Israeli Navy
The Israeli Navy (Hebrew: חיל הים הישראלי, Ḥeil HaYam HaYisraeli (English: Sea Corps of Israel); Arabic: البحرية الإسرائيلية) is the naval warfare service arm of the Israel Defense Forces, operating primarily in the Mediterranean Sea theater as well as the Gulf of Eilat and the Red Sea theater. The current commander in chief of the Israeli Navy is Aluf Eli Sharvit. The Israeli Navy is believed to be responsible for maintaining Israel's offshore nuclear second strike capability.[1]
| Israeli Navy | |
|---|---|
| חיל הים הישראלי | |
 Cadets from the Israeli Naval Academy in December 2007 | |
| Founded | 1948 |
| Country | |
| Type | Navy |
| Size | 3 corvettes (Sa'ar 5 class) 8 missile boats (Sa'ar 4.5 class) 5 submarines (Dolphin class) 45 patrol boats 2 support ships 10,000 active 10,000 reserve |
| Part of | |
| Garrison/HQ | HaKirya, Tel Aviv, Israel |
| Motto(s) | "Open Sea, Safe Coasts" |
| Engagements | 1948 Arab–Israeli War War over Water Six-Day War War of Attrition Yom Kippur War 1982 Lebanon War 1982–2000 South Lebanon conflict Second Intifada 2006 Lebanon War Blockade of the Gaza Strip Gaza War Operation Protective Edge |
| Commanders | |
| Commander of the Navy | Aluf Eli Sharvit |
| Insignia | |
| Naval ensign |  |
| Pennant |  |
History

The origins of the Israeli Navy lay in the founding of the Betar Naval Academy, a Jewish naval training school established in Civitavecchia, Italy, in 1934 by the Revisionist Zionist movement under the direction of Ze'ev Jabotinsky, with the agreement of Benito Mussolini. The Academy trained cadets from all over Europe, Palestine and South Africa and produced some of the future commanders of the Israeli Navy. In September 1937, the training ship Sarah I visited Haifa and Tel Aviv as part of a Mediterranean tour.
In 1938, encouraged by the Jewish Agency, Dr. Shlomo Bardin founded the Marine High School in Bosmat, the Technion's Junior Technical College. 1943 witnessed the founding of the Palyam, the naval branch of the Palmach, whose training was undertaken at the maritime school. The Jewish merchant marine was also raised, operating SS Tel-Aviv and cargo ships such as Atid.
In 1942, eleven hundred Haganah volunteers joined the Royal Navy, mostly in technical roles (12 of them were officers by the nomination agreement of the Jewish Agency with the Royal Navy). A few reached sea service and combat service. Two of them served with the Fleet Air Arm (FAA), one of whom was Edmond Wilhelm Brillant and the other Zvi Avidror. With the end of the Second World War and the start of the Jewish insurgency in Mandatory Palestine, Palyam members took part in clandestine immigration activities, bringing Europe's Jews to Palestine, as well as commando actions against Royal Navy deportation ships. Royal Navy volunteers, meanwhile, rejoined the Haganah.
During the last months of British Mandate in Palestine, the former Royal Navy volunteers started work on the captured clandestine immigration ships (known as the Fleet of Shadows) in Haifa harbor, salvaged a few and pressed them into service. These were to become the Navy's first ships and saw service in the 1948 Israeli War of Independence.

At the outset of the 1948 war and with the founding of the IDF, the Israeli Navy consisted of four former Aliyah Bet ships impounded in Haifa harbor. These ships were refurbished by a newly formed naval repair facility with the assistance of two private shipbuilding and repair companies. In October 1948, a submarine chaser was purchased from the United States. With the founding of the IDF in early 1948, the Israeli Navy was therefore formed from a core of the following personnel:[2][3]
- Royal Navy volunteers with the technical skills and discipline acquired from the Royal Navy, though with no active sea service and experience on Royal Navy ships.
- Palyam members who had led the clandestine and immigration effort, but had no sea background in navigation or leading a ship into a battle. The captains of clandestine and immigration ships were Italian, while Palyam personnel were commanding the ship under instructions from the Haganah. Ike Aharonowitch, captain of Exodus and a Jew, was the exception rather than the rule.
