Kamma (caste)
Kamma is a Hindu caste from South India. The community of Kammas is believed to have originated from agriculturists of the Kammanadu region of the Guntur and Prakasam districts in Andhra Pradesh.[1][2] Propelled by their military activity in the Vijayanagara Empire, Kammas are believed to have spread out from the region during the Vijayanagara period, followed by some in-migration during the British period and out-migration again during the twentieth century.[3] Today they are regarded as the richest group in Andhra Pradesh[4] and are a dominant caste from Coastal Andhra with socio-economic and political prominence throughout the Telugu-speaking regions of India (the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana).[5][6]
| Kamma | |
|---|---|
| Religions | Hinduism |
| Languages | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Status | Forward caste |
They also have a notable, albeit smaller, presence in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.[7] In recent times, a sizeable number of Kammas have migrated to the United States.[8]
Origins
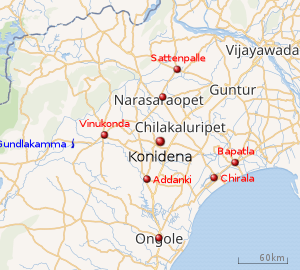 |
The modern community of Kammas is believed to have originated from agriculturists of the Kammanadu region in coastal Andhra Pradesh.[2][9] The region, lying between the Gundlakamma river and the Krishna river in the erstwhile Guntur district (which included the three subdistricts later transferred to the Ongole district in 1970), had an identity dating back to ancient times. The term "kamma" either referred to the two rivers that formed the boundaries of the region,[10] or to the Buddhist monastic institutions called sanghakammas believed to have been once prevalent in the region.[11]
As the people of the region migrated to other parts, they were often referred to as the Kamma community (kamma-kula).[12] Terms such as kamma-brahmana, kamma-komati, kamma-sreshti and kamma-kapu are attested in inscriptions as descriptions of people.[13][14][15] The migration was apparently quite extensive, and was made by possible by the Kammanadu's strategic location with access to the Deccan plateau as well as to the regions in the south and southwest.[16] By 1872, only one-fourth of their total population was living in the original region. But the migrants retained links to the homeland and returned to it whenever the situation was favourable.[17]
Medieval history
Post-Kakatiya period
The tradition holds that the Kammas, along with Velamas and Reddis, evolved out of the community of Kapus (cultivators) in the post-Kakatiya period. A popular legend collected by Edgar Thurston narrates that Kammas originated from the youngest son of a certain Belthi Reddi, who managed to recover his mother's ear-ornament (called "kamma" in Telugu) that had been appropriated by Emperor Prataparudra's minister. The other sons of Belthi Reddi are similarly said to have given rise to the other prominent caste communities of the Telugu people.[18]
Vijayanagara period
Kammas served as ministers, military generals, and governors in the Vijayanagara Empire[19]. During the reign of Krishnadevaraya, Kammas are said to have formed the bulwark of the Vijayanagara army. Their role in protecting the last great Hindu kingdom of India was significant.[20] Krishnadevaraya's court had a significant presence of Kamma officers, and they entered into matrimonial alliances with the royal family.[21] It's possible that the influence of Kamma generals led to the importance of the Telugu language in Vijayanagara and the rise of Telugu colonies in Tamil Nadu.[22] During the reign of the Vijayanagara Empire, Kamma Nayaks (commanders) were appointed as governors in many areas of Tamil Nadu.[23] Some of the notable Kamma Nayak clans of Vijayanagara include the Pemmasanis, Sayapanenis, and Ravellas.
