Inguinal triangle
In human anatomy, the inguinal triangle is a region of the abdominal wall. It is also known by the eponym Hesselbach's triangle, after Franz Kaspar Hesselbach.[1]
| Inguinal triangle | |
|---|---|
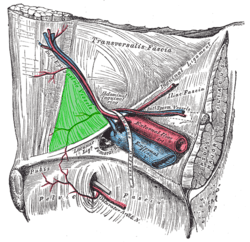 Internal (from posterior to anterior) view of right inguinal area of the male pelvis. Inguinal triangle is labeled in green. The three surrounding structures: inferior epigastric vessels: Run from upper left to center. inguinal ligament: Runs from upper right to bottom left. rectus abdominis muscle: Runs from upper left to bottom left, labeled rectus at upper left. | |
 External view. Inguinal triangle is labeled in green. Borders: inferior epigastric artery and vein: labeled at center left, and run from upper right to bottom center. inguinal ligament: not labeled on diagram, but runs a similar path to the inguinal aponeurotic falx, labeled at bottom. rectus abdominis muscle: runs from upper left to bottom left. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum inguinale |
| TA | A10.1.02.433 |
| FMA | 256506 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Boundaries
It is defined by the following structures:[2]
- Medial border: Lateral margin of the rectus sheath, also called linea semilunaris
- Superolateral border: Inferior epigastric vessels
- Inferior border: Inguinal ligament, sometimes referred to as Poupart's ligament
This can be remembered by the mnemonic RIP (Rectus sheath (medial), Inferior epigastric artery (lateral), Poupart's ligament (inguinal ligament, inferior).
Clinical significance
The inguinal triangle contains a depression referred to as the medial inguinal fossa, through which direct inguinal hernias protrude through the abdominal wall.[3]
gollark: Haskell→Lua compilation through gluing together bits of your projects, then?
gollark: GHCJS produced *horribly* sized output during my brief testing.
gollark: I imagine it would produce larger Lua files than CC likes.
gollark: Bad idea #12501285981: "run" Haskell "in" CC by running a Haskell program on some remote server somewhere and having it send commands to an ingame CC computer and receive info back.
gollark: Have you tried using it?
See also
- Terms for anatomical location
- Inguinal hernia surgery
References
- synd/3216 at Who Named It?
- Courtney M. Townsend Jr., MD, R. Daniel Beauchamp, MD, B. Mark Evers, MD and Kenneth L. Mattox, MD (2008). "Ch.43". Sabiston Textbook of Surgery (18th ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-1-4160-5233-3.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- MedNote. Red Anatomy. URL: http://www.mednote.co.kr/Rednote/RedAnatom.htm Archived 2006-04-23 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed December 15, 2005.
External links
- Anatomy image:7110 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - superior border
- Anatomy image:7111 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - medial border
- Anatomy image:7112 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - inferior border
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.