Ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as articular ligament, articular larua,[1] fibrous ligament, or true ligament. Other ligaments in the body include the:
- Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes.
- Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure.
- Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone.
| Ligament | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| System | Musculoskeletal system |
| Function | Connect bones to other bones; maintain position of organs |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Ligamentum (Plural: Ligamenta) |
| MeSH | D008022 |
| TA | A03.0.00.034 |
| FMA | 30319 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Ligaments are similar to tendons as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences in them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regeneration of periodontist ligament.
The study of ligaments is known as desmology
Articular ligaments
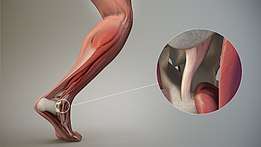
"Ligament" most commonly refers to a band of dense regular connective tissue bundles made of collagenous fibers, with bundles protected by dense irregular connective tissue sheaths. Ligaments connect bones to other bones to form joints, while tendons connect bone to muscle. Some ligaments limit the mobility of articulations or prevent certain movements altogether.
Capsular ligaments are part of the articular capsule that surrounds synovial joints. They act as mechanical reinforcements. Extra-capsular ligaments join together in harmony with the other ligaments and provide joint stability. Intra-capsular ligaments, which are much less common, also provide stability but permit a far larger range of motion. Cruciate ligaments are paired ligaments in the form of a cross.[2]
Ligaments are viscoelastic. They gradually strain when under tension and return to their original shape when the tension is removed. However, they cannot retain their original shape when extended past a certain point or for a prolonged period of time.[3] This is one reason why dislocated joints must be set as quickly as possible: if the ligaments lengthen too much, then the joint will be weakened, becoming prone to future dislocations. Athletes, gymnasts, dancers, and martial artists perform stretching exercises to lengthen their ligaments, making their joints more supple.
The term hypermobility refers to people with more-elastic ligaments, allowing their joints to stretch and contort further; this is sometimes still called double-jointedness.
The consequence of a broken ligament can be instability of the joint. Not all broken ligaments need surgery, but, if surgery is needed to stabilise the joint, the broken ligament can be repaired. Scar tissue may prevent this. If it is not possible to fix the broken ligament, other procedures such as the Brunelli procedure can correct the instability. Instability of a joint can over time lead to wear of the cartilage and eventually to osteoarthritis.
Artificial ligaments
One of the most often torn ligaments in the body is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL is one of the ligaments crucial to knee stability and persons who tear their ACL often seek to undergo reconstructive surgery, which can be done through a variety of techniques and materials. One of these techniques is the replacement of the ligament with an artificial material. An artificial ligament is a reinforcing material that is used to replace a torn ligament, such as the ACL. Artificial ligaments are a synthetic material composed of a polymer, such as polyacrylonitrile fiber, polypropylene, PET (polyethylene terephthalate), or polyNaSS poly(sodium styrene sulfonate).[4]
Examples
|
|
Peritoneal ligaments
Certain folds of peritoneum are referred to as ligaments. Examples include:
- The hepatoduodenal ligament, that surrounds the hepatic portal vein and other vessels as they travel from the duodenum to the liver.
- The broad ligament of the uterus, also a fold of peritoneum.
Fetal remnant ligaments
Certain tubular structures from the fetal period are referred to as ligaments after they close up and turn into cord-like structures:
| Fetal | Adult |
|---|---|
| ductus arteriosus | ligamentum arteriosum |
| extra-hepatic portion of the fetal left umbilical vein | ligamentum teres hepatis (the "round ligament of the liver"). |
| intra-hepatic portion of the fetal left umbilical vein (the ductus venosus) | ligamentum venosum |
| distal portions of the fetal left and right umbilical arteries | medial umbilical ligaments |
See also
References
- "ligament" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- Daniel John Cunningham (1918). Cunningham's text-book of anatomy (5th ed.). Oxford Press. p. 1593.
- R.A., Hauser; E.E., Dolan; H.J., Phillips; A.C., Newlin; R.E., Moore; B.A., Woldin (2013-01-23). "Ligament Injury and Healing: A Review of Current Clinical Diagnostics and Therapeutics" (PDF). The Open Rehabilitation Journal. 6 (1): 5. doi:10.2174/1874943701306010001.
- Lessim S, Migonney V, Thoreux P, Lutomski D, Changotade S. (June 2013). "PolyNaSS bioactivation of LARS artificial ligament promotes human ligament fibroblast colonisation in vitro". Biomed Mater Eng. 23 (4): 289–297. doi:10.3233/BME-130753. PMID 23798650.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ligaments. |