Of the Pemmasani Nayaks, they controlled parts of Rayalaseema and had large mercenary armies that were the vanguard of the Vijayanagara Empire in the sixteenth century.[24] Pemmasani Ramalinga Nayudu was a leading military commander under Krishnadevaraya, and Aliya Rama Raya and the Aravidus rose to power following a civil war largely because of the support of Pemmasani Erra Timmanayudu.[25] Pemmasani Pedda Timmaraja was the minister of Sriranga I and later for Venkata II, the latter of whom oversaw the revival of the Vijayanagara Empire.[26] It is also known that a Pemmasani Nayak, Timmanayudu, had court poets and ministers of his own, such as Channamaraju.[27] Pemmasani Timmanayudu also assisted Venkata II in putting down a rebellion by the Nandyala Chiefs led by Krishnamaraja in 1580.[28] The Pemmasani Nayaks are associated with Gandikota, where they started as commandants and later gained control of Gandikota Seema from the Nandyala Chiefs. Numerous Hindu temples, such as Bugga Ramalingeshwara Swamy Temple[29] and Chintalarayaswamy Temple[30], were constructed and patronized by the Pemmasanis.
The Sayapaneni Nayaks started in service of Vijayanagara when Krishnadevaraya granted administrative control of the Dupadu Region to Shayappanayadu, a twenty-year old from the family.[31] According to the Dupati Kaifiyat, this area was consolidated by Vengala Nayudu and Venkatadri Nayudu, who are Shayappa Nayudu's descendants, and their rule is presented as a peaceful epoch.[32] Although modest actors in the Deccan, their main strength lay in their ability to shift allegiances, facilitated by Niyogi Brahmins, as seen with their initial allegiance to the Vijayanagara Empire and later to the Qutb Shahis and the Nizams after Vijayanagara's demise.[33]
The Ravella Nayaks were another prominent clan that served the Vijayanagara Empire militarily and administratively since the Sangama Dynasty[19], and they exercised control (on behalf of Vijayanagara) over Srisailam[19], Udayagiri, Podili, and Kochcherlakota Seemas (regions) at various periods.[34] The exploits of this clan are described by the poet Ratnakaram Gopala Kavi in Sovgandhika Prasavapaharanamu, including mentions of defeating the Qutb Shahis, Gajapatis, and recapturing forts like Adoni.[34][35] Noted individuals in the Ravella Nayaks include Ravella Linga II, who is surmised to be one of the chief generals of the Vijayanagara Army during the reign of Aliya Rama Raya.[34]
When the Vijayanagara Empire was troubled after the Battle of Tallikota in 1565, the Pemmasani Nayaks, Ravella Nayaks and Sayapaneni Nayaks helped the Aravidu Dynasty in keeping the Muslims at bay. It took another 90 years to consolidate the Muslim power in Andhra country with the capture of Gandikota in 1652 and the defeat of Pemmasani Timmanayudu by Mir Jumla.[28] Following the Battle of Talikota, many Kamma Nayaks either migrated to the dominions of the Madurai and Thanjavur Nayaks or obtained favours from the Qutb Shahis and Mughals and settled in Telugu regions as local military chiefs.[36]
Qutb Shahi and Nizam period
Kammas were also in service of the Qutb Shahis.[37] Their roles included serving as the regional aristocracy[38], revenue officers[39] and military commanders[37]. During the reign of the Qutb Shahis and Nizams, the Sayapaneni Nayaks (1626–1802) ruled a block of territory between the Krishna River and Nellore as vassals.[40][41] It was also in the Qutb Shahi period that the Vasireddy clan of Vasireddy Venkatadri Nayudu received the Deshmukhi of the Nandigama pargana in 1670.
