Interstate 95 in New York
Interstate 95 (I-95) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Miami, Florida, to the Canada–United States border near Houlton, Maine. In the U.S. state of New York, I-95 extends 23.50 miles (37.82 km) from the George Washington Bridge in New York City to the Connecticut state line at Port Chester. From the George Washington Bridge, which carries I-95 across the Hudson River from New Jersey into New York City, it runs across upper Manhattan on the Trans-Manhattan Expressway and continues east across the Harlem River on the Alexander Hamilton Bridge and onto the Cross Bronx Expressway. In the Bronx, I-95 leaves the Cross Bronx at the Bruckner Interchange, joining the Bruckner Expressway to its end. North of the interchange with Pelham Parkway, it then continues northeast via the New England Thruway (which is part of the New York State Thruway system) out of New York City into Westchester County and to the Connecticut state line, where I-95 continues on the Connecticut Turnpike.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
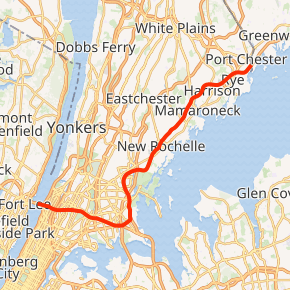
Map of northern New York City and southern Westchester County with I-95 highlighted in red | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by NYSDOT, NYSTA and PANYNJ | ||||
| Length | 23.44 mi[1] (37.72 km) | |||
| Existed | August 14, 1957[2]–present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| South end | ||||
| ||||
| North end | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | New York, Bronx, Westchester | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Route description
Manhattan
I-95 enters New York from New Jersey on the George Washington Bridge on a concurrency with U.S. Route 1 (US 1) and US 9. As the bridge's eastern approach enters Fort Washington Park, I-95 enters exit 1, which services New York State Route 9A (NY 9A, the Henry Hudson Parkway). Access is also provided to 181st Street. After crossing Fort Washington Avenue, the interstate goes underground, providing a ramp to 178th Street, which is where US 9 forks to Broadway. I-95 continues east under Washington Heights, entering an interchange with the Harlem River Drive along with Amsterdam Avenue.[3]
The Bronx
After exit 2, I-95 crosses over the Harlem River and enters the Bronx, entering an interchange with the Major Deegan Expressway (I-87), which is marked both exit 1C (following with the Cross Bronx Expressway) and exit 3A B (matching with the Trans-Manhattan Expressway). Now the Cross-Bronx Expressway, I-95 and US 1 continue east over University Avenue and enter exit 2A, which serves Jerome Avenue. Crossing over the Grand Concourse, the six-lane expressway crosses into exit 2B, which is for Webster Avenue. This interchange also marks the eastern end of the I-95/US 1 concurrency. Passing south of Tremont Park, the Cross Bronx westbound serves exit 3, which serves Third Avenue.[3]

At East 176th Street, the Cross Bronx Expressway turns southeast, entering exit 4A eastbound, which marks the northern terminus of NY 895 (Sheridan Boulevard). After crossing the Bronx River, the expressway enters a full interchange, exit 4B, with the Bronx River Parkway.[3] After a curve from the parkway, the Cross Bronx begins paralleling East 177th Street[4] and enters exit 5A, which connects to White Plains Road in Parkchester. Continuing southeast, the roadway enters exit 5B, Castle Hill Avenue, which is an eastbound-only exit. After Castle Hill Avenue, the route enters exit 6A, which reaches the Hutchinson River Parkway at the Bruckner Interchange. Changing to the Bruckner Expressway, which runs to the northeast, I-95 enters the Bruckner Interchange with the northern termini of I-678 and I-278; the Cross Bronx Expressway Extension turns southeast along I-295 at the same interchange.[3]
After the Bruckner Interchange, I-95 crosses Tremont Avenue before crossing over I-695 (the Throgs Neck Expressway). Southbound, exit 7A serves I-695, while northbound the two interstates merge. Continuing north, the Bruckner Expressway and I-95 parallel Bruckner Boulevard and run along the western edge of Pelham Bay Park. Entering exit 8A southbound services Westchester Avenue while northbound, exits 8B and 8C serve the Pelham Parkway and Shore Road through the park, which marks the northern end of the Bruckner Expressway. Now known as the New England Thruway, I-95 leaves Pelham Bay Park and enters exit 9, a junction with the Hutchinson River Parkway. In the middle of the interchange with the Hutchinson River, exit 10 forks to the left, reaching Gun Hill Road.[3]
