered decarboxylase. Krista L. Morley, Stephan Grosse, Hannes Leischa and Peter C. K. Lau, Green Chem., 2013,n15, pages 3312-3317, doi:10.1039/C3GC40748A