Lampshade spider
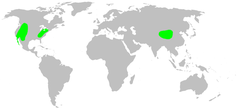
Lampshade spiders, family Hypochilidae, are among the most primitive of araneomorph spiders. There are two genera and twelve species currently recognized. Like mygalomorphs, most hypochilids have two pairs of book lungs, but like araneomorphs they have intersecting fangs, with the exception of some species which have chelicerae in an angle that is neither orthognathous or labidognathous.[1] These long-legged spiders build typical "lampshade" style webs under overhangs and in caves. In the United States the fauna is primarily associated with the Appalachian, Rocky and California Mountains. Ten of the known species are found in these ranges, all in the genus Hypochilus. The genus Ectatosticta is found in China.
| Lampshade spiders | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Hypochilus pococki in web | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Hypochilidae Marx, 1888 |
| Genera | |
| Diversity | |
| 2 genera, 12 species | |
 | |
_rotated.jpg)
In one analysis, the Hypochilidae are a sister clade to the Neocribellatae, which contains all other spider species in the Araneomorphae (Coddington & Levi, 1991, p. 576). A more recent study groups them with the Haplogynae.[2]
Species
Ectatosticta Simon, 1892 – China
- Ectatosticta davidi (Simon, 1889)
- Ectatosticta deltshevi Platnick & Jäger, 2009
Hypochilus Marx, 1888 – US
- Hypochilus bernardino Catley, 1994
- Hypochilus bonneti Gertsch, 1964
- Hypochilus coylei Platnick, 1987
- Hypochilus gertschi Hoffman, 1963
- Hypochilus jemez Catley, 1994
- Hypochilus kastoni Platnick, 1987
- Hypochilus petrunkevitchi Gertsch, 1958
- Hypochilus pococki Platnick, 1987
- Hypochilus sheari Platnick, 1987
- Hypochilus thorelli Marx, 1888
See also
- List of Hypochilidae species
- Spider families
References
- Spiders--webs, Behavior, and Evolution
- Bond, Jason E.; Garrison, Nicole L.; Hamilton, Chris A.; Godwin, Rebecca L.; Hedin, Marshal & Agnarsson, Ingi (2014). "Phylogenomics Resolves a Spider Backbone Phylogeny and Rejects a Prevailing Paradigm for Orb Web Evolution". Current Biology. 24 (15): 1765–1771. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.034. PMID 25042592. |p. 1766.
- Coddington, J.A.; Levi, H.W. (1991). "Systematics and Evolution of Spiders (Araneae)". Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 22: 565–592. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.22.110191.003025.
- Kaston, B. J. (1953). How to Know the Spiders (1st ed.). Dubuque, IA: W.C. Brown Co. OCLC 681432632.
Further reading
- Forster, R.R., Platnick, N.I. and Gray, M.R. (1987). A review of the spider superfamilies Hypochiloidea and Austrochiloidea (Araneae, Araneomorphae). Bulletin of the AMNH 185(1):1-116 Abstract - PDF (50Mb)
- Shear, W.A. (1969). "Observations on the predatory behavior of the spider Hypochilus gertschi Hoffman (Hypochilidae)" (PDF). Psyche. 76: 407–417. doi:10.1155/1969/59683. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-27.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Hypochilidae |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hypochilidae. |