River Tweed
The River Tweed, or Tweed Water (Scottish Gaelic: Abhainn Thuaidh, Scots: Watter o Tweid, Welsh: Tuedd), is a river 97 miles (156 km) long that flows east across the Border region in Scotland and northern England. Tweed derives its name from its association with the River Tweed.[1] The Tweed is one of the great salmon rivers of Britain and the only river in England where an Environment Agency rod licence is not required for angling. The river generates a large income for the local borders region, attracting anglers from all around the world, acting as one of the best salmon rivers in Scotland.[2] Tweed is an Old Brythonic (Celtic) name meaning "border".[3]
| River Tweed | |
|---|---|
 The River Tweed at Abbotsford | |
| Location | |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Part | Scotland, England |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Tweed's Well |
| • location | Tweedsmuir, Scottish Borders, Scotland |
| • coordinates | 55.445°N 3.496°W |
| Mouth | North Sea |
• location | Berwick-upon-Tweed, Northumberland, England |
• coordinates | 55.7652°N 1.9909°W |
| Length | 156 km (97 mi) |
Course
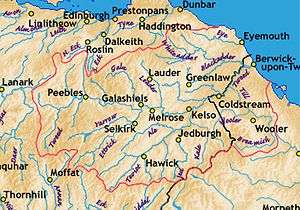
It flows primarily through the scenic Borders region of Scotland, and eastwards from the settlements on opposing banks of Birgham and Carham forms the historic boundary between Scotland and England.
It rises in the Lowther Hills at Tweed's Well near to where the Clyde, draining northwest (10 kilometres (6.2 mi) from the Tweed's Well), and the Annan draining south (1.9 kilometres (1.2 mi) from the Tweed's Well) also rise. "Annan, Tweed and Clyde rise oot the ae hillside" is a saying from the Border region.[4] East of Kelso, it becomes a section of the eastern part of the border. Entering England, its lower reaches are in Northumberland, where it enters the North Sea at Berwick-upon-Tweed.
Catchment
The river's valley floor is a drumlin field. It is the relic of a paleo-ice stream that flowed through the area during the last glaciation. Major towns through which the Tweed flows include Innerleithen, Peebles, Galashiels, Melrose, Kelso, Coldstream and Berwick-upon-Tweed, where it flows into the North Sea. Tweed tributaries include:
- Whiteadder Water
- River Till
- Eden Water
- Teviot Water
- Leader Water
- Gala Water
- Leithen Water
- Quair Water
- Eddleston Water
- Manor Water
- Lyne Water
- Holms Water
The upper parts of the catchment of the Tweed in Scotland form the area known as Tweeddale, part of which is protected as the Upper Tweeddale National Scenic Area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development.[5]
See also
- List of places in the Scottish Borders
- Tweeddale
- Anglo–Scottish border
- Union Bridge
- Rivers and Fisheries Trusts of Scotland
- Rivers of the United Kingdom
- Both sides the Tweed
Gallery
 The River Tweed at Abbotsford, near Melrose
The River Tweed at Abbotsford, near Melrose The River Tweed from Mertoun House, near St Boswells
The River Tweed from Mertoun House, near St Boswells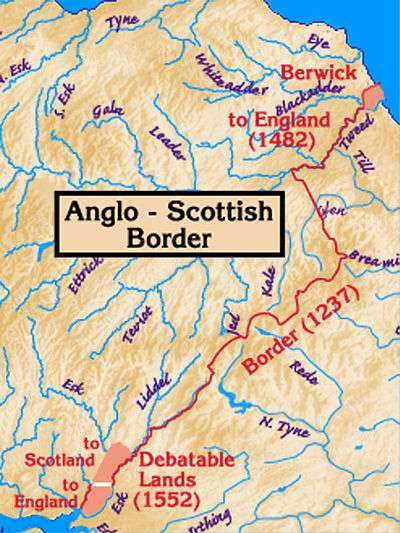 The Anglo-Scottish border, with the Tweed on the east. Its estuary and the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed were a late annexation by England.
The Anglo-Scottish border, with the Tweed on the east. Its estuary and the town of Berwick-upon-Tweed were a late annexation by England.
Notes
- "Article on Tweed Cloth". Archived from the original on 2014-12-16. Retrieved 2014-12-16.
- https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-scotland-33844266
- "University of Wales Dictionary". University of Wales Dictionary. University of Wales. Archived from the original on 31 May 2019. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- The Tweed: Take a trip on a river flowing with history Archived 2019-07-31 at the Wayback Machine, The Independent, 21 April 2007
- "National Scenic Areas". Scottish Natural Heritage. Archived from the original on 2018-01-18. Retrieved 2018-01-17.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of a 1921 Collier's Encyclopedia article about River Tweed. |
- British Waterways: River Tweed
- The River Tweed Commission website
- The Tweed Foundation
- Tweed Forum website
- River Tweed: Special Area of Conservation (SAC)
- SEPA (Scottish Environment Protection Agency): River Level Data
- River Tweed map
- Gazetteer for Scotland: River Tweed
- Paper describing palaeo-icestream and landforms in the Tweed Valley
- Map and aerial photo sources for Tweed's Well and Tweedmouth
- Open Canoe Hire Specialists