Styria
Styria (German: Steiermark [ˈʃtaɪ̯ɐˌmaʁk] (![]()
Styria Steiermark | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Graz |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Hermann Schützenhöfer (ÖVP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 16,401.04 km2 (6,332.48 sq mi) |
| Population (1 January 2020) | |
| • Total | 1,246,576 |
| • Density | 76/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | AT-6 |
| HDI (2017) | 0.902[1] very high · 4th |
| NUTS Region | AT2 |
| Votes in Bundesrat | 9 (of 62) |
| Website | www.verwaltung.steiermark.at |
Etymology
The March of Styria derived its name from the original seat of its ruling Otakar dynasty: Steyr, in today's Upper Austria. In German, the area is still called "Steiermark" while in English the Latin name "Styria" is used. The ancient link between Steyr and Styria is also apparent in their nearly identical coats of arms, a white Panther on a green background.
Geography
- The term "Upper Styria" (German: Obersteiermark) refers to the northern and northwestern parts of the federal-state (districts Liezen, Murau, Murtal, Leoben, Bruck-Mürzzuschlag).
- The term "Western Styria" (Weststeiermark) is used for the districts to the west of Graz (Voitsberg, Deutschlandsberg, western part of the district Leibnitz).
- The districts east of Graz (Weiz, Hartberg-Fürstenfeld, and Südoststeiermark) are referred to as "Eastern Styria" (Oststeiermark).
The western and eastern parts of the district Graz-Umgebung (literally, surroundings of Graz) may or may not be considered parts of West and East Styria, respectively. The southern parts of the Duchy of Styria, which formed part of former Yugoslavia and later Slovenia (with the exception of World War II), were (and sometimes colloquially still are) referred to as "Lower Styria" (Untersteiermark; Slovene: Štajerska).
History


