Lower Austria
Lower Austria (German: Niederösterreich [ˈniːdɐˌʔøːstɐʁaɪ̯ç] (![]()
Lower Austria Niederösterreich | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Sankt Pölten |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Johanna Mikl-Leitner (ÖVP) |
| • Deputy Governors |
|
| Area | |
| • Total | 19,186 km2 (7,408 sq mi) |
| Population (1 January 2020) | |
| • Total | 1,684,623 |
| • Density | 88/km2 (230/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | AT-3 |
| HDI (2017) | 0.872[1] very high · 8th |
| NUTS Region | AT1 |
| Votes in Bundesrat | 12 (of 62) |
| Website | www.noe.gv.at |
Geography
With a land area of 19,186 km2 (7,408 sq mi) situated east of Upper Austria, Lower Austria is the country's largest state. Lower Austria derives its name from its downriver location on the Enns River which flows from the west to the east. Lower Austria has an international border, 414 km (257 mi) long, with the Czech Republic (South Moravia Region) and Slovakia (Bratislava and Trnava Regions). The state has the second longest external border of all Austrian states. It also borders the other Austrian states of Upper Austria, Styria and Burgenland as well as surrounding Vienna.
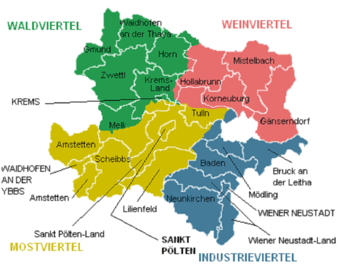
Lower Austria is divided into four regions, known as Viertel (quarters):
- Weinviertel or Tertiary Lowland (below the Manhartsberg)
- Waldviertel or Bohemian Plateau (above the Manhartsberg)
- Mostviertel (above the Vienna Woods)
- Industrieviertel (below the Vienna Woods).
These regions have different geographical structures. Whilst the Mostviertel is dominated by the foothills of the Limestone Alps with mountains up to 2,000 m (AA) high, most of the Waldviertel is a granite plateau. The hilly Weinviertel lies to the northeast, descends to the plains of Marchfeld in the east of the state, and is separated by the Danube from the Vienna Basin to the south, which in turn is separated from the Vienna Woods by a line of thermal springs (the Thermenlinie) running north to south.[3]
Mountains
- Schneeberg (Klosterwappen; 2,076 m)
- Rax (Scheibwaldhöhe; 1,943 m; highest summit: Heukuppe; 2,007 m – Styria)
- Ötscher (1,893 m)
- Dürrenstein (1,878 m)
- Schneealpe (Ameisbühel; 1,828 m; highest summit: Windberg; 1,903 m – Styria)
- Hochkar (1,808 m)
- Gamsstein (1,774 m)
- Stumpfmauer (1,770 m)
- Göller (1,766 m)
- Hochwechsel (1,743 m)
- Gippel (1,669 m)
- Großer Sonnleitstein (1,639 m)
- Großer Zellerhut (1,639 m)
- Gemeindealpe (1,626 m)
- Scheiblingstein (1,622 m) (not to be confused with Scheiblingstein (2,197 m), which is in Styria)
- Drahtekogel (1,565 m)
- Sonnwendstein (1,523 m)
- Obersberg (1,467 m)
- Königsberg (1,452 m)
- Großer Sulzberg (1,400 m)
- Reisalpe (1,399 m)
- Gahns (1,380 m)
- Tirolerkogel (1,377 m)
- Türnitzer Höger (1,372 m)
- Unterberg (1,342 m)
- Traisenberg (1,230 m)
- Dürre Wand (1,222 m)
- Hohenstein (1,195 m)
- Eisenstein (1,185 m)
- Hohe Wand (1,132 m)
- Großer Peilstein (1,061 m)
- Weinsberg (1,041 m)
- Hocheck (1,036 m)
- Nebelstein (1,017 m)
- Eibl (1,007 m)
- Hohe Mandling (967 m)
- Jauerling (961 m)
- Hoher Lindkogel also named Eisernes Tor (834m)
- Anninger (675 m)
- Buschberg (491 m)
Other mountains in Lower Austria may be found at Category:Mountains of Lower Austria.
Rivers

Almost all of Lower Austria is drained by the Danube. The only river that flows into the North Sea (via the Moldau and the Elbe) is the Lainsitz in northern Waldviertel, the Erlauf river.
The most important rivers north of the Danube (on its left bank) are the Ysper, Kamp, Krems, Lainsitz, March and Thaya. South of the Danube (on its right bank) are the Enns, Ybbs, Erlauf, Melk, Pielach, Traisen, Schwechat, Fischa, Schwarza, Triesting, Pitten and the Leitha.
