Pap test
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE),[1] cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE),[2] or smear test (BE) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or colon (in both women and men). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Dr. Georgios Papanikolaou and Dr. Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957.
| Papanicolaou test | |
|---|---|
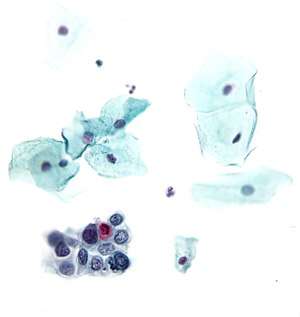 High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion | |
| Specialty | anatomical pathology |
| ICD-9-CM | 795.00 |
| MeSH | D014626 |
| MedlinePlus | 003911 |
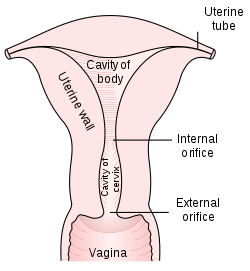
A Pap smear is performed by opening the vaginal canal with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells). Similar method is used to collect cells in anus of both women and men. The collected cells are examined under a microscope to look for abnormalities. The test aims to detect potentially precancerous changes (called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical dysplasia; the squamous intraepithelial lesion system (SIL) is also used to describe abnormalities) caused by human papillomavirus, a sexually transmitted DNA virus. The test remains an effective, widely used method for early detection of precancer and cervical cancer. While the test may also detect infections and abnormalities in the endocervix and endometrium, it is not designed to do so.
In the United States, Pap smear screening is recommended starting around 21 years of age until the age of 65.[3] However, other countries do not recommend Pap testing in non-sexually active females [4]. Guidelines on frequency vary from every three to five years.[3][5][6] If results are abnormal, and depending on the nature of the abnormality, the test may need to be repeated in six to twelve months.[7] If the abnormality requires closer scrutiny, the patient may be referred for detailed inspection of the cervix by colposcopy. The person may also be referred for HPV DNA testing, which can serve as an adjunct to Pap testing. Additional biomarkers that may be applied as ancillary tests with the Pap test are evolving.[8]
Medical uses
| Summary of reasons for testing | ||
|---|---|---|
| patient's characteristic | indication | rationale |
| never had sexual contact | no test | HPV usually transmitted by sexual contact[9] |
| under age 21, regardless of sexual history | no test | more harms than benefits[10][11] |
| age 20–25 until age 50–60 | test every 3–5 years if results normal | broad recommendation[9][12] |
| over age 65; history of normal tests | no further testing | recommendation of USPSTF, ACOG, ACS and ASCP;[5][9][13][14] |
| had total hysterectomy for non-cancer disease – cervix removed | no further testing | harms of screening after hysterectomy outweigh the benefits[10][11] |
| had partial hysterectomy – cervix remains | continue testing as normal | |
| has received HPV vaccine | continue testing as normal | vaccine does not cover all cancer-causing types of HPV[12] |
| history of endometrial cancer | discontinue routine testing[15] | test no longer effective and likely to give false positive[15] |
Screening guidelines vary from country to country. In general, screening starts about the age of 20 or 25 and continues until about the age of 50 or 60.[13] Screening is typically recommended every three to five years, as long as results are normal.[9][12]
Women should wait a few years after they first have intercourse before they start screening, and should not be screened before age 21. American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and others recommend starting screening at age 21 (since that is a few years after sexual debut for most American women).[5][16] Many other countries wait until age 25 or later to start screening. For instance, some parts of Great Britain start screening at age 25. ACOG's general recommendation is that people with female reproductive organs age 30–65 have an annual well-woman examination, that they not get annual Pap tests, and that they do get Pap tests at three-year intervals.[17]
HPV is passed through skin to skin contact; sex does not have to occur, although it is a common way for it to spread.[18] It takes an average of a year, but can take up to four years, for a person's immune system to control the initial infection. Screening during this period may show this immune reaction and repair as mild abnormalities, which are usually not associated with cervical cancer, but could cause the patient stress and result in further tests and possible treatment. Cervical cancer usually takes time to develop, so delaying the start of screening a few years poses little risk of missing a potentially precancerous lesion. For instance, screening people under age 25 does not decrease cancer rates under age 30.[19]
There is little or no benefit to screening people who have not had sexual contact. For example, United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends waiting at least three years after first sex.[9] HPV can be transmitted in sex between females, so those who have only had sex with other females should be screened, although they are at somewhat lower risk for cervical cancer.[20]
Guidelines on frequency of screening vary—typically every three to five years for those who have not had previous abnormal smears.[9][12] Some older recommendations suggested screening as frequently as every one to two years, however there is little evidence to support such frequent screening; annual screening has little benefit but leads to greatly increased cost and many unnecessary procedures and treatments.[5] It has been acknowledged since before 1980 that most people can be screened less often.[21] In some guidelines, frequency depends on age; for instance in Great Britain, screening is recommended every 3 years for women under 50, and every 5 years for those over.
