Misszhouia
Misszhouia is a genus of small to average sized (up to 6 centimetres (2.4 in) long)[1] marine arthropods within the Naraoiidae family, that lived during the early Cambrian period. The only species presently known is Misszhouia longicaudata (the genus is monotypic).
| Misszhouia longicaudata | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | †Misszhouia |
| Species: | †M. longicaudata |
| Binomial name | |
| Misszhouia longicaudata (Zhang & Hou 1985) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Naraoia longicaudata Zhang & Hou 1985 | |
Etymology
Misszhouia was named after "Miss Zhou" (Guiqin Zhou), to honour her for her skilled preparation of Chengjiang fossils.[2]
Description
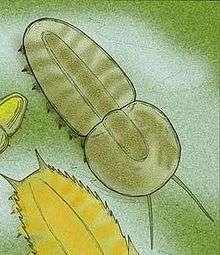
Misszhouia longicaudata is almost flat (dorso-ventrally). The upper (or dorsal) side of the body consists of a non-calcified headshield (cephalon) and tailshield (pygidium) without body segments between. The body is narrowed at the articulation between cephalon and pygidium. The long many-segmented antennae are directed forward. There are no eyes. The gut has a relatively small diameter, and there are four pairs of relatively small digestive sacs (or caeca) in the cephalon only, and no branches towards the edge of the cephalon (unlike Naraoia). There are 25 limb pairs[1] with two branches on a common base, like Naraoia and trilobites. The outer branch (or exopod) has many parallel long fine flattened side branches (setae) that probably functioned as gills with a large surface area. This exopod is attached along the whole length of the base segment (coxa) and at least the proximal part of the first segment of the inner branch (endopod). The shaft of the exopod tapers gently towards its tip. The endopod is composed of seven podomeres including a terminal claw.[2]
Differences from Naraoia
The sister genus Naraoia differ from Misszhouia longicaudata in having the following characteristics:
- A large, ramifying anterior pair of digestive branches (or diverticula) almost reaching the cephalon edges.
- A bloated, mud-filled gut.
- Laterally deflected antennae.[2]
Distribution
Misszhouia has been collected from the Lower Cambrian (late Atdabanian) of China (Yu'anshan Member of the Heilinpu Formation at Maotia’shan, the classic Chengjiang locality).[2] It has also been found in the Niutitang Formation.[3]
Ecology
All Naraoids were probably marine bottom dwellers. Misszhouia probably lived as a predator or scavenger. This can be deduced from the robust and spiny basal segments of the legs, which resemble the gnathobases of trilobites. These were likely used for chewing. Such carnivorous behaviour is confirmed by the relatively small digestive system, that indicates high nutrition value food.[2]
Taxonomy
Misszhouia longicaudata was formerly considered a member of the genus Naraoia, originally known as "Naraoia longicaudata", until separated in 1997.[2] [4]
References
- L. Ramskold, J.-Y. Chen, G.D. Edgecombe, and G.-Q. Zhou ( 1996). Preservational folds simulating tergite junctions in tegopeltid and naraoiid arthropods. Lethaia 29:15-20. ISSN 0024-1164.
- Chen, J.-Y., G.D. Edgecombe and L. Ramskjöld. Morphological and ecological disparity in naraoiids (Arthropoda) from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Fauna, China. Records of the Australian Museum 49(1), pp. 1-24. 1997
- Steiner, M., M. Zhu, Y. Zhao and B.-D. Erdtmann. Lower Cambrian Burgess Shale-type fossil associations of South China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 220, pp. 129-152. 2005.
- Genus †Misszhouia - Hierarchy - The Taxonomicon
External links
- Misszhouia longicaudata The Virtual Fossil Museum