Now paralleling Baychester Avenue, which also services exit 11 and Bartow Avenue, the New England Thruway continues north and enters exit 12 which connects to Baychester. Conner Street is connected to via exit 13 before I-95 turns east and crosses over the Hutchinson River. After crossing the river, the route enters an interchange once again with the Hutchinson River Parkway (exit 14) but this time westbound only.[3]
Westchester

Crossing through the northern reaches of Pelham Bay Park, I-95 turns more northeast and enters Westchester County. Now in Pelham Manor, the route crosses through Pelham Country Club, entering exit 15, which connects to US 1 (Main Street). After US 1, the route crosses out of the Pelham Country Club, entering New Rochelle.[3]
Crossing over Metro-North Railroad tracks, the interstate turns northeast and crossing through downtown New Rochelle, reaching exit 16, serving several local streets including Cross Avenue, Cedar Street and Garden Street. North of exit 16, the New England Thruway enters its lone toll gantry along the alignment, serving the northbound direction only. The road continues northeast through New Rochelle, passing exit 17 as it enters the town of Mamaroneck. Exit 17 connects to Chatsworth Avenue in the Larchmont section. Passing a pedestrian footbridge for the Larchmont station, crossing over NY 125 (Weaver Street). Winding north through Mamaroneck, I-95 enters exit 18A, servicing Fenimore Road in the village of Mamaroneck.[3]
Turning northeast again, I-95 enters exit 18B, a partial cloverleaf interchange with Mamaroneck Avenue before crossing into the town of Harrison. The road turns east, crossing over NY 127 (Harrison Avenue), and enters exit 19, the western terminus of the Playland Parkway, which connects the expressway to Rye Playland as the road enters Rye. The route crosses through the Rye Village area, entering exit 20, which connects to US 1 (Boston Post Road) and the village. Almost immediately after exit 20, exit 21 marks the eastern end of the Cross-Westchester Expressway (I-287). Proceeding westbound, exit 21 and nearby exit 22 (Midland Avenue and Port Chester) are merged, but are separate exits going eastbound. Crossing through the eastern edges of Port Chester, I-95 reaches the Byram River and crosses into Connecticut, becoming the Connecticut Turnpike.[3]
History
Robert Moses first recommended the construction of what became the New England Thruway in 1940. Construction began in 1951, but major work on the highway did not commence until 1956-1957. By 1950, the New York State Thruway Authority assumed control of the construction and made the New England Thruway a part of the Thruway toll system.[5] Construction lasted until 1961.
I-95 was assigned on August 14, 1957, as part of the establishment of the Interstate Highway System,[2] and has always run along its current path in New York. The route was overlaid on the under-construction New England Thruway northeast of New York City and assigned to the then-proposed Cross Bronx and Bruckner Expressways through New York City.[6] The thruway opened in October 1958, connecting the Bruckner Expressway and the Connecticut Turnpike.[7] The final sections of the Cross Bronx and Bruckner Expressways were finished in 1963 and 1972, respectively. Prior to the 1972 completion of the Bruckner, coinciding with the completion of the new Bruckner Interchange, the old Bruckner Boulevard (once part of NY 164) was used by through traffic.[8][9]
Exit numbers
The first change to exit numbers along the New England Thruway section of Interstate 95 was in April 1980 when the section was converted for sequential exits.[10] Prior to the change, the Cross Bronx Expressway and New England Thruway sections had different exit numbering systems. More specifically, exit 19 on the Cross Bronx Expressway was followed immediately by exit 2 on the New England Thruway. As a result, because exit numbers on I-95 repeated themselves in close succession, the old exit numbering system frequently caused confusion.[11]
As part of an experiment, I-95 was one of the few roads in New York to receive mileage-based exit numbers. This was implemented over both the Port Authority section and the NYSDOT section of the highway (Exits 1A through 8C). The Thruway section (which had originally carried its own sequential exit numbers) was then renumbered by the Thruway Authority to a system of sequential numbers starting from 9 (where the mileage-based system left off). This led to a situation in which Exits 1 through 8 were mileage based (all but one of which contained lettered suffixes as a result) and Exits 9 through 22 were sequential.