Screening should stop at about age 65 unless there is a recent abnormal test result or disease. There is probably no benefit in screening people aged 60 or over whose previous tests have been negative.[14] If a woman's last three Pap results were normal, she can discontinue testing at age 65, according to the USPSTF, ACOG, ACS, and ASCP;[5][9] England's NHS says 64. There is no need to continue screening after a complete hysterectomy for benign disease.
Pap smear screening is still recommended for those who have been vaccinated against HPV[12] since the vaccines do not cover all HPV types that can cause cervical cancer. Also, the vaccine does not protect against HPV exposure before vaccination.
Those with a history of endometrial cancer should discontinue routine Pap tests after hysterectomy.[15] [22]Further tests are unlikely to detect recurrence of cancer but do bring the risk of giving false positive results, which would lead to unnecessary further testing.[15]
More frequent Pap smears may be needed to follow up after an abnormal Pap smear, after treatment for abnormal Pap or biopsy results, or after treatment for cancer.
Effectiveness
The Pap test, when combined with a regular program of screening and appropriate follow-up, can reduce cervical cancer deaths by up to 80%.[12]
Failure of prevention of cancer by the Pap test can occur for many reasons, including not getting regular screening, lack of appropriate follow-up of abnormal results, and sampling and interpretation errors.[23] In the US, over half of all invasive cancers occur in females who have never had a Pap smear; an additional 10 to 20% of cancers occur in those who have not had a Pap smear in the preceding five years. About one-quarter of US cervical cancers were in people who had an abnormal Pap smear but did not get appropriate follow-up (patient did not return for care, or clinician did not perform recommended tests or treatment).
Adenocarcinoma of the cervix has not been shown to be prevented by Pap tests.[23] In the UK, which has a Pap smear screening program, adenocarcinoma accounts for about 15% of all cervical cancers.[24]
Estimates of the effectiveness of the United Kingdom's call and recall system vary widely, but it may prevent about 700 deaths per year in the UK. A medical practitioner performing 200 tests each year would prevent a death once in 38 years, while seeing 152 people with abnormal results, referring 79 for investigation, obtaining 53 abnormal biopsy results, and seeing 17 persisting abnormalities lasting longer than two years. At least one woman during the 38 years would die from cervical cancer despite being screened.[25]
Since the population of the UK is about 61 million, the maximum number of people who could be receiving Pap smears in the UK is around 15 million to 20 million (eliminating the percentage of the population under 20 and over 65). This would indicate that the use of Pap smear screening in the UK saves the life of 1 woman for every approximately 20,000 women tested (assuming 15,000,000 are being tested yearly). If only 10,000,000 are actually tested each year, then it would save the life of 1 woman for every approximately 15,000 women tested.
Results
In screening a general or low-risk population, most Pap results are normal.
In the United States, about 2–3 million abnormal Pap smear results are found each year.[26] Most abnormal results are mildly abnormal (ASC-US (typically 2–5% of Pap results) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) (about 2% of results)), indicating HPV infection. Although most low-grade cervical dysplasias spontaneously regress without ever leading to cervical cancer, dysplasia can serve as an indication that increased vigilance is needed.
In a typical scenario, about 0.5% of Pap results are high-grade SIL (HSIL), and less than 0.5% of results indicate cancer; 0.2 to 0.8% of results indicate Atypical Glandular Cells of Undetermined Significance (AGC-NOS).
As liquid-based preparations (LBPs) become a common medium for testing, atypical result rates have increased. The median rate for all preparations with low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions using LBPs was 2.9% compared with a 2003 median rate of 2.1%. Rates for high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (median, 0.5%) and atypical squamous cells have changed little.[27]
Abnormal results are reported according to the Bethesda system.[28] They include:
- Squamous cell abnormalities (SIL)
- Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US)
- Atypical squamous cells – cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
- Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LGSIL or LSIL)
- High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL or HSIL)
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Glandular epithelial cell abnormalities
- Atypical glandular cells not otherwise specified (AGC or AGC-NOS)
Endocervical and endometrial abnormalities can also be detected, as can a number of infectious processes, including yeast, herpes simplex virus and trichomoniasis. However it is not very sensitive at detecting these infections, so absence of detection on a Pap does not mean absence of the infection.
