Programmable unijunction transistor
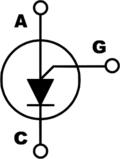
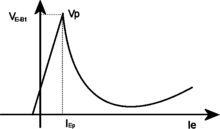
A programmable unijunction transistor (PUT) is a three-lead electronic semiconductor device which is similar in its characteristics to a unijunction transistor, except that it is programmable. In a unijunction transistor, the base region is divided into two parts by the emitter. The two parts of the base form a voltage divider, which sets the operating point of the UJT. That voltage divider can be programmed with two physical resistors connected to the gate terminal of the PUT. This allows the designer some control over the operating point of the PUT.[2]
| Type | Passive |
|---|---|
| Invented | General Electric[1] |
| Pin configuration | anode, gate and cathode |
| Electronic symbol | |
 | |
Construction
In construction, the programmable unijunction transistor is similar to the silicon controlled rectifier. It consists of four layers, two p-type layers and two n-type layers in equal proportion.[1]
Applications
- It is used to trigger thyristors.
- It is also used as a relaxation oscillator.
As of 2012 ON Semiconductor manufactured a part: 2N6027. 2N6028 was also made in the past.[1]