N-Acetylglucosamine
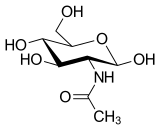
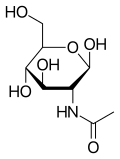
N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) is an amide derivative of the monosaccharide glucose. It is a secondary amide between glucosamine and acetic acid. It is significant in several biological systems.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
β-D-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-glucopyranose | |
| Other names
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GlcNAc NAG | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1247660 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.517 |
| EC Number |
|
| 721281 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 221.21 |
| Melting point | 211 |
| Related compounds | |
Related Monosaccharides |
N-Acetylgalactosamine |
Related compounds |
Glucosamine Glucose |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is part of a biopolymer in the bacterial cell wall, which is built from alternating units of GlcNAc and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc), cross-linked with oligopeptides at the lactic acid residue of MurNAc. This layered structure is called peptidoglycan (formerly called murein).
GlcNAc is the monomeric unit of the polymer chitin, which forms the exoskeletons of arthropods like insects and crustaceans. It is the main component of the radulas of mollusks, the beaks of cephalopods, and a major component of the cell walls of most fungi.
Polymerized with glucuronic acid, it forms hyaluronan.
GlcNAc has been reported to be an inhibitor of elastase release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (range 8–17% inhibition), however this is much weaker than the inhibition seen with N-acetylgalactosamine (range 92–100%).[1]
Medical uses
It has been proposed as a treatment for autoimmune diseases,[2] and recent tests have claimed some success.[3]
O-GlcNAcylation
O-GlcNAcylation is the process of adding a single N-acetylglucosamine sugar to the serine or threonine of a protein.[4] Comparable to phosphorylation, addition or removal of N-acetylglucosamine is a means of activating or deactivating enzymes or transcription factors.[4] In fact, O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation often compete for the same serine/threonine sites. [4] O-GlcNAcylation most often occurs on chromatin proteins, and is often seen as a response to stress.[4]
Hyperglycemia increases O-GlcNAcylation, leading to insulin resistance.[5] Increased O-GlcNAcylation due to hyperglycemia is evidently a dysfunctional form of O-GlcNAcylation. O-GlcNAcylation decline in the brain with age is associated with cognitive decline. When O-GlcNAcylation was increased in the hippocampus of aged mice, spatial learning and memory improved.[6]
See also
- Keratan sulfate
- N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc)
- N-Acetyllactosamine synthase
- Wheat germ agglutinin, a plant lectin that binds to this substrate
References
- Kamel, M.; Hanafi, M.; Bassiouni, M. (1991). "Inhibition of elastase enzyme release from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by N-acetyl-galactosamine and N-acetyl-glucosamine". Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 9 (1): 17–21. PMID 2054963.
- "Sugar supplement may treat immune disease - health - 07 June 2007 - New Scientist". Retrieved 8 June 2007.
- "Glucosamine-Like Supplement Suppresses Multiple Sclerosis Attacks, Study Suggests". Science Daily.
- Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G, Lagerlof O (2011). "Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease". Annual Review of Biochemistry. 80: 825–858. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-060608-102511. PMC 3294376. PMID 21391816.
- Ma J, Hart GW (2013). "Protein O-GlcNAcylation in diabetes and diabetic complications". Expert Review of Proteomics. 10 (4): 365–380. doi:10.1586/14789450.2013.820536. PMC 3985334. PMID 23992419.
- Wheatley EG, Albarran E, White CW 3rd, Bieri G, Sanchez-Diaz C, Pratt K, Snethlage CE, Ding JB, Villeda SA (2019). "Neuronal O-GlcNAcylation Improves Cognitive Function in the Aged Mouse Brain". Current Biology. 29 (20): 3359–3369. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.003. PMID 31588002.