_Smear.jpg) Micrograph of a normal pap smear
Micrograph of a normal pap smear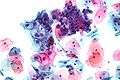 Micrograph of a Pap test showing a low-grade intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and benign endocervical mucosa. Pap stain.
Micrograph of a Pap test showing a low-grade intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and benign endocervical mucosa. Pap stain.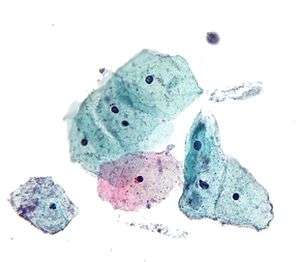 Micrograph of a Pap test showing trichomoniasis. Trichomonas organism seen in the upper right. Pap stain.
Micrograph of a Pap test showing trichomoniasis. Trichomonas organism seen in the upper right. Pap stain.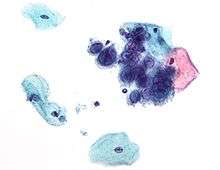 Micrograph of a Pap test showing changes of herpes simplex virus. Pap stain.
Micrograph of a Pap test showing changes of herpes simplex virus. Pap stain.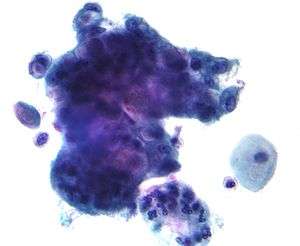 Endocervical adenocarcinoma on a pap test.
Endocervical adenocarcinoma on a pap test. Candida organisms on a pap test.
Candida organisms on a pap test. Viral cytopathic effect consistent with herpes simplex virus on a pap test.
Viral cytopathic effect consistent with herpes simplex virus on a pap test. Normal squamous epithelial cells in premenopausal women
Normal squamous epithelial cells in premenopausal women- Atrophic squamous cells in postmenopausal women
- Normal endocervical cells should be present into the slide, as a proof of a good quality sampling
- The cytoplasms of squamous epithelial cells melted out; many Döderlein bacilli can be seen.
- Infestation by Trichomonas vaginalis
- An obviously atypical cell can be seen
Pregnancy
Pap tests can usually be performed during pregnancy up to at least 24 weeks of gestational age.[29] Pap tests during pregnancy have not been associated with increased risk of miscarriage.[29] An inflammatory component is commonly seen on Pap smears from pregnant women[30] and does not appear to be a risk for subsequent preterm birth.[31]
After childbirth, it is recommended to wait 12 weeks before taking a Pap test because inflammation of the cervix caused by the birth interferes with test interpretation.[32]
Procedure
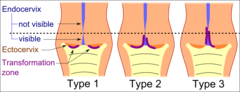
Type 1: Completely ectocervical.
Type 2: Endocervical component but fully visible.
Type 3: Endocervical component, not fully visible.
For best results, a Pap test should not occur when a woman is menstruating, partly because the additional cells can obscure cervical cells and partly because this part of the menstrual cycle is when the female organs are most inflamed[34]. However, Pap smears can be performed during a woman's menstrual period, especially if the physician is using a liquid-based test; if bleeding is extremely heavy, endometrial cells can obscure cervical cells, and it is therefore inadvisable to have a Pap smear if bleeding is excessive.
Obtaining a Pap smear should not cause much pain,[35] but it can if the woman has certain untreated vaginal problems such as cervical stenosis or vaginismus, or if the person performing it is too harsh or uses the wrong size speculum.
It is, however, not comfortable, for two reasons: the cervix is full of nociceptors (pain nerves),[36] and the brush used to collect cells has to be stiff enough to scrape them off of the surrounding tissue. So it can be uncomfortable, but it is generally quick, and the information obtained may be critical.
People with underlying pain or tissue diseases that can react to nociceptors being scraped or to excessive cold in the mucous membranes should take appropriate precautions and discuss the process ahead of time with their providers, in writing if necessary. A smaller speculum, lidocaine gel, and warming the instruments and lubricant ahead of time, along with extra time in the exam room and gentle technique, can all contribute to reducing the risk to manageable levels. These are reasonable accommodations to ask for and are aligned with good practice.
Many people experience spotting or mild diarrhea afterward. The spotting is usually from the scrape on the cervix, and the diarrhea may be due to indirect stimulation of the lower intestine during the exam.
