Medellín Metro
The Medellín Metro (Spanish: Metro de Medellín) is a rapid transit system that crosses the Metropolitan Area of Medellín from North to South and from Centre to West. It first opened for service on 30 November 1995.[4] As one of the first implementations of modern mass transportation in Colombia and the only metro system in the country, the Medellín Metro is a product of the urban planning of the Antioquia department of Colombia. It is part of the Aburrá Valley Integrated Transport System (Sistema Integrado de Transporte del Valle de Aburrá, SITVA).
 | |||
 | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | Department of Antioquia, Medellín City | ||
| Locale | Medellín, Antioquia, Colombia | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit | ||
| Number of lines | 2[1] | ||
| Line number |
| ||
| Number of stations | 27[2] | ||
| Annual ridership | 228 million (2019)[3] | ||
| Website | Medellín Metro | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 30 November 1995[4] | ||
| Operator(s) | Metro de Medellín | ||
| Number of vehicles | 80 trains (3 cars per train)[2] | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 31.3 km (19.4 mi)[2] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 1500 V DC overhead | ||
| |||
The city of Medellín and its urban complex (ten cities in the Aburrá Valley) had a period of relatively recent industrial development that started in the 1930s. The streetcar (tranvía) at the beginning of the 20th century can be considered a predecessor of the current Medellín Metro. The company known in Spanish as Empresa de Transporte Masivo del Valle de Aburrá - Metro de Medellín Ltda was created on 31 May 1979.[4]
History
The railway history of Colombia and Antioquia has not been indifferent to the industrialization process that started at the end of the 19th century and that only has been restrained by the social and political conflicts of this South American nation.
The Antioquia Department, and the Paisa Region in general, owe their progress to the construction of railways that put them in direct contact with the rest of the country (especially with Bogotá, Cali and the Colombian Caribbean Littoral).
Although the famous Antioquia Railway came to a decline and is now only remembered by the so-called towns of the train, an urban railway system received the attention of the region. In the same way Antioquia's Railways had a century ago, the Medellín Metro became an important social, cultural and development axis in one of the most important cities of Colombia and South America.
The city's speedy urban growth, especially since the 1960s, has filled the entire Aburrá Valley and made towns touch its borders: Bello, Copacabana, Girardota, Barbosa, Envigado, Itagüí, San Antonio de Prado, La Estrella, Sabaneta and Caldas, among others. With the growth of the city placing Medellín among the most economically important cities in the nation, local leaders were compelled to view the city as a complex, urban system comparable to other industrialized cities in the world, rather than as a provincial town.
In the same sense, Medellín and its Metropolitan Area had to face the appearance of cartels during the 1970s, which produced serious problems of urban violence exacerbated by speedy urban growth and slow answers to the needs of the surrounding communities. The city grew due to big waves of migrants coming from the Colombian countryside looking for refuge from internal political conflict. This background explains why the young city would face urban violence with the same intensity as large metropolitan areas such as New York City, Mexico City or Rio de Janeiro and why the city had to create urban projects in answer to its conflicts and growth. The Medellín Metro was created not only as a massive urban transport solution for the working class residents of the city, but also as an important cultural symbol that would help develop marginalized sectors. The Metro would change the concept of public space in a city built for business and factories that had the systematic issue of lacking space for things like tourism.
As a company, the Medellín Metro was created for the administration and operation of the Metro system. It was founded with the association of the Medellín Municipality and the Antioquia Government. In 1979, research on economic and technical possibilities began, performed by the company Mott, Hay and Anderson Ltd.
In 1980 the project was presented to the National Government, and in 1982 it was approved by the National Council of Economic and Social Policies. It also gave the company an external contract of 100% of the required resources for the work. In 1984 the company subcontracted German and Spanish firms.
On 30 November 1995,[2][4] 11:00 (local time), the first journey between Niquía and Poblado Stations began. The first phase of the metro network was completed in 1996.
