Hokuto, Yamanashi
Hokuto (北杜市, Hokuto-shi) is a city located in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. As of 31 May 2019, the city had an estimated population of 46,888 in 21,332 households,[1] and a population density of 78 persons per km2. The total area of the city is 602.48 square kilometres (232.62 sq mi).
Hokuto 北杜市 | |
|---|---|
 Keep farm in Kiyosato Plateau | |
Flag Seal | |
 Location of Hokuto in Yamanashi Prefecture | |
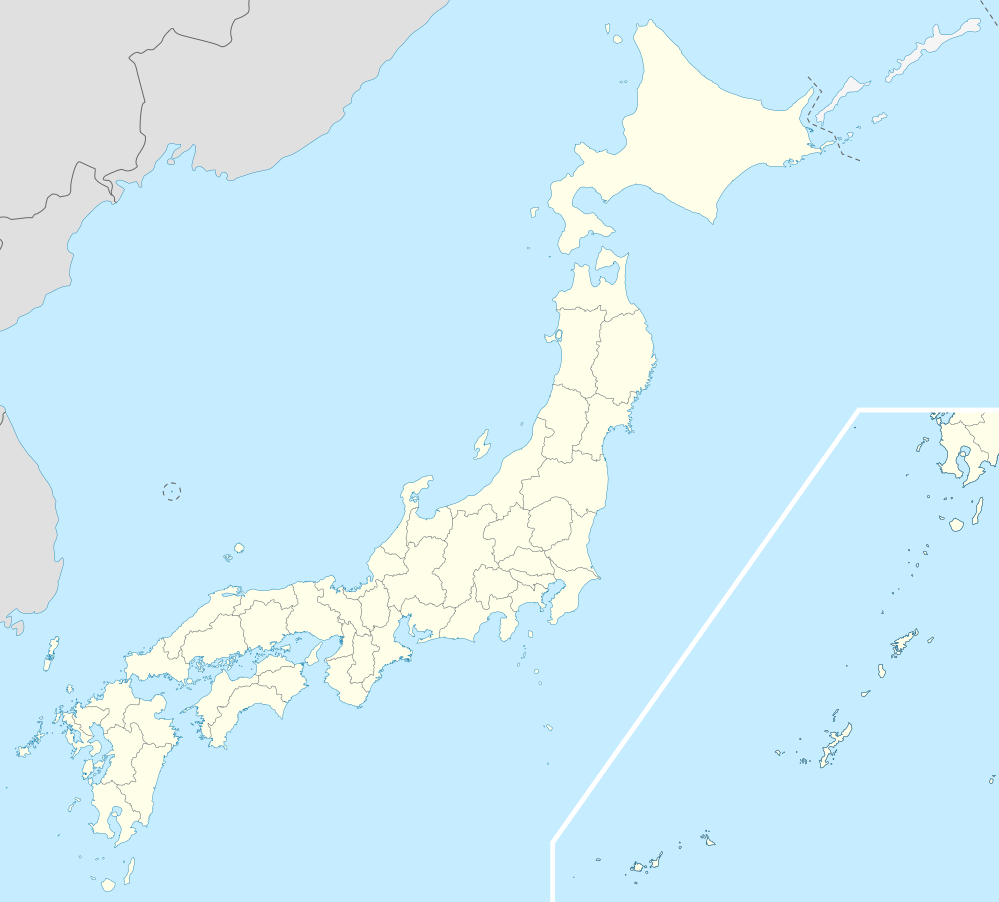 Hokuto | |
| Coordinates: 35°46′35.3″N 138°25′25.1″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūbu (Kōshin'etsu) |
| Prefecture | Yamanashi Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • - Mayor | Masashi Shirakura (since November 2004) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 602.48 km2 (232.62 sq mi) |
| Population (May 1, 2019) | |
| • Total | 46,888 |
| • Density | 78/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| City symbols | |
| • Tree | Japanese red pine |
| • Flower | Sunflower |
| • Bird | Ural owl |
| Phone number | 0551-42-1111 |
| Address | 961-1 Daizu-namada, Sutama-chō, Hokuto-shi, Yamanashi-ken 408-0188 |
| Website | Official website |
Geography
Hokuto is located in far northwest Yamanashi Prefecture. Most of the area of the city is elevated highland and forested, with one third of the city located on the alpine southeastern slopes of Mount Yatsugatake, With a cooler alpine climate in summer, smaller towns such as Kiyosato are a popular location for second homes.
Neighboring municipalities
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[2] the population of Hokuto has remained relatively stable over the past 30 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1940 | 51,131 | — |
| 1950 | 68,254 | +33.5% |
| 1960 | 59,831 | −12.3% |
| 1970 | 47,356 | −20.9% |
| 1980 | 44,320 | −6.4% |
| 1990 | 46,200 | +4.2% |
| 2000 | 47,888 | +3.7% |
| 2010 | 46,872 | −2.1% |
Climate
The city has a climate characterized by characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification Cfa). The average annual temperature in Hokuto is 11.2 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1296 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 23.8 °C, and lowest in January, at around -1.0 °C.[3]
| Climate data for Ōizumi(1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.5 (40.1) |
5.4 (41.7) |
9.3 (48.7) |
15.7 (60.3) |
20.1 (68.2) |
23.0 (73.4) |
26.6 (79.9) |
28.2 (82.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
17.9 (64.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
7.4 (45.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.4 (31.3) |
0.2 (32.4) |
3.7 (38.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
21.6 (70.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
18.7 (65.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
7.3 (45.1) |
2.3 (36.1) |
10.9 (51.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.2 (22.6) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
3.9 (39.0) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.9 (57.0) |
17.8 (64.0) |
18.6 (65.5) |
14.7 (58.5) |
8.2 (46.8) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 39.8 (1.57) |
42.7 (1.68) |
76.6 (3.02) |
80.8 (3.18) |
102.8 (4.05) |
146.4 (5.76) |
153.6 (6.05) |
139.4 (5.49) |
170.0 (6.69) |
113.4 (4.46) |
50.9 (2.00) |
29.6 (1.17) |
1,145.8 (45.11) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency(JMA)[4] | |||||||||||||
History
During the Edo period, all of Kai Province was tenryō territory under direct control of the Tokugawa shogunate. During the cadastral reform of the early Meiji period on April 1, 1889, the rural district of Kitakoma was formed.
The modern city of Hokuto was established on November 1, 2004, from the merger of the towns of Hakushū, Nagasaka, Sutama and Takane, and the villages of Akeno, Mukawa and Ōizumi (all from Kitakoma District). On March 15, 2006, Hokuto absorbed the town of Kobuchisawa (also from Kitakoma District). Kitakoma District was dissolved as a result of this merger.
Government
Hokuto has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 22 members.
Economy
The economy of Hokuto is primarily agricultural, with seasonal tourism, precision manufacturing and food processing playing secondary roles.
Education
- Teikyo-Gakuen Junior College
- Hokuto has eight public elementary schools and nine public middle schools operated by the city government and two public high schools operated by the Yamanashi Prefectural Board of Education.
Transportation
Railway
Sister cities







.svg.png)
Local attractions
- Kiyosato Plateau
- Musée Kiyoharu Shirakaba
- Kinsei ruins, a Jomon-period settlement trace and National Historic Site.
- Umenoki ruins, a Jomon-period settlement trace and National Historic Site.
- Yato Castle, ruins of a Sengoku period castle, and National Historic Site
- Kitashōji Falls, one of Japan's Top 100 Waterfalls
References
- Hokuto City Official statistics(in Japanese)
- Hokuto population statistics
- Hokuto climate data
- "大泉 1981-2010年". JMC. Retrieved January 7, 2012.
- "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
External links
![]()
- Official Website (in Japanese)