Lakes
- Ottenstein Reservoir (4.3 km2)
- Lunzer See (0.69 km2)
- Erlaufsee (0.56 km2, of which about half lies in Lower Austria)
- Erlauf Reservoir
- Wienerwaldsee (0.32 km2)
Caves
Lower Austria is rich in natural caves; in all 4,082 have been recorded. Most of the caves have formed in limestone and dolomite rocks and are therefore called karst caves. Cavities also form in the marble of the Central Alps and the Bohemian Massif. Among the largest caves in Lower Austria are:
- Ötscherhöhlensystem (Ötscher): 27,003 m long; union of the Taubenloch and Geldloch
- Pfannloch (Ötscher): 5,287 m long
- Lechnerweidhöhle (Dürrenstein): 5,252 m long
- Trockenes Loch (Schwarzenbach an der Pielach): 4,510 m long
- Hermannshöhle (Kirchberg am Wechsel): 4,430 m long
- Eisensteinhöhle (Bad Fischau): 2,341 m long
The last two are open as show caves, along with the Allander stalactite cave, the Unicorn Cave, the Hochkarschacht, the Nixhöhle and the Ötschertropfsteinhöhle.
Land use
| Type of land use | Area in km2 | Percent of total area |
|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 7,000 | 42 |
| Woods | 6,711 | 40 |
| Grassland | 1,750 | 11 |
| Alpine pastures | 300 | 1.7 |
| Vineyards | 315 | 1.9 |
History
The history of Lower Austria is very similar to the history of Austria. Many castles are located in Lower Austria. Klosterneuburg Abbey, located here, is one of the oldest abbeys in Austria. Before World War II, Lower Austria had the largest number of Jews in Austria.
The names Lower Austria and Upper Austria are derived from the earlier names Austria below the Enns and Austria above the Enns, references to the river Enns. Going down from its source on the northern edge of the Central Eastern Alps, the river crosses Upper Austria, then on its lower reaches forms the boundary between Upper Austria and Lower Austria.[4]
Economy
The gross domestic product (GDP) of the state was 61.0 billion € in 2018, accounting for 15.8% of Austria's economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 32,300 €, or 107% of the EU27 average in the same year. Burgenland is the state with the second-lowest GDP per capita in Austria.[5]
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1869 | 1,077,232 | — |
| 1880 | 1,152,767 | +7.0% |
| 1890 | 1,213,471 | +5.3% |
| 1900 | 1,310,506 | +8.0% |
| 1910 | 1,425,238 | +8.8% |
| 1923 | 1,426,885 | +0.1% |
| 1934 | 1,446,675 | +1.4% |
| 1939 | 1,455,373 | +0.6% |
| 1951 | 1,400,471 | −3.8% |
| 1961 | 1,374,012 | −1.9% |
| 1971 | 1,420,816 | +3.4% |
| 1981 | 1,426,370 | +0.4% |
| 1990 | 1,455,968 | +2.1% |
| 1995 | 1,518,489 | +4.3% |
| 2000 | 1,535,083 | +1.1% |
| 2005 | 1,568,949 | +2.2% |
| 2010 | 1,605,897 | +2.4% |
| 2015 | 1,636,287 | +1.9% |
| 2020 | 1,684,623 | +3.0% |
Administrative divisions

Lower Austria is divided into four regions: Waldviertel, Mostviertel, Industrieviertel, and Weinviertel. The Wachau valley, situated between Melk and Krems in the Mostviertel region, is famous for its landscape, culture, and wine.
Administratively, the state is divided into 20 districts (Bezirke), and four independent towns (Statutarstädte). In total, there are 573 municipalities within Lower Austria.[6]
Independent towns
Districts
- Amstetten
- Baden
- Bruck an der Leitha
- Gänserndorf
- Gmünd
- Hollabrunn
- Horn
- Korneuburg
- Krems-Land
- Lilienfeld
- Melk
- Mistelbach
- Mödling
- Neunkirchen
- Sankt Pölten-Land
- Scheibbs
- Tulln an der Donau
- Waidhofen an der Thaya
- Wiener Neustadt-Land
- Zwettl
References
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- "About the State Parliament of Lower Austria – NÖ Landtag". noe-landtag.gv.at (in German). Retrieved 2020-01-14.
- "Visitor-Information". www.lower-austria.info. Retrieved 2020-01-14.
- "History of Lower Austria – NÖ Landtag". noe-landtag.gv.at (in German). Retrieved 2020-01-14.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- "Lower Austria in Numbers" (PDF).
External links
![]()
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Austria, Lower. |
- Country of Lower Austria - official webpage
- Lower Austria - official visitor information webpage
- PhotoGlobe - georeferenced photos of Lower Austria