In the 1600-1800s, Kammas acquired land in the interior Deccan Plateau due to grants that were given by the Nizam of Hyderabad to encourage cultivation in uncultivated areas of Telangana.[42][43] Moreover, in the Telangana region, Muslim rulers collected taxes through intermediaries from the dominant castes, such as the Kammas, who were given the title Chowdary.[43]
Modern history
Kamma landholdings were consolidated, and their influence consequently increased, by the introduction of the ryotwari system as a replacement for the zamindari system in the 19th century.[44]
In the 1872 census, the Kammas made up 40 per cent of the agricultural population of the Krishna district (which included the present Guntur district until 1904). Along with Brahmins, they formed the dominant community of the district.[45] By 1921, their population in the district increased to 47 per cent, representing a large in-migration. Following Brahminical traditions, the literate Kammas learned the Vedas, wore the sacred threads, taught Sanskrit and even performed pujas for the lower-caste members, which is said to have generated controversies.[46] Despite their attachment to Brahminical orthodoxy, the Kammas also related to the Kapus in a narrative.[46] The Kammas were also politically active, associating themselves with the Indian National Congress almost from its inception, and agitated for farmers' interests. They formed the Kamma Mahajana Sabha, a caste association, in 1910, which received encouragement from the political leaders. Ranga also started a Madras Kamma Association in 1919 and founded a journal Kamma Patrika, later renamed to Ryot Patrika.[47] The Kammas constituted 6 per cent of the population in the Telugu-speaking areas of the Madras Presidency in 1921, a figure slightly higher than Brahmins, but lagging far behind the 'Kapu or Reddi'.[48]
Construction of dams and barrages and establishment of an irrigation system in Godavari and Krishna River deltas by Arthur Cotton was a great boon to the Kamma farmers. Availability of water and the natural propensity for hard work made the Kammas wealthy and prosperous.[49] The money was put to good use by establishing numerous schools and libraries and encouraging their children to take up modern education.[50] The Kammas of Southern Tamil Nadu have also excelled in the cultivation of black cotton soils and later diversified into various industrial enterprises, particularly in Coimbatore and Kovilpatti.[51][52]
Today they are regarded as the wealthiest group in Andhra Pradesh[4] and an entrepreneurial community influential in various industries, such as information technology, real estate, media and Telugu cinema.[53][54][55] They are a dominant caste from Coastal Andhra with socio-economic and political prominence throughout the Telugu-speaking regions of India (the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana).[5][6] In united-Andhra Pradesh (including present-day Andhra Pradesh and Telangana), Kammas made up 4.8% of the total state population in the last census.[53] Kammas also have a notable, albeit smaller, presence in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.[7] In recent times, a sizeable number of Kammas have migrated to the United States.[8]
Classification
The varna system of Brahmanic ritual ranking never took hold in South Indian society outside Kerala. There were essentially three classes: Brahmin, non-Brahmin and Dalit.[56] Kammas naturally fall into the non-Brahmin class.[57] Classification of social groups in the Andhra region has changed frequently as the various communities jostle for status.[58] During the British Raj, the Kammas were considered to be "upper Shudra", along with the Reddy and Velama castes, under the varna system.[59][60]
Selig Harrison said in 1956 that
Kamma lore nurtures the image of a once-proud warrior clan reduced by Reddi chicanery to its present peasant status. Reddi duplicity, recounted by Kamma historian K. Bhavaiah Choudary, was first apparent in 1323 AD at the downfall of Andhra's Kakatiya dynasty. Reciting voluminous records to prove that Kammas dominated the Kakatiya court, Chaudary suggests that the Reddis, also influential militarists at the time, struck a deal at Kamma expense with the Moslem conquerors of the Kakatiya regime. The Kammas lost their noble rank and were forced into farming.[61]
Politics
Prior to the bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh, creating the new state of Telangana, the Kammas and the Reddys were politically and economically dominant in the state.[6] During the 1980s, they played a key role in state and national politics with the inception of the Telugu Desam Party by its then President Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao also called as NTR.[62]
Notable people
- N. T. Rama Rao[63]
- Velagapudi Ramakrishna[63]
- Akkineni Nageswara Rao[63]
- D. Ramanaidu[63]
- Mullapudi Harishchandra Prasad[63]
References
- Nāgabhūṣaṇaśarma, M.; Sastry, M. V.; Śēṣagirirāvu, C. (1995), History and culture of the Andhras, Telugu University, p. 80 Quote: "Next to birth and profession, it was region which accounted for sectarian sub-divisions in all the castes like those of Kammanadu being called Kamma-Brahmana, Kamma-Kapu, Kamma-Sresthi and so on."
- Sastry, P. V. Parabrahma (1996), Rural Studies in Early Andhra, V.R. Publication, p. 59 Quote: "The modern Kamma sect of people in Andhra desa is originally of the Kapu families hailing from Kamma nadu or Kamma rashtra of the medieval period."