The citizens soon welcomed the new service, and the social and cultural impact was significant. The Medellín Metro soon became a symbol of the city (it was the first, and still the only, rail-based Metro system in Colombia) which encouraged tourism and new business growth in areas of the city. There were visitors first from other regions and cities of Colombia and afterwards from abroad. Importantly, the metro bridged previously disparate poor urban and wealthy urban areas. The Metro passes through districts with widely varied socio-economic compositions. For example, it passes through both "Lovaina" and "Poblado".
Commuters also saw a vast improvement in transit times. Previously, workers from Bello spent two hours by bus travelling to Envigado. With the Metro, travel times between those two cities was shortened to just 30 minutes.
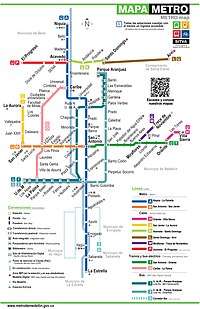
Network
The Medellín Metro currently comprises two lines: Line A, which is 25.8 kilometres (16.0 mi) long and serves 21 stations, and Line B, which is 5.5 kilometres (3.4 mi) long and serves 6 stations (plus San Antonio station, the transfer station with Line A). There is also a tram line: Line T-A (Ayacucho Tram).[2][5]
Additionally, the aerial cable car system, Metrocable, which supplements the Metro system, comprises five lines: Line J with 3 stations (plus one transfer station with Metro Line B),[1][2] Line K with 3 stations (plus one transfer station with Line L),[2][5] Line L with one station (plus one transfer station with Line K), Line H with two stations (plus one transfer station with Line T-A) and Line M with two stations (plus one transfer station with Line T-A).[5]
As of 2019, there are 27 Metro stations, 15 Metrocable stations, 3 Tramway stations (+ 6 stops), 20 BRT stations (+ 8 feeding buses stops) in the Medellín network, all listed in the following table; for a total of approx. 79 stations (14 stops); transfer stations are in bold, and the transfer station between Metro Lines A and B is shown in bold-italic:
| Name | Stations | Date of opening/Start of commercial service | Fleet | Commercial speed | Capacity (per vehicle) | Capacity (passengers/time-direction) | Time of travel for one journey | Top frequency (rush hour) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metro services | ||||||||
.svg.png) Line A |
30 November 1995 | 80 three-car trains; for a total of 240 cars | 40 km/h (25 mph); max. speed 80 km/h (50 mph) | 300 users per car | 41,480 | 42 minutes | 3 minutes | |
.svg.png) |
29 February 1996 | 16,231 | 10.5 minutes | 3:50 minutes | ||||
| Metrocable services | ||||||||
.svg.png) |
7 August 2004 | 93 gondolas | 18 km/h (11 mph) | 8 users sitting, 2 standing; for a total of 10 users per gondola | 3,000 | 9 minutes | 0:12 minutes | |
.svg.png) |
3 March 2008 | 119 gondolas | 12 minutes | |||||
.svg.png) Line L |
9 February 2010 | 55 gondolas | 1,200 | 15 minutes | 0:14 minutes | |||
.svg.png) |
|
17 December 2016 | 44 gondolas | 1,800 | 5 minutes | 0:13 minutes | ||
.svg.png) |
|
28 February 2019 | 49 gondolas | 2,500 | 4 minutes | 0:09 minutes | ||
.svg.png) Line P West to Northwest 2.7 km (1.7 mi)[2] 4 stations[5] |
|
Under construction | 138 gondolas (expected) | 19 km/h (12 mph) (expected) | 10 users sitting, 2 standing; for a total of 12 users per gondola (expected) | 40,000 (expected) | 10 minutes (expected) | 0:11 minutes (expected) |
| BRT services | ||||||||
.png) |
|
22 December 2011 | 30 gas working buses, 1 fully electric bus; for a total of 31 articulated buses | 16 km/h (9.9 mph); max. speed 60 km/h (37 mph) | 154 users per bus | 3,270 | 45 minutes | 2:45 minutes |
.png) Line 3 Southwest/Southeast |
South Corridor | Under development | ||||||
| Feeding bus services | ||||||||
.png) Line 2 |
|
22 April 2013 | 47 gas feeding buses | 13 km/h (8.1 mph); max. speed 60 km/h (37 mph) | 90 users per bus | 1,417 | 52 minutes | 4:17 minutes |
| Tram services | ||||||||
.svg.png) Line T-A |
|
31 March 2016 | 12 tramway vehicles | 19 km/h (12 mph); max. speed 70 km/h (43 mph) | 300 users per ? | 3,807 | 19 minutes | 4:44 minutes |
| Total | ||||||||
| 79 stations (14 stops) | Oldest: Newest:
|
|
Fastest: Slowest: |
Most capacity: Least capacity: |
81,705 | Fastest journey: Slowest journey: |
Least wait time: Most wait time:
| |
Expansions
Metrocable

On 7 August 2004,[4] the city inaugurated a new line known as "Metro Cable" (Line K). The line starts in the Acevedo Station and goes to the up hill district of Santo Domingo Savio.[6] This important addition integrated new additions to the city that since the 1960s that previously were not considered part of the "real city".

