KV46
Tomb KV46 in the Valley of the Kings is the tomb of Yuya and his wife Tjuyu, the parents of Queen Tiye, Anen, and possibly Ay. It was discovered in February 1905 by James E. Quibell under the sponsorship of Theodore M. Davis.
| KV46 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Burial site of Yuya and Tjuyu | |||
 KV46 | |||
| Coordinates | 25°44′27″N 32°36′10″E | ||
| Location | East Valley of the Kings | ||
| Discovered | February 1905 | ||
| Excavated by | James E. Quibell | ||
Layout
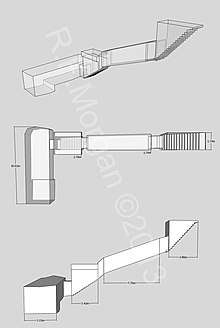
KV46 consists of a 15-step staircase leading to a descending corridor, a further set of short stairs, a second corridor with stairs and niches, and a rectangular burial chamber, the western third of which is 1 metre (3.3 ft) deeper than the rest of the floor.[1][2] The walls of the tomb are not decorated and were not smoothed, possibly due to the poor quality of the limestone; the only markings on the walls are black dots 40 centimetres (16 in) apart on the smoother walls;[1] they may be mason's marks.[2]
Location and discovery
KV46 was discovered on 6 February 1905 in excavations undertaken by James Quibell on behalf of Theodore Davis. Davis' 1902–1903 excavation season had discovered the tombs of Thutmose IV (KV43) and Hatshepsut (KV20) in a small side valley and excavations resumed in this area on 17 December 1904.[1] Finding that nothing had been uncovered upon his arrival in January 1905, excavations shifted to an as-yet unexplored area between the tombs of Ramesses III (KV3) and Ramesses XI (KV4). Despite characterising the location as "most unpromising", excavation commenced on 25 January 1905. On 6 February Davis was shown the first step of the tomb cutting by his excited foreman and workers and by the evening of 12 February the door was completely exposed. The door and decorated lintel were cut into the solid rock and measured 4.02 by 1.35 metres (13.2 ft × 4.4 ft). The doorway had been blocked by stones cemented with mud plaster but was open for the top 18 inches (46 cm), indicating that the tomb had been opened and probably robbed in antiquity. Despite it being nearly dark, Davis and Arthur Weigall, the new Chief Inspector of Antiquities, peered through the gap in the blocking. They saw a steeply declining corridor and Davis spotted a cane lying close to the door. Lacking a ladder, a small boy was lifted in to retrieve the item; he returned with a stone scarab and the yoke of a chariot in addition to the cane. That evening, Davis showed these items to Gaston Maspero who, intrigued both by the items and the identity of the tomb's owner, asked to be present at the entry into the tomb the next day.[3]
Investigation

On 13 February, after taking down the blocking, Davis, Maspero, and Weigall entered the tomb. Quibell was not present as he was at Edfu acting as the official guide of the Duke of Connaught.[4][1] After descending down the steep corridor, a blocked and plastered doorway stamped with seals was encountered; this too had been breached at the top in antiquity. On either side of the doorway were pottery bowls containing the remains of the mud plaster used to seal the blocking. Catching glimpses of gold glittering in the candlelight, the trio took down the top course of the blocking and entered the burial chamber. Davis describes the first moments:
The chamber was as dark as dark can be and extremely hot... We held up our candles, but they gave so little light and so dazzled our eyes that we could see nothing except the glitter of gold.[3]
Looking to identify the owner of the tomb, they inspected a large wooden coffin on which Maspero read the name 'Iouiya'; in the excitement, Davis nearly touched the candles to the black resin surface. Realising how close they had come to a possible firey death, they made a hurried exit and returned with electric lights. The space was filled with a jumble of objects including sarcophagi, gilded and silvered coffin sets, canopic chests, a chariot, beds, chairs and other items of furniture, and various vessels. The rifled but intact mummies of Yuya and Tjuyu were still lying in their coffins.[3]
The risk of robbery was felt to be very real despite the presence of guards, so the contents were planned, recorded, photographed, and packed for transport to the Egyptian Museum in Cairo as quickly as possible. On 3 March the entire contents of the tomb had reached the river; they were loaded onto a train the next day and arrived under armed guard to the museum.[1]
Contents
