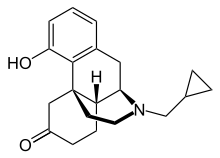
Ketorfanol
Ketorfanol (INN, USAN) (developmental code name SBW-22), or ketorphanol, is an opioid analgesic of the morphinan family that was found to possess "potent antiwrithing activity" in animal assays but was never marketed.[1][2][3] It is a 17-cycloalkylmethyl derivative of morphinan and as such, is closely related structurally to butorphanol, cyclorphan, oxilorphan, proxorphan, and xorphanol, which act preferentially as κ-opioid receptor agonists and to a lesser extent as μ-opioid receptor partial agonists/antagonists.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 311.425 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 720–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Andrejus Korolkovas (16 August 1988). Essentials of Medicinal Chemistry. Wiley. p. 243. ISBN 978-0-471-88356-2.
- Chemical Abstracts. American Chemical Society. 4 January 1982. p. 22.
- Neumeyer, John L.; Bidlack, Jean M.; Zong, Rushi; Bakthavachalam, Venkatesalu; Gao, Peng; Cohen, Dana J.; Negus, S. Stevens; Mello, Nancy K. (2000). "Synthesis and Opioid Receptor Affinity of Morphinan and Benzomorphan Derivatives: Mixed κ Agonists and μ Agonists/Antagonists as Potential Pharmacotherapeutics for Cocaine Dependence†". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 43 (1): 114–122. doi:10.1021/jm9903343. ISSN 0022-2623.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.