On 3 March 2008,[4] a second "Metro Cable" line (Line J) was inaugurated. The line starts in the San Javier Station and goes through Juan XXIII and Vallejuelos to the La Aurora district.[6] This new line benefits approximately 150,000 new users.
A new Metrocable line (line L) was inaugurated in 2009[4] with a transfer station at Santo Domingo Savio Station. This line continues further uphill to El Tambo[6] in Arví park near Guarne. The reason for constructing this line is because the city wants to promote tourism in the rural area near Lake Guarne. It takes 14 minutes to ascend to El Tambo and there are no intermediate stations.
Line A extension
Line A was expanded from Itagüí to La Estrella, in the south of the metropolitan area. A new intermediate station, Sabaneta, built near 67th South Street, was opened on 5 August 2012[7] and the final station, La Estrella, was built near 77th South Street and opened on 17 September 2012.[8]
Train line
In February 2020 it was announced that Medellín will reactivate the train line between Bello and Caldas.[9]
Rolling stock
Initially there were 42 three-car train sets from the manufacturer MAN, since 2009, 38 three-car train sets have been purchased from CAF and currently the system has 80 trains.[10][11]
References
- "Mapa esquemático" [Schematic map] (pdf) (in Spanish). Metro de Medellín. Retrieved 10 March 2019 – via https://www.metrodemedellin.gov.co/en/travelwithus/maps.
- "Datos del sistema" [System data] (jpg) (in Spanish). Metro de Medellín. Archived from the original on 11 March 2019. Retrieved 10 March 2019 – via https://www.metrodemedellin.gov.co/en/travelwithus/maps.
- "Boletín Técnico Encuesta de Transporte Urbano de Pasajeros (ETUP) Cuarto trimestre de 2019". p. 13.
- "Historia" [History] (in Spanish). Metro de Medellín. 4 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "Mapa Esquematico Trazado 2019" (PDF). Metro de Medellín. June 24, 2019.
- "Metrocable - Metrocable Lines". Metro de Medellín. 15 November 2013. Archived from the original on 2015-06-10. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- "ESTE DOMINGO 5 DE AGOSTO INICIA LA OPERACIÓN COMERCIAL HASTA LA NUEVA ESTACIÓN SABANETA" (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- "ESTE LUNES 17 DE SEPTIEMBRE EL METRO INAUGURARÁ LA EXTENSIÓN AL SUR" (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 January 2013.
- El Colombiano. "Antioquia definió el primer tramo para reactivar su ferrocarril". Retrieved 22 February 2020.
- "Medellín orders CAF metro trains". Railway Gazette International. 4 December 2009. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "Medellín metro orders more CAF cars". Railway Gazette International. 5 July 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
External links
![]()
- Official website
- Civica – official webpage of the AFC of Metro de Medellín (in Spanish)
- Metro de Medellín at urbanrail.net