Biebrich scarlet
Biebrich scarlet (C.I. 26905) is a molecule used in Lillie's trichrome.[1]
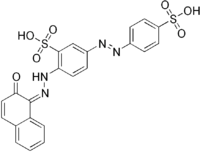 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[(2Z)-2-(2-oxonaphthalen-1-ylidene)hydrazinyl]-5-(4-sulfophenyl)diazenyl-benzenesulfonic acid | |
| Other names
Croceine scarlet | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.895 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Biebrich+scarlet |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H16N4O7S2 | |
| Molar mass | 512.517 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The dye was created in 1878 by the German chemist Rudolf Nietzki.[2]
See also
References
- Lillie, R. D. (1940). "Further Experiments with the Masson Trichrome Modification of Mallory's Connective Tissue Stain". Stain Technology. 15 (1). doi:10.3109/10520294009110327.
- Schwarz, Holm-Dietmar (1999). "Nietzki, Rudolf Hugo". Neue Deutsche Biographie (in German). 19. Retrieved 2015-10-12.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.