Around 2005, NYSDOT began a project to renumber I-95 with sequential numbers throughout. However the idea never fully got traction with all three agencies. The Port Authority did complete the renumbering on its section of the road. NYSDOT itself renumbered only one section of the road in Parkchester. Meanwhile, the Thruway Authority did not renumber any of the exits on its stretch of the road. This led to a situation from 2005 through 2012 in which some exits were signed with two different numbers, while some numbers were repeated twice, but only on some of the signs.
Finally, in 2012, NYSDOT restored the mileage-based numbers to its portion of the highway, which once again line up with the Thruway portion. This has eliminated all of the exit number conflicts, with one exception. The exception exists because the Port Authority has not changed the numbers back on its portion of the road creating a confusing situation at the Amsterdam Avenue exit, which is maintained by NYSDOT southbound but the Port Authority northbound. The exit is signed as Exit 1B southbound (which is the proper number within the mileage-based), but as Exit 2 northbound (a holdover from the failed renumbering project).
Exit list
Exit numbers on the New England Thruway (north of exit 8C) are sequential, but exit numbers on the remaining section are mileage-based.
| County | Location | mi [1][12][13] | km | Old exit | New exit | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hudson River | 0.00 | 0.00 | – | Continuation into New Jersey at the river's center; eastern terminus of US 46 | |||
| 0.00– 0.43 | 0.00– 0.69 | George Washington Bridge (northbound toll plaza in New Jersey) | |||||
| Manhattan | Washington Heights | 0.43 | 0.69 | 1 | 1 | Northern terminus of US 9 concurrency; southbound access via Lower Level lanes; exit 14 on NY 9A / H.H. Parkway; signed as exit 1A southbound | |
| 1.16 | 1.87 | 1B | 2 | Northbound exit and southbound entrance; exit 24 on H.R. Drive | |||
| Harlem River | 1.24– 1.41 | 2.00– 2.27 | Alexander Hamilton Bridge (Route transition between Trans-Manhattan and Cross Bronx Expressways) | ||||
| The Bronx | Morris Heights | 1.41 | 2.27 | 2 | 1B | To Amsterdam Avenue | Southbound exit and northbound entrance; shared ramp with exits 1C–D |
| 3 | 3 1C–D | Signed as exits 1C (north) and 1D (south) southbound; signed as exit 3 northbound[14] | |||||
| 2.08 | 3.35 | 4 | 2A | Jerome Avenue | |||
| Tremont | 2.66 | 4.28 | 5 | 2B | Northern terminus of US 1 concurrency; northbound exit and southbound entrance | ||
| 2.95 | 4.75 | 6 | 3 | Southbound exit and northbound entrance | |||
| West Farms | 3.97 | 6.39 | 7 | 4A | Southbound exit via exit 4B; former I-895 | ||
| Soundview | 4.34 | 6.98 | 8 | 4B | Southbound entrance via exit 4A; exit 4 on Bronx Parkway; serves Bronx Zoo | ||
| Parkchester | 5.05 | 8.13 | 9 | 5A | White Plains Road / Westchester Avenue | ||
| Castle Hill | 5.60 | 9.01 | 10 | 5B | Castle Hill Avenue | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | |
| Throggs Neck | 5.76 | 9.27 | 11 | 6A | Bruckner Interchange; no northbound access to Bruckner Boulevard; northern terminus of I-678 | ||
| 5.81 | 9.35 | 12 | 6B | Bruckner Interchange; southbound exit and northbound entrance; eastern terminus of I-278 | |||
| Route transition between Cross Bronx and Bruckner Expressways | |||||||
| 6.02 | 9.69 | 12 | 6B | Bruckner Interchange; northbound exit and southbound entrance; northern terminus of I-295 | |||
| Schuylerville | 7.40 | 11.91 | 13 | 7A | Southbound exit and northbound entrance; northern terminus of I-695 | ||
| 14 | 7B | East Tremont Avenue | Southbound exit only | ||||