Many health care providers are under the false impression that only sterile water, or no lubricant at all, should be used to lubricate the speculum. This may result in unnecessary discomfort. A number of studies have shown that using a small amount of water-based gel lubricant does not interfere with, obscure, or distort the Pap smear. Further, cytology is not affected, nor are some STD testing.[37]
The health care worker begins by inserting a speculum into the woman's vagina, which spreads the vagina open and allows access to the cervix. The health care provider then collects a sample of cells from the outer opening or os of the cervix by scraping it with an Aylesbury spatula. An endocervical brush is rotated in the central opening of the cervix. The cells are placed on a glass slide and taken to the laboratory to be checked for abnormalities.
A plastic-fronded broom is sometimes used in place of the spatula and brush. The broom is not as good a collection device, since it is much less effective at collecting endocervical material than the spatula and brush.[38] The broom is used more frequently with the advent of liquid-based cytology, although either type of collection device may be used with either type of cytology.
The sample is stained using the Papanicolaou technique, in which tinctorial dyes and acids are selectively retained by cells. Unstained cells cannot be seen with a light microscope. Papanicolaou chose stains that highlighted cytoplasmic keratinization, which actually has almost nothing to do with the nuclear features used to make diagnoses now.
In some cases, a computer system may prescreen the slides, indicating those that do not need examination by a person or highlighting areas for special attention. The sample is then usually screened by a specially trained and qualified cytotechnologist using a light microscope. The terminology for who screens the sample varies according to the country; in the UK, the personnel are known as cytoscreeners, biomedical scientists (BMS), advanced practitioners and pathologists. The latter two take responsibility for reporting the abnormal sample, which may require further investigation.
Automated analysis
In the last decade, there have been successful attempts to develop automated, computer image analysis systems for screening.[39] Although, on the available evidence automated cervical screening could not be recommended for implementation into a national screening program, a recent NHS Health technology appraisal concluded that the 'general case for automated image analysis ha(d) probably been made'.[40] Automation may improve sensitivity and reduce unsatisfactory specimens.[41] Two systems have been approved by the FDA and function in high-volume reference laboratories, with human oversight.
Types of screening
- Conventional Pap—In a conventional Pap smear, samples are smeared directly onto a microscope slide after collection.
- Liquid-based cytology—The sample of (epithelial) cells is taken from the transitional zone, the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix, between the ectocervix and the endocervix. Liquid-based cytology often uses an arrow-shaped brush rather than the conventional spatula.[42] The cells taken are suspended in a bottle of preservative for transport to the laboratory, where they are analyzed using Pap stains.
Pap tests commonly look for epithelial abnormalities/ metaplasia/ dysplasia/ borderline changes, all of which may be indicative of CIN. Nuclei will stain dark blue, squamous cells will stain green and keratinised cells will stain pink/ orange. Koilocytes may be observed where there is some dyskaryosis (of epithelium). The nucleus in koilocytes is typically irregular, indicating possible cause for concern; requiring further confirmatory screens and tests.
In addition, human papillomavirus (HPV) test may be performed either as indicated for abnormal Pap results, or in some cases, dual testing is done, where both a Pap smear and an HPV test are done at the same time (also called Pap co-testing).
Practical aspects
The endocervix may be partially sampled with the device used to obtain the ectocervical sample, but due to the anatomy of this area, consistent and reliable sampling cannot be guaranteed. Since abnormal endocervical cells may be sampled, those examining them are taught to recognize them.
The endometrium is not directly sampled with the device used to sample the ectocervix. Cells may exfoliate onto the cervix and be collected from there, so as with endocervical cells, abnormal cells can be recognised if present but the Pap test should not be used as a screening tool for endometrial malignancy.
In the United States, a Pap test itself costs $20 to $30, but the costs for Pap test visits can cost over $1,000, largely because additional tests are added that may or may not be necessary.[43]
History
The test was invented by and named after the Greek doctor Georgios Papanikolaou, who started his research in 1923. Aurel Babeș of Romania independently made similar discoveries in 1927.[44] However, Babeș' method was radically different from Papanicolaou's.[45]
Papanicolaou's name was repeatedly submitted to the Nobel Committee and rejected every time. The Nobel Committee delegated the in-depth investigation of Papanicolaou's merits and demerits to Professor Santesson, who was at that time the head of pathology at the Stockholm Cancer Institute (Radiumhemmet). Santesson discovered Babeș' contributions that had never been cited by Papanicolaou and duly reported this fact to the Committee, which then rejected Papanicolaou's Nobel award.[46]
Experimental techniques
In the developed world, cervical biopsy guided by colposcopy is considered the "gold standard" for diagnosing cervical abnormalities after an abnormal Pap smear. Other techniques such as triple smear are also done after an abnormal Pap smear.[47] The procedure requires a trained colposcopist and can be expensive to perform. However, Pap smears are very sensitive and some negative biopsy results may represent undersampling of the lesion in the biopsy, so negative biopsy with positive cytology requires careful follow-up.[48]
Experimental visualization techniques use broad-band light (e.g., direct visualization, speculoscopy, cervicography, visual inspection with acetic acid or with Lugol's, and colposcopy) and electronic detection methods (e.g., Polarprobe and in-vivo Spectroscopy). These techniques are less expensive and can be performed with significantly less training. They do not perform as well as Pap smear screening and colposcopy. At this point, these techniques have not been validated by large-scale trials and are not in general use.
