Metam sodium
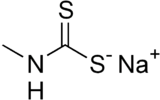
Metam sodium is an organosulfur compound (formally a dithiocarbamate), which is used as a soil fumigant, pesticide, herbicide, and fungicide. It is one of the most widely used pesticides in the United States, with approximately 60 million pounds used in 2001.[2] Metam sodium is the sodium salt of methyl dithiocarbamate.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium methylaminomethanedithioate | |
| Other names
Metham sodium Carbathion Carbathione Carbothion Metamsodium Metam-sodium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.812 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H4NNaS2 | |
| Molar mass | 129.18 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Metam sodium can be prepared from methylamine, carbon disulfide, and sodium hydroxide; or from methyl isothiocyanate and sodium thiolate.[1]
Upon exposure to the environment, metam sodium decomposes to form methyl isothiocyanate.[3]
Metam sodium is a documented cause of reactive airways dysfunction syndrome.
In 1991 a tank car with 19,000 gallons of metam sodium spilled into Sacramento River above Lake Shasta. This killed all fish in a 41-mile stretch of the river. By 20 years later the rainbow trout population had recovered.[4]
See also
- Zineb - A related dithiocarbamate salt which is also used as a fungicide
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5860.
- 2000-2001 Pesticide Market Estimates Archived 2009-02-07 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- Review of Metam Sodium, Dazomet, Methylisothiocyanate (MITC), Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority, June 1997
- "Largest chemical spill in California history". dtsc.ca.gov. Retrieved 2017-12-11.
External links
- Metam sodium in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)