| Country Club | 7.70 | 12.39 | 15 | 7C | Country Club Road – Pelham Bay Park | Northbound exit and entrance | |
| 8.40 | 13.52 | 16 | 8A | Westchester Avenue | Southbound exit and entrance | ||
| Pelham Bay Park | 8.66 | 13.94 | 17 | 8B | Orchard Beach, City Island | Access via Shore Road | |
| 18 | 8C | Eastern terminus of Pelham Parkway | |||||
| Route transition between Bruckner Expressway and New England Thruway | |||||||
| 8.99 | 14.47 | 1 19 | 9 | Exit 4 on Hutchinson Parkway; signed for Palmer northbound, Erskine southbound | |||
| Baychester | 2 | 10 | Gun Hill Road | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | |||
| 9.56 | 15.39 | 3 | 11 | Bartow Avenue / Co-op City Boulevard | |||
| 9.71 | 15.63 | 4 | 12 | Baychester Avenue | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | ||
| Eastchester | 10.82 | 17.41 | 5 | 13 | Conner Street / Baychester Avenue | No northbound signage for Baychester Avenue; to NY 22 | |
| Pelham Bay Park | 11.41 | 18.36 | 6 | 14 | Southbound exit and northbound entrance; exit 6 on Hutchinson Parkway | ||
| Westchester | New Rochelle | 13.04 | 20.99 | 7 | 15 | ||
| 13.97 | 22.48 | – | Division Street | Southbound entrance only | |||
| 14.20 | 22.85 | 8 | 16 | North Avenue / Cedar Street – New Rochelle | Serves New Rochelle station | ||
| 15.60 | 25.11 | 9 | 17 | Chatsworth Avenue – Larchmont | Northbound exit (with toll gantry) and southbound entrance; serves Larchmont station | ||
| New Rochelle Toll Gantry (northbound) | |||||||
| Village of Mamaroneck | 17.57 | 28.28 | 10 | 18A | Fenimore Road – Mamaroneck | Northbound exit only | |
| 18.46 | 29.71 | 18B | Mamaroneck Avenue – Mamaroneck, White Plains | Signed as 18A (east) and 18B (west) southbound; serves Mamaroneck station | |||
| City of Rye | 20.91 | 33.65 | 11 | 19 | Playland Parkway – Rye, Harrison | Western terminus of Playland Parkway | |
| 22.14 | 35.63 | 12 | 20 | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | |||
| 22.54– 22.68 | 36.27– 36.50 | 13 | 21 | Eastern terminus of I-287; no southbound signage for US 1; serves Port Chester station | |||
| 14 | 22 | Midland Avenue – Port Chester, Rye | Northbound exit only | ||||
| Byram River | 23.44 | 37.72 | – | Bridge; continues into Connecticut as the Connecticut Turnpike | |||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||||
Auxiliary routes
Current
- I-295 runs southeast from the Bruckner Interchange along the Cross Bronx Expressway, then south over the Throgs Neck Bridge and Clearview Expressway to its terminus at Hillside Avenue, just south of the Grand Central Parkway.[15] It was once signed as part of I-78[16][17] and was planned to terminate at the John F. Kennedy International Airport.[18][19][16]
- I-495 runs from the Queens–Midtown Tunnel east along the Long Island Expressway to Riverhead, crossing I-295 in Queens.[15] It was once planned to continue west to I-95 in New Jersey; that part is now Lincoln Tunnel and New Jersey Route 495. It was also to go east and meet I-95 again in either Connecticut or in Rhode Island. This would have made I-495 a bypass road for I-95.[20]
- I-695 is a short route along the Throgs Neck Expressway, connecting I-295 to I-95 in the Bronx.[15] It was once signed as part of I-78.[21] The number had been used for other plans, including a route parallel to Woodhaven Boulevard and an upgrade of the West Side Highway and Henry Hudson Parkway.
Former
- I-895, also known as the Sheridan Expressway, was a short connection from I-278 to I-95 in the Bronx.[15] It was planned to continue north from I-95 to rejoin it near Pelham Bay Park, making it another bypass road.[22][23] I-895 was downgraded to NY 895 in 2017,[24] and was converted to a boulevard between 2018 and 2019.