Access
Australia
Australia has used the Pap test as part of it's cervical screening program since its implementation in 1991 which required women past the age of 18 be tested every 2 years.[49] In December 2017 Australia discontinued its use of the Pap test and replaced it with a new HPV test that is only required to be conducted once every 5 years from the age of 25.[50] Medicare covers the costs of testing, however, if your doctor does not allow bulk billing you may have to pay for the appointment and then claim the Medicare rebate.[51]
Taiwan
Free Pap tests were offered from 1974 - 84 before being replaced by a system in which all women over the age of 30 could have the cost of their Pap test reimbursed by the National Health Insurance in 1995.[52] This policy was still ongoing in 2018 and encouraged women to screen at least every 3 years.[53]
Despite this, the number of people receiving Pap tests remain lower than countries like Australia. Some believe this is due to a lack of awareness regarding the test and its availability. It has also been found that women who have chronic diseases or other reproductive diseases are less likely to receive the test.[54][55][56]
England
As of 2020 the NHS maintains a cervical screening program in which women between the age of 25 - 49 are invited for a smear test every 3 years, and women past 50 every 5 years. Much like Australia, England uses a HPV test before examining cells that test positive using the Pap test.[57] The test is free as part of the national cervical screening program.[58]
Coccoid bacteria
The finding of coccoid bacteria on a Pap test is of no consequence with otherwise normal test findings and no infectious symptoms. However, if there is enough inflammation to obscure the detection of precancerous and cancerous processes, it may indicate treatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic for streptococci and anaerobic bacteria (such as metronidazole and amoxicillin) before repeating the smear. Alternatively, the test will be repeated at an earlier time than it would otherwise.[59] If there are symptoms of vaginal discharge, bad odor or irritation, the presence of coccoid bacteria also may indicate treatment with antibiotics as per above.[59]
References
- Notes
- "Pap Smear: MedlinePlus Lab Test Information". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- "Cervical Screening". NHS. 2017-10-20. Retrieved 2018-09-04.
- Moyer, VA; U.S. Preventive Services Task, Force (Jun 19, 2012). "Screening for cervical cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement". Annals of Internal Medicine. 156 (12): 880–91, W312. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-156-12-201206190-00424. PMID 22711081.
- "Pap Test". Cancer.Net. 2011-02-23. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- Saslow, D; et al. (2012). "American Cancer Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology Screening Guidelines for the Prevention and Early Detection of Cervical Cancer". Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease. 16 (3): 175–204. doi:10.1097/LGT.0b013e31824ca9d5. PMC 3915715. PMID 22418039.
- American Cancer Society. (2010). Detailed Guide: Cervical Cancer. Can cervical cancer be prevented? Retrieved August 8, 2011.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2009). "ACOG Education Pamphlet AP085 – The Pap Test". Washington, DC. Archived from the original on June 15, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- Shidham, VinodB; Mehrotra, Ravi; Varsegi, George; D′Amore, KristaL; Hunt, Bryan; Narayan, Raj (2011-01-01). "p16 INK4a immunocytochemistry on cell blocks as an adjunct to cervical cytology: Potential reflex testing on specially prepared cell blocks from residual liquid-based cytology specimens". CytoJournal. 8 (1): 1. doi:10.4103/1742-6413.76379. PMC 45765. PMID 21369522.
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2003). "Screening for Cervical Cancer: Recommendations and Rationale. AHRQ Publication No. 03-515A". Rockville, MD.: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (March 2012). "Screening for Cervical Cancer: Clinical Summary of USPSTF Recommendation". uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org. Archived from the original on 7 August 2012. Retrieved 31 July 2012.
