Hedmark
Hedmark ([ˈhêːdmɑrk] (![]()
Hedmark fylke | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
 Hedmark within Norway | |
| Country | Norway |
| County | Hedmark |
| Region | Østlandet |
| County ID | NO-04 |
| Administrative centre | Hamar |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Sigbjørn Johnsen Arbeiderpartiet (1997-2009–present) |
| • County mayor | Arnfinn Nergård Senterpartiet (2007–present) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 27,397 km2 (10,578 sq mi) |
| • Land | 26,084 km2 (10,071 sq mi) |
| Area rank | #4 in Norway, 8.57% of Norway's land area |
| Population (30 September 2019) | |
| • Total | 197,831 |
| • Rank | 11 (3.72% of country) |
| • Density | 7.5/km2 (19/sq mi) |
| • Change (10 years) | |
| Demonym(s) | Hedmarking |
| Time zone | UTC+01 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02 (CEST) |
| Official language form | Neutral |
| Income (per capita) | 132,200 NOK |
| GDP (per capita) | 204,205 NOK (2001) |
| GDP national rank | 11 (2.52% of country) |
| Website | www |
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 173,167 | — |
| 1961 | 177,324 | +2.4% |
| 1971 | 179,204 | +1.1% |
| 1981 | 187,223 | +4.5% |
| 1991 | 187,314 | +0.0% |
| 2001 | 187,999 | +0.4% |
| 2011 | 191,622 | +1.9% |
| 2021? | 204,065 | +6.5% |
| 2031? | 216,105 | +5.9% |
| Source: Statistics Norway.[1] | ||
Hedmark and Oppland counties were merged into Innlandet county on 1 January 2020, when Norway's former 19 counties became 10 bigger counties / regions
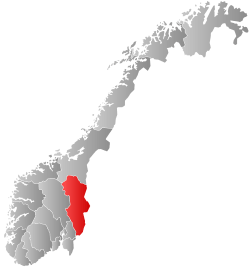
Hedmark made up the northeastern part of Østlandet, the southeastern part of the country. It had a long border with Sweden to the east (Dalarna County and Värmland County). The largest lakes were Femunden and Mjøsa, the largest lake in Norway. Parts of Glomma, Norway's longest river, flowed through Hedmark. Geographically,
Hedmark was traditionally divided into: Hedemarken (east of the lake Mjøsa), Østerdalen ("East Valley" north of the town Elverum), and Solør / Glåmdalen (south of Elverum) and Odal in the very south. Hedmark and Oppland were the only Norwegian counties with no coastline. Hedmark also hosted some events of the 1994 Winter Olympic Games.
Hamar, Kongsvinger, Elverum and Tynset were cities in the county. Hedmark was one of the less urbanized areas in Norway; about half of the inhabitants lived on rural land. The population was mainly concentrated in the rich agricultural district adjoining Mjøsa to the southeast. The county's extensive forests supplied much of Norway's timber; at one time, logs were floated down Glomma to the coast but are now transported by truck and train.
The Hedmark municipality of Engerdal had the distinction of marking the current southernmost border in Norway of Sápmi, the traditional region of the Sami people.
The county was divided into three traditional districts. Those were Hedmarken, Østerdalen and Solør (with Odalen and Vinger).
Hedmark was originally a part of the large Akershus amt, but in 1757 Oplandenes amt was separated from it. Some years later, in 1781, this was divided into Kristians amt (now Oppland) and Hedemarkens amt. Until 1919, the county was called Hedemarkens amt.
Etymology
The Old Norse form of the name was Heiðmǫrk. The first element is heiðnir, the name of an old Germanic tribe and is related to the word heið, which means moorland. The last element is mǫrk 'woodland, borderland, march'. (See also Telemark and Finnmark.)[5]
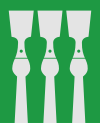
Coat of arms
The coat of arms is from modern times (1987). It shows three barkespader (adzes used to remove bark from timber logs).
Politics
Every four years the inhabitants of Hedmark elect 33 representatives to Hedmark Fylkesting, the Hedmark County Assembly. After the elections of September 2007 the majority of the seats of the assembly were held by a three-party coalition consisting of the Labour Party (14 seats), the Centre Party (5 seats) and the Socialist Left Party (2 seats). Eight parties are represented in the assembly, the remaining 5 being the Progress Party (4 seats), the Conservative Party (4), the Liberal Party (2), the Christian Democratic Party (1) and the Pensioners Party (1). The assembly is headed by the county mayor (Norwegian: Fylkesordfører). As of the 2007 elections the county mayor is Arnfinn Nergård. He represents the Centre Party. In 2003 a parliamentary system was established, which means that the county assembly elects a political administration or council to hold executive power. This county council reflects the majority of the county assembly and includes the three parties holding the majority of the assembly seats, i.e., the Labour Party, the Center Party and the Socialist Left Party. The council is led by Siv Tørudbakken, a member of the Labour Party.
