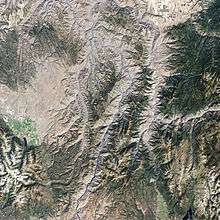
Hells Canyon National Recreation Area
Hells Canyon National Recreation Area is a United States National Recreation Area located on the borders of the U.S. states of Oregon and Idaho. The recreation area, which is managed by the United States Forest Service as part of the Wallowa-Whitman National Forest, was established by U.S. Congress and signed by President Gerald Ford in 1975 to protect the historic and archaeological values of the Hells Canyon area and the area of the Snake River between Hells Canyon Dam and the Oregon-Washington border.[3][5][6]
| Hells Canyon National Recreation Area | |
|---|---|
Hells Canyon | |
 | |
| Location | Oregon & Idaho, United States |
| Nearest city | Grangeville, Idaho |
| Coordinates | 45.6°N 116.5°W[1] |
| Area | 652,488 acres (2,640.53 km2) |
| Established | December 31, 1975 [3][4][5] |
| Governing body | United States Forest Service |
| Website | Hells Canyon NRA |
Roughly 215,000 acres (900 km2) of the recreation area are designated the Hells Canyon Wilderness. There are nearly 900 miles (1,400 km) of hiking trails in the recreation area. The largest portion of the area lies in eastern Wallowa County, Oregon. Smaller portions lie in southwestern Idaho County, Idaho, northwestern Adams County, Idaho, and northeastern Baker County, Oregon.
Hells Canyon Archeological District
Hells Canyon Archeological District | |
| Area | 12,000 acres (4,900 ha) |
|---|---|
| NRHP reference No. | 84000984[7] |
| Added to NRHP | August 10, 1984 |
All or partly included in the HCNRA is the Hells Canyon Archeological District, a 12,000-acre (4,900 ha) historic district that is listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. The district includes 536 contributing sites, 23 contributing buildings, and 58 other contributing structures.[7]
Snake River National Recreation Trail
The Snake River National Recreation Trail #102[8](SRNRT) lies within the Hells Canyon National Recreation Area and along the Idaho side of the Snake River, from near Lamont Springs, downstream, to Pittsburg Landing. The SRNRT was designated in 1980 under the National Trails System Act. It was constructed during the period of the late 1800s to about the 1930s. Access to the SRNRT can be gained via road to the trailhead[9] at Pittsburg Landing on the north end of the trail, or, by boat access near Hells Canyon Dam on the south end of the trail. Access can also be gained via trails leading from Seven Devils Wilderness Area trail head at Windy Saddle (elevation 7200') via either the Granite Creek trails or Sheep Creek trails.
References
- Ewert, Sara E. Dant. "Evolution of an Environmentalist: Senator Frank Church and the Hells Canyon Controversy." Montana: The Magazine of Western History 51 (Spring 2001): 36–51.
- "Hells Canyon National Recreation Area". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
- "Hells Canyon National Recreation Area". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
- "Ford signs NRA bill". Lewiston Morning Tribune. (Idaho). Associated Press. January 2, 1976. p. 16A.
- "Ford signs canyon bill". Spokesman-Review. (Spokane, Washington). Associated Press. January 2, 1976. p. 1.
- Husk, Lee Lewis (July 16, 2018). "Hells Canyon Fifty-Year Anniversary". 1859: Oregon's magazine. Retrieved March 21, 2019.
- "Establishment of HCNRA". U.S. Forest Service. Archived from the original on 2010-12-03. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
- "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- https://www.fs.usda.gov/recarea/wallowa-whitman/recarea/?recid=51661
- https://www.fs.usda.gov/recarea/wallowa-whitman/recreation/recarea/?recid=51665