Styria was inhabited by Celtic tribes. After its conquest by the Romans, the eastern part of what is now Styria was part of Pannonia, while the western one was included in Noricum. During the Barbarian invasions, it was conquered or crossed by the Visigoths, the Huns, the Ostrogoths, the Rugii, and the Lombards. Slavs under the domination of the Avars settled in the valleys around 600. At the same time, Bavarians under Frankish domination began to expand their area to the south and east, ultimately absorbing the Slavic population.
In 1180, Styria separated from the Duchy of Carinthia and became a Duchy of its own; in 1192 the Austrian Duke Leopold V became also Duke of Styria. Later, Styria formed the central part of Inner Austria.
Styria developed culturally and economically under Archduke John of Austria between 1809 and 1859.
In 1918, after World War I, it was divided into a northern section (forming what is the current Austrian state), and a southern one, called Lower Styria, now inhabited by Slovenians, and which was annexed to Yugoslavia, and later became part of Slovenia. As a result of the turbulence of the two world wars, the German-speaking population of Lower Styria, which had been concentrated in the cities, migrated out of the region or was expelled.
Economy
The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the state was 49.6 billion € in 2018, accounting for 12.9% of the Austria's economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 35,400 € or 118% of the EU27 average in the same year.[2]
As elsewhere in the developed world, there has been a shift away from the manufacturing sector towards the service sector in Styria. This has had negative consequences for the industrial regions of upper Styria which have suffered a steady decline in population in recent years.
In 2004, Styria had the strongest economic growth rate in Austria at 3.8%—mainly due to the Graz area which saw strong economic growth that year and has continued to grow in economic and population terms since then.
Styria is home to more than 150 clean technology companies of which one dozen are world technology leaders in their field. The revenue of Styrian cleantech companies totals €2.7 billion. This equals 8 percent of the Gross Regional Product (GRP) and is one of the highest concentrations of leading clean technology companies in Europe. The companies have an average (real) growth rate of 22 percent per year—well above the worldwide cleantech market growth of 18 percent per year. The region created roughly 2,000 additional green jobs in 2008 alone.[3]
The Formula One Austrian Grand Prix has been held in the region, first at the Zeltweg Airfield in 1964 and then at the Osterreichring from 1970 to 1987. The sport returned to the circuit, now redesigned and rebranded as the A1-Ring, from 1997 to 2003. Formula One once again returned to the circuit, now renamed the Red Bull Ring, in 2014 and has been held at the track every year since. The COVID-19 pandemic saw the 2020 Formula One calendar massively revised, resulting in the Red Bull Ring becoming the first circuit to host consecutive Formula One World Championship Grands Prix, with the first round running under the Austrian Grand Prix name and the second held as the Styrian Grand Prix.
Administrative divisions
The state is divided into 13 districts (Bezirke), one of them a statutory city.
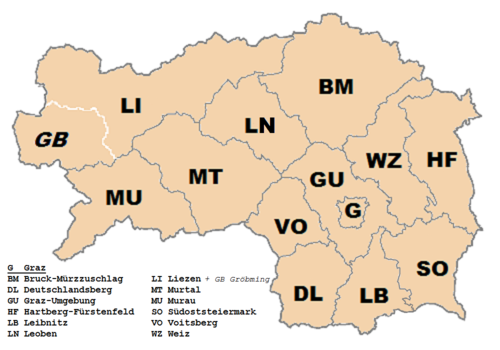
Statutory city
Districts
- Bruck-Mürzzuschlag
- Deutschlandsberg
- Graz-Umgebung
- Hartberg-Fürstenfeld
- Leibnitz
- Leoben
- Liezen (with the subdistrict Gröbming)
- Murau
- Murtal
- Südoststeiermark
- Voitsberg
- Weiz
Politics
The state had been a stronghold of the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) since 1945. Graz however is more left leaning than the more rural parts of the province, with strong representation of the Green Party in local politics and elections, and a less-than-marginal presence of the far left Communist Party (KPÖ).
The governor (Austrian political term: Landeshauptmann) has usually been a member of the ÖVP.
Recent elections
In the 2005 elections for state parliament the Social Democrats (SPÖ) under their regional chairman Franz Voves won the majority after the ÖVP had damaged its credibility through scandals and the secession of a high-ranking party member who took part in the 2005 elections after setting up his own party. In these elections, the KPÖ also received many votes after it had gained much popularity through its role in local politics in Graz during the preceding few years. The two right-wing populist parties, the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) and the Alliance for the Future of Austria (BZÖ), failed to win seats.
In subsequent elections in 2010 and 2015, the Social Democrats, the Austrian People's Party, and the Communist Party each lost between one fourth and one third of their shares of the vote relative to 2005. The Freedom Party grew from 4.6 percent to 26.8 percent.[4][5] The current government of Styria is a coalition of Social Democrats and People's Party, with each party holding 4 seats of the 8 seats available. The governor, Hermann Schützenhöfer, is a representative of the People's Party. His deputy, Michael Schickhofer, is a Social Democrat.[6][7][8]
Notable people
- Palman (fl. 1310–1363), knight and mercenary commander of the Serbian Empire
- Johann Joseph Fux (1660–1741), composer and music theorist, wrote Gradus ad Parnassum – a composition manual used by Beethoven and Mozart
- Archduke John of Austria (1782–1859)
- Peter Rosegger (1843–1918), honoured poet
- Johann Puch (1862–1914), founded Johann Puch Erste Steiermärkische Fahrrad-Fabriks-Aktiengesellschaft at Graz in 1899.
- Robert Stolz (1880-1975), composer born in Graz
- Karl Böhm, (1894-1981), conductor
- Erik von Kuehnelt-Leddihn (1909-1999), political scientist
- Bert Isatitsch (1911–1994), first president of the International Luge Federation
- Frank Stronach (b. 1932), founder of Magna International, billionaire
- Jochen Rindt (1942–1970), Formula 1 World Champion
- Dr. Helmut Marko (b. 1943), former racing driver
- Dietrich Mateschitz (b. 1944), founder and CEO of Red Bull, billionaire
- Klaus Maria Brandauer (b. 1944), actor and director
- Elfriede Jelinek (b. 1946), Nobel Prize in Literature winner
- Arnold Schwarzenegger (b. 1947), bodybuilder, film actor and former Governor of California
- Getty Kaspers (b. 1948), lead vocals of Dutch band Teach-In, who won the 1975 Eurovision Song Contest.
- Eva Rueber-Staier (b. 1951), Miss Austria 1969, Miss World 1969
- Wolfgang Muthspiel (b. 1965), jazz composer and guitarist
- Ulla Weigerstorfer (b. 1967), Miss Austria 1987 and Miss World 1987
- Thomas Muster (b. 1967), former World No. 1 tennis player
- Renate Götschl (b. 1975), alpine skiing World Champion
- Elisabeth Görgl (b. 1981), professional alpine skier
- Christoph Strasser (b. 1982), champion ultra cyclist
- Conchita Wurst (b. 1988), singer and winner of the Eurovision Song Contest 2014
See also
- Lower Styria
References
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- "Regional GDP per capita ranged from 30% to 263% of the EU average in 2018". Eurostat.
- Lesser, Shawn. "Top 10 cleantech cluster organizations for 2010". Clean Tech Group. Archived from the original on 22 May 2011. Retrieved 14 April 2011.
- "Landtagswahl 2010" (PDF).
- "Landtagswahl 2015" (PDF).
- "Regierungsmitglieder".
- "Skepsis gegenüber schwarz-roter Neuauflage".
- "Schwarz-rot in der Steiermark".
External links


- Imperial Austria: Treasures of Art, Arms and Armor from the State of Styria – The Canadian Museum of Civilization
- Official Tourism Website of Styria

.png)