NGC 694
NGC 694 is a spiral galaxy approximately 136 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Aries.[3] It was discovered by German astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest on December 2, 1861 with the 11-inch refractor at Copenhagen.[4]
| NGC 694 | |
|---|---|
 NGC 694 (SDSS) | |
| Observation data (J2000.0 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Aries |
| Right ascension | 01h 50m 58.50s [1] |
| Declination | +21° 59′ 51.00″ [1] |
| Redshift | 0.009840 [1] |
| Helio radial velocity | 2950 ± 4 km/s [1] |
| Distance | 136 Mly |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 13.30 [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 14.30 [2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | S0 [2] |
| Apparent size (V) | 0.6 x 0.4 [2] |
| Other designations | |
| PGC 6816, MCG +04-05-020, UGC 1310 | |
Nearby galaxies
NGC 694 is a member of a small galaxy group known as the NGC 691 group, the main other members of which are NGC 680, NGC 691 and NGC 697.[5][6] IC 167 lies 5.5 arcminutes to the south-southeast.[4]
Supernova SN 2014bu
Supernova SN 2014bu was discovered in NGC 694 on June 17, 2014 by Berto Monard. [7]
SN 2014bu had magnitude about 15.5 and was located at (coordinates: RA 01h50m58.4s, DEC +22d00m00s, J2000.0).[1] It was classified as type II-P supernova. [7]
Image gallery
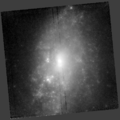 NGC 694 (NASA/ESA HST)
NGC 694 (NASA/ESA HST)
gollark: It can generate ~100MHz square waves and you can connect up an antenna, which is *basically* what a radio transmitter would do but stupider and worse.
gollark: Yes, a clock or something.
gollark: A quirk of the raspberry pi means it can transmit FM radio with horrible interference because it can only broadcast square waves or something, because of happening to have a somewhat adjustable ~100MHz clock exposed on external pins or something.
gollark: Technically I *could* transmit FM radio. Also technically, I can't transmit it at any significant power and doing so would be illegal.
gollark: idea: replace osmarks internet radio™ with a constant 440Hz buzzing noise.
References
- "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". ned.ipac.caltech.edu. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- "Revised NGC Data for NGC 694". spider.seds.org. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- "NGC 694". Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- "Data for NGC 694". www.astronomy-mall.com. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
- Garcia, A. M. (1993). "General study of group membership. II - Determination of nearby groups". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 100 (1): 47–90. Bibcode:1993A&AS..100...47G. ISSN 0365-0138.
- Noordermeer, E.; van der Hulst, J. M.; Sancisi, R.; Swaters, R. A.; van Albada, T. A. (2005). "The Westerbork HI survey of spiral and irregular galaxies. III. HI observations of early-type disk galaxies". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 442 (1): 137–157. arXiv:astro-ph/0508319. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053172.
- "Transient Name Server (TNS)". wis-tns.weizmann.ac.il. Retrieved March 3, 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to NGC 694. |
- NGC 694 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- SEDS
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.