Nephrolenellus
Nephrolenellus is an extinct genus of trilobite, fossil marine arthropods, of relatively small size (sagittal length of cephalon rarely exceeds 11 mm). Currently two species are attributed to it. Nephrolenellus lived at the end of the Lower Cambrian. Species are known from the Great Basin of California, Nevada and Arizona, with one specimen from Canada.[2]
| Nephrolenellus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| juvenile Nephrolenellus multinodus, 9mm, frontal glabellar lobe broken | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Superfamily: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | Nephrolenellus Palmer & Repina, 1993 |
| Species | |
Taxonomy
N. geniculatus may have been a direct descendant of N. multinodus.[2]
Distribution
Nephrolenellus multinodus occurs in the late Lower Cambrian of California (Toyonian, Pyramid Shale Member, Carrara Formation, Inyo County, 35.8° N, 116.2° W).[3] and of Nevada (Toyonian, Lincoln County; and C-Shale Member, Pioche Formation, Ruin Wash, Chief Range, 37.8° N, 114.6° W).[4]
Description
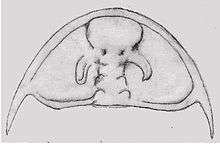
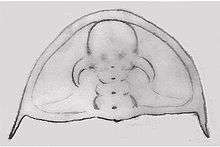
As with most early trilobites, Nephrolenellus has an only thinly calcified exoskeleton. Although most of the body is rather flat, the frontal lobe (L4) of the central area of the cephalon (or glabella) is raised, but not bulbous, and does not overlap the border at the front in dorsal view. It also has the crescent-shaped eye ridges typical for the earliest trilobites. As part of the Olenellina suborder, Nephrolenellus lacks dorsal sutures. Like all other members of the Olenelloidea superfamily, the eye-ridges spring from the back of the frontal lobe (L4) of the glabella. Typically for Nephrolenellus the eyeridges are pointing backwards and significantly (45°) outwards (along the tangent between the base and termination). The glabella is strongly hourglass-shaped, very much constricted at the second pair of side lobes (L2). The furrow between the second and third pair of lobes (S2) is transverse or gently convex anteriorly. S3 is pit-like and isolated from furrow defining the glabella (or axial furrow). The spine at the outer backside of the cephalon is longer than the most backward lobe of the glabella (also called occipital ring or L0), and it is based at point the cephalon is at its widest. The prothorax consist of thirteen segments, and the third segments has enlarged side lobes (or pleural lobes) that each carry trailing spine at the side that is comparable in length to the entire exoskeleton. It lacks the long axial spine where prothorax ends. The portion of the thorax where the pleural lobes are reduced (or opisthothorax) consist of at least 23 segments.
References
- Lieberman, B.S. (1999). "Systematic Revision of the Olenelloidea (Trilobita, Cambrian)" (PDF). Bulletin of the Peabody Museum of Natural History. 45.
- M., Webster (2007). "Ontogeny and evolution of the early Cambrian trilobite genus Nephrolenellus (Olenelloidea)". Journal of Paleontology. 81: 1168–1193. doi:10.1666/06-092.1.
- E.D. Fowler (1999). Biostratigraphy of upper Dyeran strata of the Carrara Formation, Emigrant Pass, Nopah Range, California. Laurentia 99: V field conference of the Cambrian Stage Subdivision Working Group, International Subcomission on Cambrian Stratigraphy. pp. 46–50.
- Palmer, A.R. (1998). "Terminal Early Cambrian Extinction of the Olenellina: Documentation from the Pioche Formation, Nevada". Journal of Paleontology. 72 (4): 650–672. JSTOR 1306693.