- Merchant Marine captains and chief engineers, possessing navigation skills but lacking combat skills.
- Jewish volunteers[4][5] from the United States Navy and Royal Navy, such as Commander Paul Shulman[6] of the U.S. Navy, and Commanders Solomon and Allen Burk of the Royal Navy.[7] These, however, were often discriminated against and their experience wasted by a navy command that was based on the Palmach and its various branches. This resulted in odd situations where unskilled officers from the Palyam were in command of far more experienced naval officers.
During the war, the warships served on coastal patrol duties and bombarded Arab targets on land, including Egyptian coastal installations in and around the Gaza area all the way to Port Said. The Israeli Navy also engaged the Egyptian Navy at sea during Operation Yoav, and the Egyptian Navy's flagship, Emir Farouk, was sunk in an operation by Israeli naval commandos.

Palyam personnel often resisted efforts to instill order, discipline and rank in the newly formed service. Mess rooms were initially shared by both officers and enlisted men. Ships possessed a captain with nautical skills, but also a commanding officer regarded as political. This would cause a great deal of debate between veterans of the Palyam, Royal Navy volunteers from the Haganah and U.S. Navy Machal volunteers about what form the Navy should take.[2][9][10] Commander Allen Burk is reputed to have said, out of despair, "You cannot make naval officers from cowboys".[3]
Royal Navy Captain Ashe Lincoln,[11] who was Jewish, advised Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion to purchase corvettes, frigates, destroyers, torpedo boats, and patrol boats to build up the Israeli Navy power. To that end, he urged Ben-Gurion to consult with professional navy advisers. This resulted in instructions to contact U.S. Navy advisors, mainly Commander Paul Shulman from the U.S. Navy.
The Israeli Navy suffered from a lack of professional command during its early days.[2] Gershon Zak, head of the IDF "Sea Service", was a teacher and bureaucrat without any relevant experience. Having never been recruited into the IDF, Zak was a civilian and had no official rank. The early days of the Israeli Navy were therefore characterized by political infighting, as many groups and individuals jockeyed for power. Palyam politics blocked the nomination of Paul Shulman (a Jewish U.S. Navy officer with a rank of Commander who volunteered for the Israeli Navy) as Navy-Commander in Chief and he resigned in 1949. The first Navy-Commander in Chief awarded the rank of Aluf was Shlomo Shamir.[2]
The conclusion of the 1948 war afforded the navy the time to build up its strength. Beginning in the early 1950s the navy purchased frigates, torpedo boats, destroyers, and eventually submarines. The material build-up was accompanied by the training of Israeli Navy officers in Royal Navy academies in the UK and Malta, as well as in France.
Three distinct periods characterize the history of the Israeli Navy:
- Foundation and early days
- The destroyers' age
- The missile boats era, beginning in 1965 and bearing fruit during the 1973 Yom Kippur War.[12][13]
Until 1967 the Naval Headquarters were located at Stella-Marris, on the slopes of Mount Carmel, Haifa. After the Six-Day War it was relocated to the Kirya in Tel Aviv, next to IDF Headquarters.
Yom Kippur War
In the most significant engagement in its history, during the Yom Kippur War five Israeli Navy missile boats sank five Syrian ships without losses during the Battle of Latakia. As a result, the Syrian Navy remained in port for the remainder of the conflict.[14] It was the first naval battle in history between surface-to-surface missile-equipped missile boats.
Another significant engagement is the Battle of Baltim, during which six Israeli Navy missile boats engaged four Egyptian Navy missile boats sinking three, again, without losses.
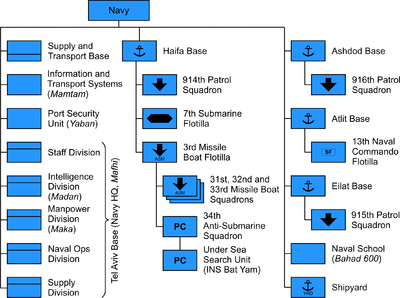
Bases


- Haifa – Missile Boats Flotilla, the Submarine Flotilla, Patrol Boats Squadron 914.
- The emblem of the Haifa naval base is two arrows – one signifying the Missile Boats Flotilla and the other the Submarine Flotilla.