-
- Benbabaali, Caste Dominance and Territory in South India (2018), pp. 6–7: "These waves of military migration towards the South of the Indian peninsula from the fifteenth century onwards explain the significant presence of Kammas in Tamil Nadu, where they again turned into agriculturalists in times of peace."
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), pp. 357–359: "Interestingly, their population in the Krishna delta in the 1872 census was one-fourth of their total strength in the entire Madras Presidency, but had increased by 1921 to about 47 per cent."
- Benbabaali, Caste Dominance and Territory in South India (2018), p. 14: "The post-independence territorial recompositions provided them with new opportunities for investment in Telangana, where they bought land in the proximity of irrigation projects."
- Xiang, Biao (2007). Global "Body Shopping": An Indian Labor System in the Information Technology Industry. Princeton University Press. p. 31. ISBN 978-0-691-11852-9.
- Benbabaali, Caste Dominance and Territory in South India (2018), pp. 2–3; Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), p. 356
- Srinivasulu, K. (September 2002). "Caste, Class and Social Articulation in Andhra Pradesh: Mapping Differential Regional Trajectories" (PDF). London: Overseas Development Institute. pp. 3–4. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- Benbabaali, Caste Dominance and Territory in South India (2018), pp. 6–7, 25–29, 29–30
- Bhaskar, T. L. S.; Bhat, Chandrashekhar (2007). "Contextualising Diasporic Identity". In Oonk, Gijsbert (ed.). Global Indian Diasporas: Exploring Trajectories of Migration and Theory. Amsterdam University Press. pp. 108–109, 112. ISBN 978-90-5356-035-8.
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), p. 356: "their actual dominance was originally limited to two districts on the lower banks of the Krishna River, namely Krishna and Guntur districts."
- Lincoln, Bommala Abraham (1992), A study of place-names of Bāpaṭla Taluk: a study on onomastics, B. Subhashini, p. 118: "Here, Kamma indicates a stream. Cf: Gundlakamma: Prakasam District; Perakamma: a big Kamma, River Krishna"
- Benbabaali, Caste Dominance and Territory in South India (2018), pp. 6–7: According to epigraphical records, the Krishna delta area was known as Kammanadu during the Chola empire—a toponym that probably came from the Buddhist monastic institutions called sanghakammas.
- Rao, B. S. L. Hanumantha (1995), Social Mobility in Medieval Andhra, Telugu University, pp. 52–53
- Pramila, Kasturi (1 January 2002), Economic and social conditions of Āndhra Deśa, A.D. 1000 to 1323 A.D., Bharatiay Kala Prakashan, p. 189
- Sarma, M Somasekhara; Sōmaśēkharaśarma, Mallampalli (1948), History of the Reddi Kingdoms (circa. 1325 A.D. to Circa 1448 A.D.), Andhra University, p. 278
- Nāgabhūṣaṇaśarma, Modali; Sastry, Mudigonda Veerabhadra; Śēṣagirirāvu, Cīmakurti (1995), History and culture of the Andhras, Telugu University, p. 80
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), p. 356: "Its historical prominence, however, derived from the fact that it opened into the extensive Deccan plateau."
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), pp. 357–359: "their population in the Krishna delta in the 1872 census was one-fourth of their total strength in the entire Madras Presidency, but had increased by 1921 to about 47 per cent."
- Talbot, Austin Cynthia (2001), Pre-colonial India in Practice: Society, Region, and Identity in Medieval Andhra, Oxford University Press, p. 206, ISBN 978-0-19803-123-9
- Rao, B. S. L. Hanumantha; India), Telugu University (Hyderabad (1995). Socio-cultural history of ancient and medieval Andhra. Telugu University. p. 158.
- Jackson, William (2005). Vijayanagara Voices. Ashgate Publishing. p. 124. ISBN 0-7546-3950-9.
