New South Wales F351 class locomotive
The F351 class (X10 post 1924) was a class of steam locomotives built for the New South Wales Government Railways in Australia.[1]
| New South Wales F351 Class | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
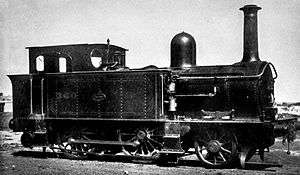 F.351 Class Locomotive | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
History
Originally ordered in 1879 but the order was stopped.[2] A follow-up order in 1882 was made, the specification originally for 2-4-0 tank locomotives with 5'0" diameter driving wheels made by the acting locomotive engineer Mr Scott. During his absence in England on official business this was changed by Mr T. Middelton to an 0-6-0 type with 4'0" diameter driving wheels, claiming that such locomotives would be capable of 30-33 mph in service. Despite Scott's protests, Commissioner Goodchap approved the changes and six locomotives were designed and built by Vulcan Foundry. The subsequent 0-6-0 locomotives became the R(285) class, later the Z18 class.[3]
In August 1884 Mr Scott informed the commissioner that more locomotives were required with the opening of the Illawarra extension. Mr Middelton wanted more of the R(285 class), but Mr Scott recommended his original proposed design from 1881. After much hesitation by the government, Beyer, Peacock and Company were asked to design and build the locomotives. These became the F(351) class and went into service on the Sydney suburban network in 1885-86, being numbered 351 to 362. In 1887 six more locomotives of this design (numbered 363 to 3680) were delivered by Henry Vale of Sydney. No. 366 featured in the Redfern collision of 1894. The design was extremely similar to a number of 2-4-0 tank locomotives supplied to the Isle of Wight Central Railway from 1864. A similar locomotive was delivered to the South Australian Railways from 1884 as their P-class.[4]
Their running life came to an end in 1901 as a result of the findings on the Sydenham derailment involving No. 363 and the whole class was taken out of passenger work. The F351 class were known to oscillate and rock at high speeds and were officially limited to 30 mph. A factor in the Sydenham derailment was the driver exceeding the official speed limit. The locomotive was believed to be doing 51 mph when the accident occurred. The entire class was subsequently withdrawn from passenger work and allocated to various shunting, yard and depot duties. A number of the class were modified with a heavy cast iron front buffer beam in an attempt to stabilise the front of the locomotive after 1901.[5] Between 1906 and 1929 ten of the class were sold to various private railway operators.
All members of the class had been withdrawn from passenger work by 1914. Eleven were still on the books at this stage and were renumbered Lo.19-Lo.26 (Lo. Indicated that they were no longer in revenue-earning service). In 1924 they were renumbered in the X10 class, bearing numbers 1031-1033, 1035-1037 and 1039-1043.[6] From 1914, members of the class still in NSWGR service were rebuilt with the same domed boilers that replaced the dome-less type originally supplied on the R285 class. A number of other modifications were made to the class such as replacing the leaf spring on the front axle with twin coil springs. For reasons unknown 1033 at some stage had the original parallel buffers on the rear replaced with longer bottle-shaped Turton buffers. In 1966, 1036 with withdrawn and scrapped, but during an overhaul the boiler was given to 1076, previously numbered R288 then 1804.
Three of the class were still in service with the NSWGR from 1940. 1033 at Eveleigh Railway Workshops, 1036 at Junee Locomotive Depot (withdrawn and scrapped in 1966) and 1042 at Cardiff Railway Workshops.1042 was given an overhaul as late as 1970 at the age of 83 years and continued working until February 1973,[7] only three months shy of 86 years in service and having completed 401,359 km (249,446 miles) of logged running. 1036 (F359) had accumulated the most mileage in service with 707,564 km (437,889 miles) at withdrawal.[8]
Preservation
- 1033 (former F355) was preserved by the former New South Wales Rail Transport Museum, now Transport Heritage NSW.[9][10]
- 1042 at Maitland Steam Park, Cardiff Locomotive Workshops shunter, under restoration[11]
References
- New South Wales Railways 1855-1955. Published by Department of Railways
- Forsyth, J.H. (1974) "Steam Locomotive Data"
- Grunbach, A (1989) "A Compendium of New South Wales Steam Locomotives" p. 74-75
- Grunbach, A (1989) "A Compendium of New South Wales Steam Locomotives" p. 85-86
- http://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/heritageapp/ViewHeritageItemDetails.aspx?ID=4807205
- http://www.australiansteam.com/1076.htm
- Oberg, L. (2007) "Locomotives of Australia"p. 73
- Forsyth, J.H. (1974) "Steam Locomotive Data"
- Heritage Register Locomotive, Steam Locomotive 1033
- NSWRTM Steam Locomotive exhibits
- Australian Steam, Cardiff Workshops Shunter 1033
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to New South Wales F351 class locomotives. |