- American Academy of Family Physicians. "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF). Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 11, 2017. Retrieved August 14, 2012{{inconsistent citations}}
- Arbyn M, Anttila A, Jordan J, Ronco G, Schenck U, Segnan N, Wiener H, Herbert A, von Karsa L (2010). "European Guidelines for Quality Assurance in Cervical Cancer Screening. Second Edition—Summary Document". Annals of Oncology. 21 (3): 448–458. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp471. PMC 2826099. PMID 20176693.
- Strander B (2009). "At what age should cervical screening stop?". Br Med J. 338: 1022–23. doi:10.1136/bmj.b809. PMID 19395422.
- Sasieni P, Adams J, Cuzick J (2003). "Benefit of cervical screening at different ages: evidence from the UK audit of screening histories". Br J Cancer. 89 (1): 88–93. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600974. PMC 2394236. PMID 12838306.
- Society of Gynecologic Oncology (February 2014). "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Retrieved 19 February 2013{{inconsistent citations}}, which cites
- Salani R, Backes FJ, Fung MF, Holschneider CH, Parker LP, Bristow RE, Goff BA (2011). "Posttreatment surveillance and diagnosis of recurrence in women with gynecologic malignancies: Society of Gynecologic Oncologists recommendations". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 204 (6): 466–78. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2011.03.008. PMID 21752752.
- Salani R, Nagel CI, Drennen E, Bristow RE (2011). "Recurrence patterns and surveillance for patients with early stage endometrial cancer". Gynecologic Oncology. 123 (2): 205–7. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.07.014. PMID 21820709.
- Bristow RE, Purinton SC, Santillan A, Diaz-Montes TP, Gardner GJ, Giuntoli RL (2006). "Cost-effectiveness of routine vaginal cytology for endometrial cancer surveillance". Gynecologic Oncology. 103 (2): 709–13. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.05.013. PMID 16797686.
- ACOG Committee on Gynecological Practice (2009). "ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice; Routine Pelvic Examination and Cervical Cytology Screening, Opinion #413". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 113 (5): 1190–1193. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181a6d022. PMID 19384150.
- American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Retrieved August 1, 2013., which cites
- Boulware LE, Marinopoulos S, Phillips KA, Hwang CW, Maynor K, Merenstein D, Wilson RF, Barnes GJ, Bass EB, Powe NR, Daumit GL (2007). "Systematic review: The value of the periodic health evaluation". Annals of Internal Medicine. 146 (4): 289–300. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-146-4-200702200-00008. PMID 17310053.
- Saslow D, Solomon D, Lawson HW, Killackey M, Kulasingam SL, Cain J, Garcia FA, Moriarty AT, Waxman AG, Wilbur DC, Wentzensen N, Downs LS, Spitzer M, Moscicki AB, Franco EL, Stoler MH, Schiffman M, Castle PE, Myers ER (2012). "American Cancer Society, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, and American Society for Clinical Pathology screening guidelines for the prevention and early detection of cervical cancer". CA Cancer J Clin. 62 (3): 147–72. doi:10.3322/caac.21139. PMC 3801360. PMID 22422631.
- Committee on Gynecologic Practice (2012). "Committee Opinion No. 534". Obstetrics & Gynecology. 120 (2, Part 1): 421–424. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e3182680517. PMID 22825111.
- Committee on Practice Bulletins—Gynecology (2012). "ACOG Practice Bulletin Number 131: Screening for cervical cancer". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 120 (5): 1222–1238. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e318277c92a. PMID 23090560.
- "Can Cervical Cancer Be Prevented?". www.cancer.org. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- Sasieni, P; Castanon, A; Cuzick, J; Snow, J (2009). "Effectiveness of Cervical Screening with Age: Population based Case-Control Study of Prospectively Recorded Data". BMJ. 339: 2968–2974. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2968. PMC 2718082. PMID 19638651.
- Marrazzo JM, Koutsky LA, Kiviat NB, Kuypers JM, Stine K (2001). "Papanicolaou test screening and prevalence of genital human papillomavirus among women who have sex with women". American Journal of Public Health. 91 (6): 947–952. doi:10.2105/AJPH.91.6.947. PMC 1446473. PMID 11392939.
- Smith, RA; et al. (2002). "American Cancer Society Guideline for the Early Detection of Cervical Neoplasia and Cancer". 52 (1): 8–22.
ACS and others have recommended, since before 1980, that conventional cytology can be safely performed up to every three years for most women.
Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Salani, R (2017). "An update on post-treatment surveillance and diagnosis of recurrence in women with gynecologic malignancies: Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) recommendations" (PDF). Gynecologic Oncology. 146 (1): 3–10. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.03.022. PMID 28372871.
