Zineb
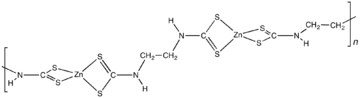
Zineb is the chemical compound with the formula {Zn[S2CN(H)CH2CH2N(H)CS2]}n. Structurally, it is classified as a coordination polymer. This pale yellow solid is used as fungicide.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
zinc ethane-1,2-diylbis(dithiocarbamate) | |
| Other names
1,2 ethanediylbis[dithiocarbamodithioato](2−) zinc, Dithane Z-78, Aphytora, Amitan | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.970 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2S4Zn | |
| Molar mass | 275.8 g/mol (monomer) |
| Appearance | pale yellow powder |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
Irritants (Xi) Sensitizers |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R37 R43 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | (S2) S8 S24/25 S46 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and applications
It is produced by treating ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) sodium salt, "nabam", with zinc sulfate. This procedure can be carried out by mixing nabam and zinc sulfate in a spray tank.[2] Its uses include control of downy mildews, rusts, and redfire disease.[1] In the US it was once registered as a "General Use Pesticide", however all registrations were voluntarily cancelled following an EPA special review.[2] It continues to be used in many other countries.
Structure
Zineb is a polymeric complex of zinc with a dithiocarbamate.[1] The polymer is composed of Zn(dithiocarbamate)2 subunits linked by an ethylene (-CH2CH2-) backbone.[3] A reference compound is [Zn(S2CNEt2)2]2, which features a pair of tetrahedral Zn centers bridged by one sulfur center.[4]
See also
- Metam sodium - A related dithiocarbamate salt which is also used as a fungicide
- Maneb - ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) with manganese instead of zinc
References
- Franz Müller, Peter Ackermann, Paul Margot (2012). "Fungicides, Agricultural, 2. Individual Fungicides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.o12_o06.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Michael A. Kamrin, (1997) Pesticide Profiles: Toxicity, Environmental Impact, and Fate, CRC Press, ISBN 1-56670-190-2
- R. Engst, W. Schnaak (1974). Gunther F.A. (ed.). "Residues of dithiocarbamate fungicides and their metabolites on plant foods". Residue Reviews. New York, NY: Springer. 52: 45–6. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-8504-6_3.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Bonamico, M.; Mazzone, G.; Vaciago, A.; Zambonelli, L., "Structural studies of metal dithiocarbamates. III. The Crystal and Molecular Structure of Zinc Diethyldithiocarbamate", Acta Crystallogr. 1965, volume 19, pp. 898-909. doi:10.1107/S0365110X65004620
External links
- Zineb in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)