- Atlit – home to Shayetet 13, the navy's elite commando unit.
- Ashdod – mainly a base for Patrol Boats Squadron 916.
- The emblem of the Ashdod naval base is two opposing arrows.
- Eilat naval base was founded in 1951 and has been responsible for the Israeli Navy's Red Sea theater since 1981, when the Red Sea Naval Command Center was withdrawn from Sharm el-Sheikh in accordance with the Egyptian–Israeli peace treaty.
- The emblem of the Eilat naval base represents the red roofs of Eilat.
- The Naval Training base – located in Haifa, contains the submarine operations school, the missile boat operations school and the naval command school. The naval training base also functions as the Israeli Naval Academy.
- The emblem of the Haifa training base is an owl, symbolizing wisdom and hard learning.
- Mamtam – IT, processing and computing.
- Mamtam is a small unit responsible for all Israeli Navy signal and IT systems, both logistic and operational. The soldiers that serve there are mainly programmers and university graduates in engineering, computer science and other technological professions.
Forces
Patrol squadrons
Based in Haifa, Eilat, and Ashdod respectively, Squadrons 914, 915, and 916 defend Israel's shores from nearby.
Unit's objectives
- Constant patrols in the seas of Israel.
- Identification of watercraft entering Israeli waters.
- Preventing smuggling through the sea
- Protecting national assets, such as drilling rigs.
- Various operations carried out alone, or with other units in and outside of the navy.
- Various other objectives that differ between the squadrons.
3rd Flotilla
The Missile Boats Flotilla, based at Haifa. It consists of the 31st, 32nd and 33rd Missile Boat Squadrons and the 34th Anti-Submarine Squadron.
Unit's objectives
- Protecting Israeli commerce at sea from foreign fleets.
- Preventing a possible naval blockade of Israeli ports during wartime.
- Blockading enemy ports at wartime.
- Fire support for ground units.
7th Flotilla
The Submarine Flotilla, a volunteer unit founded in 1959.
Unit's objectives
- Attacking enemy vessels.
- Covert intelligence gathering.
- Deployment and recovery of Shayetet 13 naval commandos.
- Acting as a support unit for other units.
- Believed to be part of the country's nuclear weapons capability.[15]
For security reasons, applicants with dual citizenship must now officially renounce all other citizenships to be accepted into the submarine service training program.[16]
13th Flotilla
Shayetet 13, or Flotilla 13, is an elite naval commando unit which specializes in sea-to-land incursions, counter-terrorism, sabotage operations, maritime intelligence gathering, maritime hostage rescue, and boarding. It is among the most highly trained and secretive units in the Israeli military.

YALTAM 707
Salvage and underwater works unit. Formed as the damage control branch of the Navy Shipyards, the unit later incorporated experienced Flotilla-13 divers.
Snapir
Force protection and harbour security unit. Also in charge of diving checkups of civilian ships entering Israeli harbours.
Intelligence
The Corps' relies on its Naval Intelligence Division for naval intelligence.
Fleet
"INS" stands for "Israeli Navy Ship".[17]
Corvettes
| Class | Photo | Ships | Commission year | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa'ar 5 |  |
1994 |
U.S. built class |
Missile boats
| Class | Photo | Ships | Commission year | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa'ar 4.5 | INS Romach, pronounced [ʁomaχ] (Lance)
INS Keshet (Bow) INS Hetz, pronounced [ˈχet͡s] (Arrow) INS Kidon (Javelin) INS Tarshish (Tarshish) INS Yaffo (Jaffa) |
1981
1982 1991 1995 1995 1998 2002 2003 |
|
Submarines
| Class | Photo | Ships | Commission year | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolphin class | INS Dolphin (Dolphin)
INS Livyathan (Whale) INS Tekumah (Revival) |
1999
1999 2000 |
German built submarines | ||
| AIP Dolphin 2 class | .jpg) |
INS Tanin (Crocodile)
INS Drakon (Dragon) |
2012
2014 2019 |
Patrol boats
| Class[18] | Photo | Number of ships | Commissioned | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dvora |  |
9 | 1988 | ||
| Super Dvora Mk II |  |
4 | 1996 | ||
| Super Dvora Mk III |  |
13 | 2004 | ||
| Shaldag |  |
5 | 1989 | ||
| Defender |  |
9 | 2002 | ||
| Rafael Protector USV |  |
2000s | Unmanned Naval Patrol Vehicles | ||
| Silver Marlin | 2006? | USV Naval Patrol Vehicles |
Support ships
- INS Bat Yam - ex-Bundesmarine Stollergrund Class FGS Kalkgrund (Y865) small multipurpose utility boat (1989)
- INS Bat Galim - ex-Bundesmarine Stollergrund Class FGS Bant (Y867) small multipurpose utility boat (1989)
Commando boats
- Dolphin type underwater craft
- Maiale (pig) type underwater craft
- Snunit boats
- Zaharon boats
- Moulit boats
- Morena rigid-hulled inflatable boats
Aircraft

Aircraft operated by the Israeli Navy, even when including on-board Navy mission specialists, are flown and maintained by Israeli Air Force personnel and are part of the air force command structure.
