Marsh sandpiper
The marsh sandpiper (Tringa stagnatilis) is a small wader. It is a rather small shank, and breeds in open grassy steppe and taiga wetlands from easternmost Europe to the Russian Far East. The genus name Tringa is the New Latin name given to the green sandpiper by Aldrovandus in 1599 based on Ancient Greek trungas, a thrush-sized, white-rumped, tail-bobbing wading bird mentioned by Aristotle. The specific stagnatilis is from Latin stagnum, "swamp".[2]
| Marsh sandpiper | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Winter plumage | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Scolopacidae |
| Genus: | Tringa |
| Species: | T. stagnatilis |
| Binomial name | |
| Tringa stagnatilis (Bechstein, 1803) | |
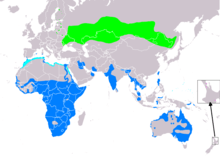 | |
| Range of T. stagnatilis Breeding Non-breeding Passage Vagrant (seasonality uncertain) | |
Description
It resembles a small elegant greenshank, with a long fine bill and very long yellowish legs. Like the greenshank, it is greyish brown in breeding plumage, paler in winter, and has a white wedge up its back that is visible in flight. However, it is more closely related to the common redshank and the wood sandpiper.[3] Together, they form a group of smallish shanks which tend to have red or reddish legs, and in breeding plumage are generally a subdued, light brown above with some darker mottling, with a pattern of somewhat diffuse small brownish spots on the breast and neck. The length is 22–26 cm (8.7–10.2 in), wingspan is 55–59 cm (22–23 in) and weight is 45–120 g (1.6–4.2 oz).[4]
Distribution
Palearctic.It is a migratory species, with majority of birds wintering in Africa, and India with fewer migrating to Southeast Asia and Australia. They prefer to winter on fresh water wetlands such as swamps and lakes and are usually seen singly or in small groups.
These birds forage by probing in shallow water or on wet mud. They mainly eat insects, and similar small prey.
The marsh sandpiper is one of the species to which the Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds (AEWA) applies.
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Tringa stagnatilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 364, 390. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- Pereira, Sérgio Luiz; Baker, Alan J. (2005). "Multiple Gene Evidence for Parallel Evolution and Retention of Ancestral Morphological States in the Shanks (Charadriiformes: Scolopacidae)". Condor. 107 (3): 514–526. doi:10.1650/0010-5422(2005)107[0514:MGEFPE]2.0.CO;2.
- "Marsh Sandpiper". Oiseaux-birds.com. Retrieved 2011-10-19.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tringa stagnatilis. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Tringa stagnatilis |
- Marsh sandpiper species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds
- BirdLife species factsheet for Tringa stagnatilis
- "Tringa stagnatilis". Avibase.

- "Marsh sandpiper media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Marsh sandpiper photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Tringa stagnatilis at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Marsh sandpiper on Xeno-canto.
- Tringa stagnatilis in the Flickr: Field Guide Birds of the World
- Marsh sandpiper media from ARKive