See also
References
- "2014 Traffic Data Report for New York State" (PDF). New York State Department of Transportation. July 22, 2016. p. 79. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- Official route numbering for the National System of Interstate and Defense Highways (Map). American Association of State Highway Officials. August 14, 1957.
- Microsoft; Nokia (September 25, 2013). "overview map of Interstate 95" (Map). Bing Maps. Microsoft. Retrieved September 25, 2013.
- "A Local Law in relation to renaming two thoroughfares and public places in the Borough of the Bronx, East 177th Street, and to amend the official map of the city of New York accordingly.". Act No. 2018-035 of January 11, 2018.
- Bennett, Charles G. (1950-03-19). "CITY SPEEDS HIGHWAY PROGRAMS; Expressways, Arterial Roads Designed to Handle New Traffic Patterns to Result From Two Projected State Thruways". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2017-10-11.
- New York and New Jersey Tourgide Map (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company. Gulf Oil Company. 1960.
- Ingraham, Joseph C. (1958-10-05). "TO CONNECTICUT; New England Thruway to Open Direct Route From Bronx to Rhode Island". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2017-10-11.
- New York and Metropolitan New York (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company. Sinclair Oil Corporation. 1964.
- New York State Highways (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company. State of New York Department of Commerce. 1969.
- "New England Thruway exit numbers to change". Gannett Westchester Newspapers. February 7, 1980. p. D3. Retrieved April 20, 2017.
- "New England Thruway to Get New Exit Numbers; Last Exit to New York". The New York Times. February 17, 1980. Retrieved September 13, 2018.
- "New York County Inventory Listing" (CSV). New York State Department of Transportation. August 7, 2015. Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- "Bronx County Inventory Listing" (CSV). New York State Department of Transportation. August 7, 2015. Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- "Westchester County Inventory Listing" (CSV). New York State Department of Transportation. August 7, 2015. Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- Google (January 24, 2020). "Interstate 95" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved January 24, 2020.
- In Manhattan, I-95 is maintained by the Port Authority of NY-NJ, who signs it as exit 3, whereas in The Bronx, I-95 is maintained by NYCDOT, who signs it as exits 1C-1D.
- New York State Department of Transportation (January 2017). Official Description of Highway Touring Routes, Bicycling Touring Routes, Scenic Byways, & Commemorative/Memorial Designations in New York State (PDF). Retrieved January 15, 2017.
- Zupan, Jeffrey M.; Barone, Richard E.; Lee, Mathew H. (January 2011). "Upgrading to World Class: The Future of the New York Region's Airports" (PDF). Regional Plan Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 24, 2015. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- Cliness, Francis X. (March 25, 1971). "Lower Manhattan Road Killed Under State Plan". The New York Times. p. 78. Retrieved April 14, 2010.
- Fowle, Farnsworth (October 23, 1968). "Van Wyck Roads Are Under Study: Better Use of Service Lanes Sought for Kennedy Traffic". The New York Times. Retrieved March 15, 2017.
- "Expressway Plans". Regional Plan News. Regional Plan Association (73–74): 1–18. May 1964. Retrieved February 27, 2017.
- Expressway Plans. Regional Plan Association. 1964. Retrieved April 19, 2018 – via nycroads.com.
- New York State Highways (Map). Cartography by Rand McNally and Company. State of New York Department of Commerce. 1969.
- "The Sheridan Expressway Study: Reconnecting the Neighborhoods Around the Sheridan Expressway and Improving Access to Hunts Point" (PDF). City of New York. December 2013. p. 3. Retrieved February 19, 2017.
- 30 Years of Progress: 1934-1965 (PDF). New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. June 9, 1964. Retrieved March 31, 2017.
- Special Committee on U.S. Route Numbering (September 24, 2017). "Special Committee on U.S. Route Numbering" (PDF) (Report). Washington, DC: American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 3, 2019. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Interstate 95 in New York (state). |
- Interstate 95 at Alps' Roads • New York Routes
- New England Thruway (I-95)
- Jeff's Expressways Site Photo Gallery
- I-95
- I-95 (Greater New York Roads)
| Previous state: New Jersey |
New York | Next state: Connecticut |