Unmanned aerial vehicles
- Aeronautics Defense Orbiter[20]
- The navy has an unmanned helicopter (manufactured by Aeronautics Defense Systems) on Sa'ar 5-class corvettes.[21]
Equipment

- Barak 1 – Point-defence SAM
- Barak 8 – Long range SAM and anti-missile defence system
- Gabriel – sea-to-sea missile
- Harpoon – anti-ship missile
- Popeye (AGM-142 Have Nap) – air/sub-launched cruise missile. Dolphin-class submarines believed to carry Popeye Turbo with a range >1500 km and the option for nuclear warheads.
- Typhoon Weapon Station – remote-operated 25mm gun system
- NAVLAR Artillery Rocket System
- EL/M-2221 STGR – Search, Track & Guidance/Gunnery Radar
- EL/M-2228S AMDR – Automatic Missile Detection Radar
- EL/M-2228X SGRS – Surveillance & Gunnery Radar System
- EL/M-2238 STAR – Surveillance & Threat Alert Radar
- EL/M-2226 ACSR – Advanced Coastal Surveillance Radar
Future
ThyssenKrupp will build four Sa'ar patrol vessels for EEZ duties such as protecting offshore gas fields.[22] The ships will be based on the MEKO A-100 design[22] like Germany's Braunschweig-class corvettes, suggesting they will be 90 m (295 ft) long and displace around 1,800 tonnes, named Sa'ar 6-class corvette. This deal was signed in December 2014 and Germany is believed to be contributing up to €115m of the €1 billion cost.[23] Previously Israel had hoped to acquire an up-armed version of the Freedom class of littoral combat ships from Lockheed Martin, but spiralling costs had made this impossible, along with a fallback option from Northrop Grumman/Huntington Ingalls Industries which built the Sa'ar 5 class.
Currently under construction is a sixth Dolphin 2 submarine (INS Drakon). Additionally, Israel signed an MoU with Germany for the construction of three more Dolphin 2 submarines with expected delivery in the late 2020s which will replace its three Dolphin 1 submarines delivered in the late 1990s.
The Israeli Navy signed an agreement with Israel Shipyards for the design and supply of a new class of missile boats based on Israel Shipyards' Sa'ar 72-class corvette that will replace its Sa'ar 4.5 ships starting in the mid-2020s. Israel Shipyards will also construct a large dry dock which will enable it to outfit the new Sa'ar 6 corvettes with various Israeli-made systems, as well as service and maintain the Sa'ar 6 corvettes and Dolphin submarines.[24]
Ranks
The Israeli Navy is small compared to other Navies and the officers chain of command is as follows with respect to Royal – Navy / United States:[25]
- Officers
| Equivalent NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) & Student officer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major General (אלוף) |
Brigadier General (תת אלוף) |
Colonel (אלוף משנה) |
Lieutenant Colonel (סגן אלוף) |
Major (רב סרן) |
Captain (סרן) |
Lieutenant (סגן) |
Second Lieutenant (סגן משנה) |
Superior Academic Officer (קצין אקדמי בכיר) |
Professional Academic Officer (קצין מקצועי אקדמי) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Enlisted
| Equivalent NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent | No insignia | No equivalent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chief warrant officer (רב-נגד (רנ"ג |
Command Sergeant Major (רב-סמל בכיר (רס"ב |
Sergeant Major (רב-סמל מתקדם (רס"מ |
Master Sergeant (רב-סמל ראשון (רס"ר |
Sergeant First Class (רב-סמל (רס"ל |
Staff Sergeant (סמל ראשון (סמ"ר |
Sergeant סמל |
Corporal (רב טוראי (רב"ט |
Private טוראי | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sleeve rank of Israeli Navy Commander-in-Chief is a rank of honor. This began as special permission from Lt. General Amnon Lipkin-Shahak (then chief of staff of the IDF) and allows the Navy Commander-in-Chief to have a sleeve rank of Vice Admiral which is equal to Lt. General, the rank of the IDF Chief of Staff. However the de facto rank of Israeli Navy Commander-in-Chief is Rear Admiral and the gesture given to the navy is ceremonial only when meeting foreign commanding officers.