- Rao, B. S. L. Hanumantha; India), Telugu University (Hyderabad (1995). Socio-cultural history of ancient and medieval Andhra. Telugu University. p. 158.
- Rao, B. S. L. Hanumantha; India), Telugu University (Hyderabad (1995). Socio-cultural History of Ancient and Medieval Andhra. Telugu University.
- Dutt, K. I. (1936). "Kamma Commanders of the Vijayanagara Empire". Journal of the Andhra Historical Society. X: 223.
- Stein 1989, p. 88: "Controlling numerous villages and many large towns, these powerful chiefs commanded large mercenary armies that were the vanguard of Vijayanagara forces during the sixteenth century."
- Murthy, N. S. Ramachandra (1 January 1996). Forts of Āndhra Pradesh: From the Earliest Times Upto 16th C. A.D. Bharatiya Kala Prakashan. p. 202. ISBN 9788186050033.
- Heras, Henry. The Aravidu Dynasty Of Vijayanagara. B. G. Paul And Co., Madras. pp. 266, 307.
- "Proceedings Of The Annual Conference". South Indian History Congress. 18: 37. 1999.
- Yellapracada, Sriramamurty. "Political History of Gandikota During the Vijayanagar Period 1336 to 1669 AD". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 21: 278–288 – via JSTOR.
- Ramaswami, N. S. (1976). Temples of Tadpatri. Govt. of Andhra Pradesh. p. 10.
- Ramaswami 1975, pp. 10–11
- D'Attilio, Daniel (1995). The Last Vijayanagara Kings: Overlordship and Underlordship in South India, 1550-1650. University of Wisconsin--Madison. p. 50.
- Narayana Rao, Velcheru (2001). Textures of Time : Writing History in South India, 1600-1800. Delhi: Other Press. ISBN 81-7824-023-8. OCLC 49616884.
The principality is consolidated by Shayappa and by his son and grandson, Vengala Nayudu and Venkatadri Nayudu, whose rule is presented as re-presenting a rather peaceful epoch.
- Narayana Rao, Velcheru (2003). Textures of Time : Writing History in South India. New York: Other Press. ISBN 1-59051-044-5. OCLC 50143515.
Their main strength lies in their capacity to shift allegiances on a pragmatic basis, usually through the mediation of a Niyogi Brahmin . . . the Kamma Nayaks thus create their political base under Vijayanagara, shift to the Qutb Shahi state of Golconda (using a common enemy, the Boyas of the region, to build a case), and then to the post-Mughal state of Asaf Jati Nizams in Hyderabad.
- Dutt, K. I. (1936). "Kamma Commanders of the Vijayanagara Empire". Journal of the Andhra Historical Society. X: 223–224.
- Ray, Nisith Ranjan (1978). Sources of the History of India. 1. Institute of Historical Studies. p. 152.
- Satyanarayana, A. (2007). Society, Economy, and Polity in Modern Andhra. Kanishka Publishers Distributors. p. 7. ISBN 978-81-7391-971-8.
- Chapter III: Economics, Political, Economic, and Social Background of Deccan 17th-18th Century, p.57 https://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/25652/10/10_chapter%203.pdfhttps://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/25652/10/10_chapter%203.pdf
- Reddy, Pedarapu Chenna (1 January 2006). Readings In Society And Religion Of Medieval South India. Research India Press. p. 163. ISBN 9788189131043.
- Proceedings of Seminar on Industries and Crafts in Andhra Desa, 17th and 18th Centuries, A.D. Department of History, Osmania University. 1996. p. 57.
- Narayanarau, V.; Shulman, D. D.; Subrahmanyam, S. (2002). Textures of Time: Writing History in South India. Other Press LLC. p. 264. ISBN 1-59051-044-5.
- Richards, John F. (1993). Power, administration, and finance in Mughal India. Variorum. p. 331. ISBN 978-0-86078-366-4.
- Sherman, Taylor C. (25 August 2015). Muslim Belonging in Secular India. Cambridge University Press. p. 60. ISBN 978-1-107-09507-6.
