Proxymetacaine
Proxymetacaine (INN) or proparacaine (USAN) is a topical anesthetic drug of the aminoester group.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical (eye drops) |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Plasma |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.169 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
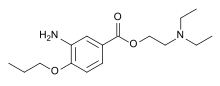
| Formula | C16H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 294.395 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Clinical pharmacology
Proxymetacaine is a local anesthetic which on topical application penetrates sensory nerve endings in the corneal tissue.[1]
Mechanism of action
Proxymetacaine is believed to act as an antagonist on voltage-gated sodium channels to affect the permeability of neuronal membranes; how this inhibits pain sensations and the exact mechanism of action of proxymetacaine are, however, unknown.[2]
Indications and usage
Proxymetacaine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution (eye drops) is indicated for procedures such as tonometry, gonioscopy, removal of foreign bodies, or other similar procedures requiring topical anesthesia of the cornea and conjunctiva.[3]
Warnings
Proxymetacaine is for topical ophthalmic use only, and it is specifically not intended for injection. Prolonged use of this or any other topical ocular anesthetic may produce permanent corneal opacification with accompanying visual loss.
How supplied
Proxymetacaine is available as its hydrochloride salt in ophthalmic solutions at a concentration of 0.5%. Although it is no longer on patent, it is still marketed under the trade names Alcaine, Ak-Taine, and others. Proparacaine 0.5% is marketed as Poencaina by Poen Laboratories.[4]
References
- Draeger J, Langenbucher H, Bannert C (1984). "Efficacy of topical anaesthetics". Ophthalmic Research. 16 (3): 135–8. doi:10.1159/000265308. PMID 6472792.
- Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (1980). The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (6th ed.). New York: MacMillan Pub. ISBN 978-0023447204.
- Murphy PJ, Ntola AM (April 2009). "Prolonged corneal anaesthesia by proxymetacaine hydrochloride detected by a thermal cooling stimulus". Contact Lens & Anterior Eye. 32 (2): 84–7, quiz 99–100. doi:10.1016/j.clae.2008.12.006. PMID 19181566.
- "Poen-Caina generic. Price of poen-caina. Uses, Indications and Description". ndrugs. Retrieved 15 March 2018.