La Teste-de-Buch
La Teste-de-Buch (French pronunciation: [la tɛst də ˈbyk]; Occitan: La Tèsta de Bug [la ˈtɛstɔ ðe ˈβyk]) is a commune in the Gironde department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France.
La Teste-de-Buch | |
|---|---|
Dune du Pilat | |
.svg.png) Coat of arms | |
Location of La Teste-de-Buch 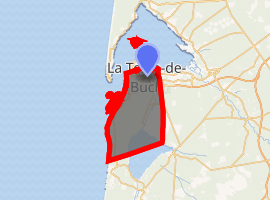
| |
 La Teste-de-Buch  La Teste-de-Buch | |
| Coordinates: 44°37′12″N 1°08′45″W | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
| Department | Gironde |
| Arrondissement | Arcachon |
| Canton | La Teste-de-Buch |
| Intercommunality | Bassin d'Arcachon Sud |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2008–2014) | Jean-Jacques Eroles |
| Area 1 | 180.20 km2 (69.58 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 26,078 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (370/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 33529 /33260 |
| Elevation | 0–101 m (0–331 ft) (avg. 4 m or 13 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
It is located on the south shore of Arcachon Bay, lying in the southwestern part of Gironde.
It is the largest of four communes that comprise the Communauté d'agglomération du Bassin d'Arcachon Sud (COBAS), a small metropolitan area of 54,204 population (1999 census). It is the eighth-largest commune in metropolitan France in geographical area.
La Teste-de-Buch is famous for the Dune du Pilat, the highest sand dune in Europe. It is also the site of a fictional battle during the Napoleonic wars depicted in Sharpe's Siege by Bernard Cornwell.
Geography
La Teste-de-Buch is located in the department of Gironde, in the middle of the Landes forest, and south of Arcachon Bay. It is the capital of the Pays de Buch. Neighbouring communes are Gujan-Mestras to the east, Arcachon to the northwest, and Biscarosse and Sanguinet to the south.
The Dune of Pilat is a famous landmark on the Atlantic coast, situated in the western corner of the commune. The seaside resort of Pyla-sur-Mer, the village of Cazaux, the bird refuge and sandbank of Arguin are also part of the town.
The Étang de Cazaux et de Sanguinet is in the southeast corner, astride the departments of Gironde and Landes. The rest of the commune area consists of old dunes, where the natural forest has changed little over centuries.
During World War I, an airfield was created near Cazaux for airplane pilots training (fighters and bombers). Most of the American volunteers pilots of the Lafayette Escadrille came to the "Camp de Cazaux" to finish their training as war pilots. When the U.S entered the war, the 36th Aero Squadron was based here.
Climate
| Climate data for La Teste-de-Buch (1981–2010 averages, extremes 1921–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.0 (71.6) |
25.0 (77.0) |
28.6 (83.5) |
22.1 (71.8) |
35.1 (95.2) |
40.2 (104.4) |
39.8 (103.6) |
42.0 (107.6) |
38.4 (101.1) |
31.4 (88.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
22.8 (73.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.9 (51.6) |
12.2 (54.0) |
15.2 (59.4) |
17.0 (62.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
23.7 (74.7) |
26.0 (78.8) |
26.3 (79.3) |
24.0 (75.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.4 (57.9) |
11.2 (52.2) |
18.5 (65.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
7.4 (45.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
11.8 (53.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.6 (69.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
14.8 (58.6) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.2 (45.0) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.5 (36.5) |
2.5 (36.5) |
4.5 (40.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
13.3 (55.9) |
15.1 (59.2) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.1 (53.8) |
9.7 (49.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
3.2 (37.8) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −15.7 (3.7) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
3.6 (38.5) |
5.0 (41.0) |
3.5 (38.3) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−12.5 (9.5) |
−15.7 (3.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 95.5 (3.76) |
74.9 (2.95) |
66.4 (2.61) |
79.6 (3.13) |
62.0 (2.44) |
56.4 (2.22) |
46.9 (1.85) |
59.1 (2.33) |
77.8 (3.06) |
99.9 (3.93) |
120.8 (4.76) |
107.0 (4.21) |
946.3 (37.26) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 12.7 | 10.5 | 11.2 | 11.6 | 10.0 | 7.6 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.9 | 11.8 | 13.3 | 12.4 | 124.9 |
| Average snowy days | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 2.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 83 | 79 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 76 | 77 | 79 | 84 | 87 | 88 | 80.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 99.9 | 115.1 | 177.1 | 192.7 | 226.7 | 245.7 | 255.9 | 244.5 | 210.6 | 148.4 | 99.3 | 85.6 | 2,101.3 |
| Source 1: Météo France[2] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Infoclimat.fr (snowy days and humidity 1961–1990)[3] | |||||||||||||
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1793 | 2,000 | — |
| 1800 | 2,301 | +15.1% |
| 1806 | 2,306 | +0.2% |
| 1821 | 2,409 | +4.5% |
| 1831 | 2,840 | +17.9% |
| 1836 | 2,986 | +5.1% |
| 1841 | 3,447 | +15.4% |
| 1846 | 3,512 | +1.9% |
| 1851 | 3,399 | −3.2% |
| 1856 | 3,891 | +14.5% |
| 1861 | 3,601 | −7.5% |
| 1866 | 4,259 | +18.3% |
| 1872 | 4,462 | +4.8% |
| 1876 | 5,314 | +19.1% |
| 1881 | 6,063 | +14.1% |
| 1886 | 6,200 | +2.3% |
| 1891 | 6,480 | +4.5% |
| 1896 | 6,663 | +2.8% |
| 1901 | 6,840 | +2.7% |
| 1906 | 7,082 | +3.5% |
| 1911 | 7,023 | −0.8% |
| 1921 | 6,321 | −10.0% |
| 1926 | 7,815 | +23.6% |
| 1931 | 8,826 | +12.9% |
| 1936 | 9,496 | +7.6% |
| 1946 | 9,066 | −4.5% |
| 1954 | 11,281 | +24.4% |
| 1962 | 11,085 | −1.7% |
| 1968 | 15,064 | +35.9% |
| 1975 | 15,831 | +5.1% |
| 1982 | 18,038 | +13.9% |
| 1990 | 20,331 | +12.7% |
| 1999 | 22,976 | +13.0% |
| 2008 | 24,384 | +6.1% |
International relations
La Teste-de-Buch is twinned with
- Binghamton, New York, United States, since 1987.
- Schwaigern, Germany, since 2004.
See also
- Arcachon - La Teste-de-Buch Airport
- Pays de Buch
- Communes of the Gironde department
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "Cazaux (33)" (PDF). Fiche Climatologique: Statistiques 1981–2010 et records (in French). Meteo France. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 26, 2018. Retrieved March 26, 2018.
- "Normes et records 1961-1990: Cazaux - La Teste de Buch (33) - altitude 23m" (in French). Infoclimat. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to La Teste-de-Buch. |
- Official website (in French)