Omapatrilat
Omapatrilat (INN,[1] proposed trade name Vanlev) is an experimental antihypertensive agent that was never marketed.[2] It inhibits both neprilysin (neutral endopeptidase, NEP) and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). NEP inhibition results in elevated natriuretic peptide levels, promoting natriuresis, diuresis, vasodilation, and reductions in preload and ventricular remodeling.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | BMS-186716 |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
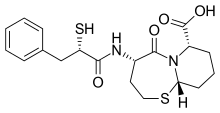
| Formula | C19H24N2O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 408.53 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
It was discovered and developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb but failed in clinical trials as a potential treatment for congestive heart failure due to safety concerns about its causing angioedema.[3]
Omapatrilat angioedema was attributed to its dual mechanism of action, inhibiting both angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and neprilysin (neutral endopeptidase), both of these enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of bradykinin which causes vasodilation, angioedema, and airway obstruction.
See also
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 40" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 190. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- "Omapatrilat". Adis Insight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- Venugopal J (2 March 2005). "Pharmacological Modulation of the Natriuretic Peptide System". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 13 (9): 1389–1409. doi:10.1517/13543776.13.9.1389.
Further reading
- Liao WC, Vesterqvist O, Delaney C, Jemal M, Ferreira I, Ford N, et al. (October 2003). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the vasopeptidase inhibitor, omapatrilat in healthy subjects". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 56 (4): 395–406. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01888.x. PMC 1884361. PMID 12968984.