- Benbabaali, Caste Dominance and Territory in South India (2018), pp. 8
- Kumar, P. Pratap (2013). "Andhra Pradesh: Economic and social relations". In Berger, Peter; Heidemann, Frank (eds.). The Modern Anthropology of India: Ethnography, Themes and Theory. Routledge. p. 18. ISBN 9781134061112.
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), p. 357.
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), pp. 358–359.
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), pp. 360–361.
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), p. 356.
- Murty, K. R. (2001). Parties, Elections and Mobilisation. New Delhi: Anmol Publications. p. 20.
- Bhattacharya, Sabyasachi (2002). Education and the disprivileged: nineteenth and twentieth century India. Orient Blackswan. p. 58. ISBN 978-81-250-2192-6.
- Stein, Burton (1989). Vijayanagara. Cambridge University Press. p. 46. ISBN 0-521-26693-9.
- Chari, Sharad (2004). Fraternal Capital. Stanford University Press. p. 162. ISBN 0-8047-4873-X.
- Murali, Kanta (2 February 2017). Caste, Class, and Capital: The Social and Political Origins of Economic Policy in India. Cambridge University Press. p. 164. ISBN 978-1-108-17954-6.
- Jodhka, Surinder S.; Naudet, Jules (15 May 2019). Mapping the Elite: Power, Privilege, and Inequality. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-909791-3.
- Keiko, Politics and representation of caste identity (2008), p. 355–356.
- Fox, Richard G. (January 1969), "Varna Schemes and Ideological Integration in Indian Society", Comparative Studies in Society and History, 11 (01): 27–45, doi:10.1017/S0010417500005132: "When recognition of a regional varna scheme has been unavoidable—such as the tripartite division into Brahmins, non-Brahmins, and Untouchables in much of the South— it has been explained in terms of an historical corruption or breakdown of the standard four-class system, rather than regarded as a functional entity in its own right."
- Gopi, K. N. (1978), Process of Urban Fringe Development: A Model, Concept Publishing Company, p. 35
- Kumar, P. Pratap (2013). "Andhra Pradesh: Economic and social relations". In Berger, Peter; Heidemann, Frank (eds.). The Modern Anthropology of India: Ethnography, Themes and Theory. Routledge. p. 14. ISBN 9781134061112.
- Bhattacharya, Sabyasachi (2002). Education and the disprivileged: nineteenth and twentieth century India. Orient Blackswan. p. 17. ISBN 978-81-250-2192-6.
- Jaffrelot, Christophe (2002). "The subordinate caste revolution". In Alyssa Ayres; Philip Oldenburg (eds.). India briefing: quickening the pace of change. M. E. Sharpe. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-7656-0813-0.
- Harrison, Caste and the Andhra Communists (1956)
- Political Parties in South Asia, S. K. Mitra and M. Enskat, 2004, Praeger/Greenwood, p.115, ISBN 0-275-96832-4
- "Khammas of AP have money power, so they just go get it". Retrieved 7 September 2016.
Bibliography
- Benbabaali, Dalel (2018), "Caste Dominance and Territory in South India: Understanding Kammas' socio-spatial mobility", Modern Asian Studies, 52 (06): 1938–1976, doi:10.1017/S0026749X16000755, ISSN 0026-749X
- Keiko, Yamada (2008), "Politics and representation of caste identity in regional historiography: A case study of Kammas in Andhra", The Indian Economic and Social History Review, 45 (3): 353–380, doi:10.1177/001946460804500302
- Harrison, Selig S. (June 1956). "Caste and the Andhra Communists". The American Political Science Review. 50 (2): 378–404. JSTOR 1951675. (subscription required)
Further reading
- Frykenberg, Robert Eric (1973) [1968]. "Traditional Processes of Power in South India: An Historical Analysis of Local Influence". In Bendix, Reinhard (ed.). State and Society: A reader in comparative political sociology. University of California Press. p. 107. ISBN 0-520-02490-7.
- Gough, Kathleen (1981). Rural Society in Southeast Asia. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-04019-1.