Until the discovery of Tutankhamun's tomb in 1922, this was the richest and best preserved tomb found in the valley, and the first to be found with major items in situ.[2]
The large wooden sarcophagi and coffin sets of Yuya and Tjuyu occupied most of the space in the tomb, with Yuya's against the northern wall and Tjuyu's against the southern; both sarcophagi faced west. Their large size meant they must have been assembled and possibly finished in the tomb, as there are no breaks in the gilded decoration. One end of Yuya's sarcophagus had been broken in and the lid displaced; the lids of his three nested coffins had been removed, with two laid on top of each other partially supported by a chair and the third on its side against the coffins. His gilt cartonnage mask was broken and his mummy had been investigated by robbers, as the body lay in the remnants of its torn wrappings. Tjuyu's sarcophagus had been partially dismantled, with the lid placed on one of the two beds and one side placed on top of it, and the southern side had been placed against the wall. This allowed her two nested coffins to be removed; the lid of the outer one had been thrown atop one of the beds while the trough had been thrown into the far corner of the tomb. The inner coffin still had its lid on.[1]
The canopic chests were placed close to the sarcophagi of their respective owners and were likewise facing west. The lids of both boxes had been moved but the embalmed viscera, shaped like mummies and wearing gilt masks, were undisturbed. Under the beds and in the corner by the door were caskets and boxes, while inside or under the upturned coffin lids and troughs were various items including cushions, a wig, alabaster vases, and lids of caskets. The chests and boxes contained items such as sandals, model tools for ushabti, cloth, and the lids of ushabti boxes.[1]
The western third of the room with the lower floor was filled with 52 large vessels containing natron; above the pots was a bed, the chariot, a large reed mat, a wig basket, the cartonage mummy bands of Tjuyu, and 18 boxes of dried foods.[1]
Differences in the embalming techniques used for Yuya and Tjuyu indicates that they died at different times and were placed in the tomb accordingly.
Robberies
KV46 was robbed in antiquity, most probably three times: a first time shortly after the closure of the tomb, and then twice during the construction of the adjacent tombs KV3 and KV4. During the first looting, only perishable products such as oil were removed. The second and third times however the looters took most of the jewellery and linen not associated with the mummies.[2]
Objects found in KV46
 Mummy mask of Tjuyu.
Mummy mask of Tjuyu. Mummy mask of Yuya.
Mummy mask of Yuya. Yuya's large outer coffin as discovered in 1905.
Yuya's large outer coffin as discovered in 1905. Second and inner coffins of Yuya.
Second and inner coffins of Yuya..jpg) Tjuyu's third coffin from KV46 (Cairo Museum)
Tjuyu's third coffin from KV46 (Cairo Museum)- Mummified entrail with cartonnage mask from KV46.
_(1906)_-_TIMEA.jpg) Blue enamelled and gold coffer from KV46 bearing the Horus name, prenomen and nomen of Amenhotep III.
Blue enamelled and gold coffer from KV46 bearing the Horus name, prenomen and nomen of Amenhotep III._(1906)_-_TIMEA.jpg) Gilded head to bedstead representing the god Bes.
Gilded head to bedstead representing the god Bes..jpg) The gilded 'ibex' chair.
The gilded 'ibex' chair..jpg) A gilded chair, the back depicts a boating scene.
A gilded chair, the back depicts a boating scene. Sealed storage jar, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Sealed storage jar, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Pair of sandals, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Pair of sandals, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art.
References
- Quibell, J. E. (1908). Tomb of Yuaa and Thuiu. Le Caire Impremerie De L'Institut Francais D'Archeologie Orientale. pp. I–VII.
- Reeves, Nicholas; Wilkinson, Richard H. (2010). The Complete Valley of the Kings: Tombs and Treasures of Egypt's Greatest Pharaohs (Paperback reprint ed.). London: Thames & Hudson. pp. 174–178. ISBN 978-0-500-28403-2.
- Davis, Theodore M. (1907). The Tomb of Iouiya and Touiyou. London: Archibald Constable and Co. pp. XXV–XXX. ISBN 0-7156-2963-8.
- Romer, John (1981). Valley of the Kings. London: Book Club Associates. pp. 197–204.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to KV46. |
- Theban Mapping Project: KV46 - Includes detailed map of the tomb.