Methyl blue
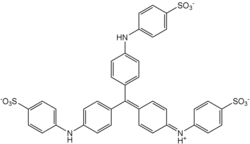
Methyl blue is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C37H27N3Na2O9S3. It is used as a stain in histology,[1] and stains collagen blue in tissue sections. It can be used in some differential staining techniques such as Mallory's connective tissue stain and Gömöri trichrome stain, and can be used to mediate electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Fungal cell walls are also stained by methyl blue.
 | |||
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
Cotton blue, Helvetia blue, Acid blue 93, C.I. 42780 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.852 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C37H27N3Na2O9S3 | |||
| Molar mass | 799.814 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | red solid | ||
| Soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Methyl blue is also available in mixture with water blue, under name Aniline Blue WS, Aniline blue, China blue, or Soluble blue; and in a solution of phenol, glycerol, and lactic acid under the name Lactophenol cotton blue (LCB), which is used for microscopic visualization of fungi.
See also
References
- R. W. Sabnis (2010). Handbook of Biological Dyes and Stains: Synthesis and Industrial Applications. John Wiley & Sons. p. 24.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