- DeMay, M. (2007). Practical principles of cytopathology. Revised edition. Chicago, IL: American Society for Clinical Pathology Press. ISBN 978-0-89189-549-7.
- "Cancer Research UK website". Archived from the original on 2009-01-16. Retrieved 2009-01-03.
- Raffle AE, Alden B, Quinn M, Babb PJ, Brett MT (2003). "Outcomes of screening to prevent cancer: analysis of cumulative incidence of cervical abnormality and modelling of cases and deaths prevented". BMJ. 326 (7395): 901. doi:10.1136/bmj.326.7395.901. PMC 153831. PMID 12714468.
- "Pap Smear". Retrieved 2008-12-27.
- Eversole GM, Moriarty AT, Schwartz MR, Clayton AC, Souers R, Fatheree LA, Chmara BA, Tench WD, Henry MR, Wilbur DC (2010). "Practices of participants in the college of american pathologists interlaboratory comparison program in cervicovaginal cytology, 2006". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 134 (3): 331–5. doi:10.1043/1543-2165-134.3.331 (inactive 2020-03-12). PMID 20196659.
- Nayar, Ritu; Solomon, Diane (2004-01-01). "Second edition of 'The Bethesda System for reporting cervical cytology' - Atlas, website, and Bethesda interobserver reproducibility project". CytoJournal. 1 (1): 4. doi:10.1186/1742-6413-1-4. PMC 526759. PMID 15504231.
- PapScreen Victoria > Pregnant women Archived 2014-02-01 at the Wayback Machine from Cancer Council Victoria 2014
- Michael CW (1999). "The Papanicolaou Smear and the Obstetric Patient: A Simple Test with Great Benefits". Diagnostic Cytopathology. 21 (1): 1–3. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0339(199907)21:1<1::AID-DC1>3.0.CO;2-0. hdl:2027.42/35304. PMID 10405797.
- Lanouette JM, Puder KS, Berry SM, Bryant DR, Dombrowski MP (1997). "Is inflammation on Papanicolaou smear a risk factor for preterm delivery?". Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy. 12 (4): 244–247. doi:10.1159/000264477. PMID 9354886.
- "Pregnant women". papscreen.org. Cancer Council Victoria. Archived from the original on 2015-01-08. Retrieved 2015-01-16.
- International Federation for Cervical Pathology and Colposcopy (IFCPC) classification. References:
-"Transformation zone (TZ) and cervical excision types". Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia.
- Jordan, J.; Arbyn, M.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Schenck, U.; Baldauf, J-J.; Da Silva, D.; Anttila, A.; Nieminen, P.; Prendiville, W. (2008). "European guidelines for quality assurance in cervical cancer screening: recommendations for clinical management of abnormal cervical cytology, part 1". Cytopathology. 19 (6): 342–354. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2303.2008.00623.x. ISSN 0956-5507. PMID 19040546. - Projectstore (2020-07-06). "Comprehensive Knowledge About Pap Test". Free Student Project Topics. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
A Pap test can be done during your menstrual period, but for good results it is better to schedule the test at another time because the additional cells can obscure cervical cells and partly because this part of the menstrual cycle is when the female organs are most inflamed
- "Excerpts from Changing Bodies, Changing Lives". Our Bodies Ourselves. Archived from the original on 2013-12-18. Retrieved 2013-07-02.
- Tingåker, Berith K; Irestedt, Lars (2010). "Changes in uterine innervation in pregnancy and during labour". Current Opinion in Anesthesiology. 23 (3): 300–303. doi:10.1097/aco.0b013e328337c881. PMID 20216064.
- Wright, Jessica L. (2010). "The Effect of Using Water-based Gel Lubricant During a Speculum Exam On Pap Smear Results". School of Physician Assistant Studies. Archived from the original on 24 May 2013. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- Martin-Hirsch P, Lilford R, Jarvis G, Kitchener HC (1999). "Efficacy of cervical-smear collection devices: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Lancet. 354 (9192): 1763–1770. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02353-3. PMID 10577637.
- Biscotti CV, Dawson AE, Dziura B, Galup L, Darragh T, Rahemtulla A, Wills-Frank L (2005). "Assisted primary screening using the automated ThinPrep Imaging System". Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 123 (2): 281–7. doi:10.1309/AGB1MJ9H5N43MEGX. PMID 15842055.