Municipalities

| Rank | Name | Inhabitants | Area km² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34,151 | 1,125 | |
| 2 | 30,930 | 339 | |
| 3 | 21,123 | 1,221 | |
| 4 | 20,646 | 642 | |
| 5 | 17,934 | 965 | |
| 6 | 7,884 | 487 | |
| 7 | 7,615 | 363 | |
| 8 | 7,279 | 1,015 | |
| 9 | 6,567 | 2,957 | |
| 10 | 6,142 | 604 | |
| 11 | 5,605 | 1,831 | |
| 12 | 5,097 | 476 | |
| 13 | 4,740 | 787 | |
| 14 | 4,480 | 1,306 | |
| 15 | 3,680 | 685 | |
| 16 | 2,490 | 2,144 | |
| 17 | 2,424 | 927 | |
| 18 | 1,936 | 1,013 | |
| 19 | 1,827 | 3,073 | |
| 20 | 1,569 | 1,266 | |
| 21 | 1,553 | 1,101 | |
| 22 | 1,294 | 1,921 | |
| Total | 196,966 | 27,388 |
| Number of minorities (1st and 2nd gen.) in Hedmark by country of origin in 2017[6] | |
| Nationality | Population (2017) |
|---|---|
| 2,204 | |
| 1,421 | |
| 1,125 | |
| 1,119 | |
| 948 | |
| 746 | |
| 721 | |
| 694 | |
| 620 | |
| 608 | |
| 605 | |
| 572 | |
| 539 | |
| 503 | |
| 418 | |
| 418 | |
| 416 | |
| 369 | |
Districts
Cities
Parishes
- Alvdal
- Austmarka (Østmark)
- Brandval
- Brøttum
- Deset
- Drevsjø (Drevsjøhytte)
- Eidskog
- Elverum
- Engerdal
- Finnskog
- Folldal
- Furnes
- Gjesås
- Grue
- Hamar
- Helgøy Kapell
- Hof
- Innset
- Kongsvinger
- Kvikne
- Lundersæter
- Løten
- Mo
- Nes
- Nord-Odal
- Nordre-Osen
- Opstad
- Os (Dalsbygda)
- Ottestad
- Rendal
- Rendalen
- Revholt
- Ringsaker
- Romedal
- Sand
- Sollia
- Stange
- Stavsjø (Ballishol)
- Stor Elvdal
- Strand
- Strøm
- Sør-Odal
- Sør Osen
- Tangen
- Tolga
- Trysil
- Tylldal
- Tynset
- Ulleren
- Vallset (Tomter)
- Vang
- Veldre
- Vestmarka
- Vingelen
- Vinger
- Våler
- Ytre Rendal
- Øvre Engerdal
- Øvre Rendal
- Åmot
- Åsnes
- Odalen Branch (LDS, 1857-1873)
- Trysil Frimenighet, (1859-1891)
Villages
- Atna
- Bergesida
- Bergset
- Braskereidfoss
- Brumunddal
- Disenå
- Drevsjø
- Espa
- Flisa
- Furnes
- Fådalen
- Fåset
- Galterud
- Grinder
- Hanestad
- Hekne
- Heimdal
- Heradsbygd
- Hjellum
- Hodalen
- Ilseng
- Ingeberg
- Innbygda
- Kirkenær
- Kjellmyra
- Knapper
- Koppang
- Kvål
- Kylstad
- Lundersæter
- Magnor
- Matrand
- Mesnali
- Mo (Gardvik)
- Moelv
- Namnå
- Nybergsund
- Os i Østerdalen
- Otnes
- Ottestad
- Plassmoen
- Rena
- Ridabu
- Risberget
- Rotberget
- Roverud
- Rudshøgda
- Sand (Sagstua)
- Sander
- Sandvika
- Sinnerud
- Sjølisand
- Skarnes
- Skasenden
- Skotterud
- Slettmoen
- Sorken
- Starhellinga
- Svullrya
- Tangen
- Telneset
- Tylldalen
- Tørberget
- Unset
- Vangsås/Slemsrud
- Våler
- Østby
- Øversjødalen
- Åbogen
- Ådalsbruk
- Åkre
- Åkrestrømmen
- Åsta
Former Municipalities
References
- Projected population - Statistics Norway
- Statistics Norway - Church of Norway.
- Statistics Norway - Members of religious and life stance communities outside the Church of Norway, by religion/life stance. County. 2006-2010 Archived 2011-11-02 at the Wayback Machine
- moderniseringsdepartementet, Kommunal- og (7 July 2017). "Regionreform". Regjeringen.no. Archived from the original on 23 March 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
- Henriksen, Petter, ed. (2007). "Hedmark". Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Oslo: Kunnskapsforlaget. Retrieved 6 July 2015.
- "Immigrants and Norwegian-born to immigrant parents, by immigration category, country background and percentages of the population". ssb.no. Archived from the original on 2 July 2015. Retrieved 26 June 2017.
External links
- Official homepage