The same resolution as mentioned above applies to the rank of Commodore. There is ceremonial-only sleeve rank of Rear–Admiral while by the IDF hierarchy and chain of command he remains a commodore.
List of commanders
See also
References
- Cirincione, Joseph; Wolfsthal, Jon B.; Rajkumar, Miriam (2005). Deadly arsenals: nuclear, biological, and chemical threats. Carnegie Endowment. pp. 263–4.
- "Anat Kidron MA Thesis, Israeli Navy Year of Foundation". Haifa University Israel. October 2000. Archived from the original on 20 December 2008. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- "The last Battle of the Destroyer INS Eilat by Commander Yitzhak Shushan". Ma’ariv Publishing House. 1993. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- "MACHAL Overseas Volunteers In Israel's War of Independence Page 28" (PDF). MOD IDF. 2007. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- "A Tiny, but Hard-Hitting Battle Force". By David Hanovice North American Volunteers In Israel's War of Independence. 2007. Retrieved 5 December 2009.
- "Paul Schulman". NY Times. 18 May 1994. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- Nadav Reis. "Known Decorations for Bravery Awarded to Machalniks who served in World War II - מח"ל עולמי". Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- "The last Battle of the Destroyer INS Eilat by Commander Yitzhak Shushan". Ma'ariv Publishing House. 1993. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- Commander Shlomo, Ya'akobson a Hagana Veteran of the Royal Navy (1997). "Betaltala". MOD House. Retrieved 5 December 2009.
- "Ashe Lincoln". Dangoor.com. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- BOATS OF CHERBOURG Abraham Rabinovich. Bluejacket Books. 1973. ISBN 1-55750-714-7. Retrieved 3 December 2009.
- "The Missile Boat War The 1973 Arab-Israeli War at Sea" (PDF). By Dave Schueler. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 October 2009. Retrieved 3 December 2009.
- "The Battle of Latakia". Jewish Virtual Library.
- "Israel seeks sixth Dolphin in light of Iranian 'threat'". Janes.com. 1 October 2009. Retrieved 1 June 2010.
- "IDF submarine fleet bans dual citizenship". ynet. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- "Ship Naming in the United States Navy". About.com. Archived from the original on 21 August 2014. Retrieved 21 August 2014.
- John Pike. "Navy Equipment - Israel". Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- The Military Balance 2017, International Institute for Strategic Studies, 14 February 2017, p. 384.
- "חדשות - צבא וביטחון nrg - ...נושאת מזל"טים: חיל הים כובש". Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- "דף בית | Israel Defense". www.israeldefense.co.il. Retrieved 26 September 2019.
- Opall-Rome, Barbara (25 December 2014). "Israel, Germany Seal Offshore Patrol Vessel Deal". Defense News.
- Hudson, Alexandra (15 December 2015). "Germany says will help finance four new Israeli warships". Reuters.
- Eshel, Tamir (20 November 2019). "Israeli-Designed Mini Corvettes to Replace Eight Hetz Missile Boats".
- "IDF Ranks". IDF Spoke Man. 2009. Archived from the original on 30 August 2009. Retrieved 3 December 2009.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Israeli Navy. |
- Sea Corps Official Site (in Hebrew)
- History of the Navy North American Volunteers In Israel's War of Independence
- Israeli submarines
- World Navies Today: Israel