- Willis BH, Barton P, Pearmain P, Bryan S, Hyde C, "Cervical screening programmes: can automation help? Evidence from systematic reviews, an economic analysis and a simulation modelling exercise applied to the UK". Health Technol Assess 2005 9(13). Archived 2008-09-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Davey E, d'Assuncao J, Irwig L, Macaskill P, Chan SF, Richards A, Farnsworth A (2007). "Accuracy of reading liquid based cytology slides using the ThinPrep Imager compared with conventional cytology: prospective study". BMJ. 335 (7609): 31. doi:10.1136/bmj.39219.645475.55. PMC 1910624. PMID 17604301.
- "Pap and HPV Testing". 2014-09-15.
- Bettigole C (2013). "The Thousand-Dollar Pap Smear". New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (16): 1486–1487. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1307295. PMID 24131176.
- M.J. O'Dowd, E.E. Philipp, The History of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, London, Parthenon Publishing Group, 1994, p. 547.
- Diamantis A, Magiorkinis E, Androutsos G (Jul 2010). "What's in a name? Evidence that Papanicolaou, not Babeș, deserves credit for the Pap test". Diagn Cytopathol. 38 (7): 473–6. doi:10.1002/dc.21226. PMID 19813255.
- Koss, Leopold G. (2003-01-01). "Aurel Babeş". International Journal of Gynecological Pathology. 22 (1): 101–102. doi:10.1097/00004347-200301000-00020. ISSN 0277-1691. PMID 12496707.
- Krunger, TF; Botha, MH (2007). Clinical gynaecology (3 ed.). South Africa: Juta. p. 23. ISBN 9780702173059. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- Bewtra, Chhanda; Pathan, Muhammad; Hashish, Hisham (2003-10-01). "Abnormal Pap smears with negative follow-up biopsies: Improving cytohistologic correlations". Diagnostic Cytopathology. 29 (4): 200–202. doi:10.1002/dc.10329. ISSN 1097-0339. PMID 14506671.
- "Cervical cancer screening". www.cancer.org.au. Retrieved 2020-08-13.
- Health, Australian Government Department of, Cervical Screening, Australian Government Department of Health, retrieved 2020-08-13
- Cancer Institute of NSW. "Do I need to pay for my cervical screen". Cancer Institute NSW.
- Chen, Y-Y; You, S-L; Chen, C-A; Shih, L-Y; Koong, S-L; Chao, K-Y; Hsiao, M-L; Hsieh, C-Y; Chen, C-J (2009-07-07). "Effectiveness of national cervical cancer screening programme in Taiwan: 12-year experiences". British Journal of Cancer. 101 (1): 174–177. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605139. ISSN 0007-0920. PMC 2713714. PMID 19536091.
- Chen, M.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.-W. (2018-10-01). "HPV Vaccination and Cervical Cancer Screening in Taiwan". Journal of Global Oncology. 4 (Supplement 2): 235s–235s. doi:10.1200/jgo.18.94300. ISSN 2378-9506.
- Fang-Hsin Leea; Chung-Yi Lic; Hsiu-Hung Wanga; Yung-Mei Yang (2013). "The utilization of Pap tests among different female medical personnel: A nationwide study in Taiwan". Preventive Medicine. 56 (6): 406–409. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2013.03.001. PMID 23524115.
- "Knowledge of Cervical Cancer Screening among Women". iprojectmaster.com. Retrieved 2020-02-10.
- NB Peterson; HJ Murff; Y Cui; M Hargreaves; JH Fowke (Jul–Aug 2008). "Papanicolaou testing among women in the southern United States". Journal of Women's Health. 17 (6): 939–46. doi:10.1089/jwh.2007.0576. PMC 2942751. PMID 18582173. Retrieved October 15, 2013.
- "Cervical screening (smear testing) | Health Information | Bupa UK". www.bupa.co.uk. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- admin (2013-08-30). "About cervical screening". Jo's Cervical Cancer Trust. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- OB-GYN 101: Introductory Obstetrics & Gynecology > Coccoid Bacteria Archived 2014-02-22 at the Wayback Machine by Michael Hughey Hughey at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center. Retrieved Feb 2014.
External links
- The Pap Test: Questions and Answers — from the U.S.'s National Cancer Institute
- MedlinePlus: Cervical Cancer Prevention/Screening — from MedlinePlus
- NHS Cervical Screening Programme — from the UK's National Health Service
- Cervical cancer screening information – from Cancer Research UK
- Pap Smear – from Lab Tests Online
- Pap Smear — from eMedicineHealth
- PapScreen – Australian information about Pap tests (or Pap smears)
- Canadian Guidelines for Cervical Cancer Screening – Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada