History of Seoul
The history of Seoul can be traced back as far as 18 BC, although humans have occupied the area now known as Seoul since Paleolithic Age. It has been the capital of numerous kingdoms on the Korean Peninsula since it was established.
Early history
Prehistoric

It is believed that humans were living in the area that is now Seoul along the lower reaches of the Han River during the Paleolithic Age and archaeological research shows that people began to lead settled lives starting in the Neolithic Age. Prehistoric remains that are unearthed in the Amsa Prehistoric Site (암사선사유적지, Amsa Seonsa Yujeokji), located in Amsa-dong, Gangdong District, date back to about 3,000 to 7,000 years ago. With the introduction of bronze ware from about 700 BC, settlements gradually began to spread from the river basin toward inland areas.
Three Kingdoms and Unified Silla period
In 18 BC, the kingdom of Baekje founded its capital city, Wiryeseong (위례성), which is believed to be inside modern-day Seoul. Baekje subsequently developed from a member state of the Mahan confederacy into one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. There are several city wall remains in the Seoul area dating from this time. Among them, Pungnap Toseong (풍납토성), an earthen wall in the southeastern part of modern-day Seoul, (in Pungnap-dong, just near Jamsil-dong area) is widely believed to be the main Wiryeseong site. Yet another earthen wall, Mongchon Toseong (몽촌토성), located nearby, is also dated from the early Baekje era.
All of these sites are in the south of the Han River, and do not belong to the historic Seoul district (centered in modern-day Jongno District), which is well in the north of the river.
As the Three Kingdoms competed for this strategic region of the Korean Peninsula, control passed from Baekje to Goguryeo in 475 and from Goguryeo to the Silla in 553.
Silla soon gained full control of the city and then the peninsula, and during the Unified Silla period, Hanyang (한양; 漢陽) first referred to a district in the city, and later the city itself.
Goryeo period
It was thought that the kingdom that controlled the Han River valley would also have strategic control of the whole peninsula, because it was a center of transportation.[1]
In 1104, King Sukjong of the Goryeo Dynasty built a palace in Kaesong (개성, 開城), which was then referred to as Namgyeong (남경; 南京) or "Southern Capital". Seoul grew into a full-scale city with political significance during this time.[2]
Joseon period
At the beginning of the Joseon Dynasty in 1394, the capital was moved to Seoul, also known as Hanyang and later as Hanseong (한성, 漢城, "Fortress city [on] the Han [River]"), where it remained until the fall of the dynasty.
Originally entirely surrounded by a massive circular wall (a 20-foot (6.1 m)-high circular stone fortress) to provide its citizens security from wild animals such as the tiger as well as thieves and attacks. The city has grown beyond those walls and although the wall no longer stands (outside of the mountains north of the downtown area), the gates remain near the downtown district of Seoul, including most notably Sungnyemun (commonly known as Namdaemun, or South Gate) and Heunginjimun (commonly known as Dongdaemun, or East Gate) but also Sukjeongmun (commonly known as Bukdaemun, or North Gate) and four smaller gates included Changuimun and Hyehwamun. During the Joseon Dynasty, the gates were opened and closed each day, accompanied by the ringing of large bells. A capital prefecture, Hanseong, consisted of inner districts (i.e. Korean: 사대문안, romanized: Sadaemun-an, lit. 'inside of the city wall') and outer districts (Korean: 성저십리, lit. 'outside of the city wall'; approximately 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) off the city wall). The Jungnangcheon River, the Han River, Mount Bukhan, and Hongjecheon formed the administrative prefectural boundary.
 Gyeonghungak was an attached two-storied building of Daejojeon Hall of Changdeok Palace. The first story was Gyeonghungak. and the second story was Jinggwangru.
Gyeonghungak was an attached two-storied building of Daejojeon Hall of Changdeok Palace. The first story was Gyeonghungak. and the second story was Jinggwangru. The street in front of Gyeongbokgung palace in the late 19th century.
The street in front of Gyeongbokgung palace in the late 19th century. Gwangwha Gate, the main gate of
Gwangwha Gate, the main gate of Seoul in 1894.
Seoul in 1894. Waryong-dong, Seoul in the late Joseon Dynasty.
Waryong-dong, Seoul in the late Joseon Dynasty.- a neighborhood of Seoul in the late Joseon Dynasty.
 A narrow street of 19th-century Seoul.
A narrow street of 19th-century Seoul. A street of 19th-century Seoul.
A street of 19th-century Seoul.- Hanseong Municipal Government.
- Temple of Heaven, a site where Korean Emperors performed the rites to Heaven.
- Seokeodang is a two-storey building of Deoksugung Palace built in the style of a private residence.
 Jibokjae, the Royal Library of Seoul in the late Joseon period.
Jibokjae, the Royal Library of Seoul in the late Joseon period.
Korean Empire period

In the late 19th century, after hundreds of years of isolation, Seoul opened its gates to foreigners and began to modernize. Seoul became the first city in East Asia to have electricity, trolley cars, water, telephone, and telegraph systems all at the same time. Much of this was due to trade with foreign countries like France and United States. For example, the Seoul Electric Company, Seoul Electric Trolley Company, and Seoul Fresh Spring Water Company were all joint Korean-American owned enterprises. In 1904, an American by the name of Angus Hamilton visited the city and said, "The streets of Seoul are magnificent, spacious, clean, admirably made and well-drained. The narrow, dirty lanes have been widened, gutters have been covered, roadways broadened. Seoul is within measurable distance of becoming the highest, most interesting and cleanest city in the East.”
 Streetcar in Seoul during the Korean Empire (1903).
Streetcar in Seoul during the Korean Empire (1903). Gwangtonggwan, the head office building of former Daehan Cheon-il Bank.
Gwangtonggwan, the head office building of former Daehan Cheon-il Bank. Seokjojeon, Imperial palace of Korean Empire.
Seokjojeon, Imperial palace of Korean Empire. Taehan Hospital of Seoul during the Gwangmu Reform.
Taehan Hospital of Seoul during the Gwangmu Reform.
Colonial Korea
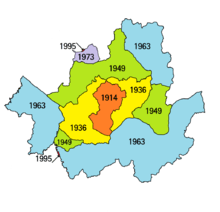
When the Empire of Japan annexed the Korean Empire, it utilized Seoul as the colonial capital. While under colonial rule (1910–1945), the city was called Keijo (京城); (Korean: 경성, romanized: Gyeongseong or Kyongsong, literally meaning "Capital City" in Hanja.).[3] Keijo was an urban city (부/府) that had 2 wards : Keijo itself and Ryusan-ku (龍山區, 용산구, りゅうさんく). Gyeongseong was part of Gyeonggi Province, instead of being an independent city or prefecture as in Joseon and present days. In 1914, several outer districts of the prefecture were annexed to neighboring Goyang County (now Goyang City, reducing the administrative size of the prefecture. In 1936, Gyeongseong expanded itself as it annexed Yeongdeungpo from Siehung County (Now Siehung City) and recombined some parts of former Gyeongseong districts (Sungin, Yeonghee, etc.) from Goyang County. The Government-General Building served as the seat of the colonial government of Colonial Korea but was torn down in 1995.
 Government-General Building, Keijo.
Government-General Building, Keijo.- Keijo Station (currently Seoul Station).
- Keijo City Hall (currently Seoul Metropolitan Library.
- Chosen Commercial Bank Head Office.
- Keijo Nippo Company Building.
Division and Korean War
After World War II and Korea's liberation, the city took its present name of Seoul. When the Republic of Korea (South Korea) was declared, the new state adopted the city as its capital. In 1949, Seoul administrative area expanded to Ui-dong to the north, and Guro-dong and Daerim-dong to the south, recombining some areas which were annexed from original Seoul to Goyang County in 1914.
In 1950, the Korean War broke out and Seoul changed hands between the North Korean forces and South Korean forces four times, leaving the city largely destroyed at the end of the war. One estimate of the extensive damage states that at least 191,000 buildings, 55,000 houses, and 1,000 factories lay in ruins. In addition, there were a flood of refugees from the North, swelling the city's population to an estimated 2.5 million persons. More than half of them were homeless.
The government considered moving its capital city to Yeongdeungpo and Bupyeong, which are south of the Han River.
Following the war, Seoul became the focus of an immense reconstruction and modernization effort. Rapid economic growth achieved during the industrialization of the 1960s and 1970s raised living standards of residents considerably in Seoul.
In 1963, Seoul greatly expanded in size by annexing a number of towns and villages from several surrounding counties in Gyeonggi Province, such as Bucheon, Siheung, Gwangju, Yangju, and Gimpo. However, many newly annexed districts were still rural until Gangnam area began to be developed into urban neighborhoods from the late 1970s. At the same time, Gwacheon Township (today's Gwacheon city) and the northern part of West Township (today's Gwangmyeong city) in Siheung County, parts of Ojeong Township in Bucheon County, and Sindo Township in Goyang County were also annexed to the Seoul Metropolitan Urban Planning Districts (Korean: 서울특별시 도시계획구역), taking these areas as provisional districts for further official municipal annexation to Seoul in the future. In 1973, some parts of Sindo Township in Goyang County (today's Jingwan-dong in the Eunpyeong District) were officially annexed to Seoul. The remaining parts of Sindo Township, Goyang and the northern part of West Township, Siheung (today's Gwangmyeong City) were provisionally planned to be annexed to Seoul, but the municipal annexation plan foundered in the end, in which the symbolic event for this was the establishment of Gwangmyeong City (other than annexation to Guro-gu) in 1981, as the rapid growth of Seoul City was a great concern for governmental officials.
High-rise office buildings and apartments began sprouting throughout the city during the construction boom of the 1980s. Pollution and traffic jams became major issues as urbanization in the country accelerated and more and more people began moving to Seoul and its surrounding areas. Despite a green belt established around the city to prevent urban sprawl, the Seoul metropolitan area soon became the third largest in the world in terms of population and one of the most crowded.
Today, the population of the Seoul area comprises 20% of the total population of South Korea.
Seoul was the host city of the 1988 Summer Olympics as well as one of the venues of the 2002 FIFA World Cup.
During the 1990s, the city began to attract many workers from other countries, changing demographics. Previously, nearly all of Seoul's residents were Korean. Today, there are an estimated 200,000 foreign nationals living in Seoul. These include tens of thousands of English teachers from the United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and other English-speaking countries as well as laborers from Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Mongolia, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines, Uzbekistan, and Vietnam.
In 1995, the boundary between Seoul and Gwangmyeong rearrangement was implemented, merging parts of Cheolsan 3-dong, Gwangmyeong in the Geumcheon District of Seoul. Around the time of the 1995 municipal annexation in South Korea, the government once seriously considered a division of Seoul into several municipal or metropolitan cities, but the division plan foundered as it would be expected to cause serious problems in aspects of metropolitan governance in Seoul.
In addition, there are many language instructors from English-speaking countries such as Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, United States, and the UK, as a major business and financial center, Seoul also has many executives and analysts from North America, Europe, and Japan. Seoul ranks seventh in the world in terms of the number of Fortune 500 transnational companies headquartered there.[4] It is also the world's second most expensive city, ahead of Tokyo and Hong Kong (ranked 3rd and 4th, respectively).[5]
Failed relocation of the capital
On 11 August 2004, the South Korean government announced they would relocate the capital city from Seoul to the Gongju area as of 2007, to ease the population pressure on Seoul and to get the government to a safer distance from North Korea in case of a Northern military invasion.[6] Gongju is approximately 120 km (75 mi) south of Seoul. The Government estimated that the move would probably not be completed before 2012.[6] Although part of the election manifesto, this plan ignited nationwide controversy. On 21 October 2004, the Constitutional Court of Korea ruled that mostly based on custom law, the special law for the relocation of the capital is unconstitutional since the relocation is a serious national matter requiring national referendum or revision of the constitution, thus effectively ending the dispute.
In late 2004, however, the South Korean government announced plans to move most of the national government branches, except the Executive Branch, to Gongju, thus evading violation of the Constitutional Court ruling and still allow Seoul to be a National Capital. Since this plan was supported by the late president Roh Moo-hyun and bitterly opposed by the current ruling party and the former president (Lee Myung-bak – the former mayor of Seoul) the planned move was scaled back dramatically when Lee Myung-bak took office. As of 2011, some preliminary work has begun on construction of new government buildings in the Gongju area. No government agencies want to move away from the center of power in Seoul, so which agencies will be forced to move is the subject of intense behind-the-scenes debate.
Sejong City was founded in 2007 as part of efforts to relocate the national capital. It was created from territory of South Chungcheong and North Chungcheong provinces to ease congestion in Seoul and encourage investment in the country's central region. Since 2012, the Government of South Korea has relocated numerous ministries and agencies to Sejong, but many still reside in other cities - namely Seoul where the National Assembly, the Blue House and many important government bodies remain.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to History of Seoul. |
- History of Korea
- Names of Seoul
- Timeline of Seoul history
References
- "Han River Park (Gangdong-gu)". Life in Korea. Retrieved 16 January 2008.
- "Central Government Complex". Government Buildings Management Service, Republic of Korea. Archived from the original on 14 May 2008. Retrieved 16 January 2008.
- Yu, Woo-Ik; Lee, Chan (4 November 2019). "Seoul". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- Richard Child Hill and June Woo Kim. GLOBAL CITIES & DEVELOPMENTAL STATES. Retrieved 27 June 2006.
- Jeanne Sahadi. World's most expensive cities. 2006. Retrieved 27 June 2006.
- S Korea chooses new capital site – BBC News
