Hatchback
A hatchback is a car with a hatch-type rear door that often opens upwards[1][2][3][4][5] and often a shared volume for the passenger and cargo areas.
When the body style of a car is described as a hatchback, typically it refers to a utilitarian small car (especially in the U.S.); however hatchbacks are also used on sports cars, SUVs, and large luxury cars. Compact hatchbacks are very popular, and midsize liftbacks (a type of hatchbacks) relatively popular, in Europe. Hatchbacks are also popular throughout Asia and North America, and is the most common body type for city cars and economy cars sold in Asia.
The modern form of the hatchback body style was developed through the 1960s and rose in popularity through the 1970s.
Characteristics
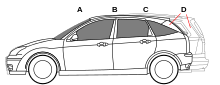
The distinguishing feature of a hatchback is a hatch-type rear door that opens upwards[6] and is hinged at roof level (as opposed to the boot/trunk lid of a saloon/sedan, which is hinged below the rear window). Most hatchbacks use a two-box design body style,[7][8] where the cargo area (trunk/boot) and passenger areas are a single volume. The rear seats can often be folded down to increase the available cargo area.[9] Hatchbacks may have a removable rigid parcel shelf,[10] or flexible roll-up tonneau cover to cover the cargo space behind the rear seats.
When describing the body style, the hatch is often counted as a door, therefore a hatchback with two passenger doors is called a three-door and a hatchback with four passenger doors is called a five-door.
Estates/station wagons and hatchbacks have in common a two-box design configuration, a shared interior volume for passengers and cargo[6][11] and a rear door (often called a tailgate in the case of an estate/wagon) that is hinged at roof level.[12][13] An estate/wagon typically differs from a hatchback by being longer (therefore more likely to have a D-pillar). Other potential differences of a station wagon include:
- steeper rake at the rear (ie the rear door is more vertical)[6][10][14]
- a third row of seats
- rear suspension designed for increased load capacity or to minimize intrusion into the cargo area[10]
- the tailgate is more likely to be a multi-part design or extend all the way down to the bumper
Liftback
_SX_liftback_(2016-01-04)_02.jpg)
Liftback is a term for hatchback models in which the rear cargo door or hatch is more horizontally angled than on an average hatchback, and as a result, the hatch is lifted more upwards than backwards, to open.[11]
The term was used officially, among others, by Toyota, for example to distinguish between two 5-door versions of the Corolla E90 sold in Europe, one of which was a conventional 5-door hatchback with a nearly vertical rear hatch while the other one was a 5-door liftback.



The term "fastback" is sometimes used interchangeably with "liftback", but in a fastback the rear of the car should have a single slope from the roof to the rear bumper;[15][16][17] in a liftback, not necessarily so.
In Europe, the term "liftback" often implies a three-box design with a profile similar to a sedan, although the length of the third box (the rear one) varies. It may be nonexistent (Nissan Primera P12), very short or vestigial (1985 Toyota Celica liftback) or long enough for the vehicle to be confused with a conventional sedan body style which may be offered alongside it (Mazda 6 GG1, Opel Vectra C, many others). While today many such cars feature smooth, curved lines making it difficult to tell where one "box" ends and another one starts, the same applies to sedans, which makes the two body styles even more difficult to tell apart at first glance.
Liftbacks were the mainstay of manufacturers' D-segment offerings in Europe in the 1990s (they were already popular in the 1980s) and until the late 2000s. It was common for manufacturers to offer the same D-segment model in three different body styles: a 4-door sedan, a 5-door liftback and a 5-door station wagon. Such models included the Ford Mondeo, the Mazda 626/Mazda6, the Nissan Primera, the Opel Vectra/Insignia and the Toyota Carina/Avensis. There were also models in this market segment available only as a 5-door liftback or a 4-door sedan, and models available only as a 5-door liftback or a 5-door station wagon. Often the liftback and the sedan shared the same wheelbase and the same overall length, and the full rear overhang length of a conventional sedan trunk was retained on the five-door liftback version of the car.
Audi, BMW and Mercedes were not part of this trend in the 1990s; they did not offer their D-segment and executive cars as 5-door liftbacks back then. However, starting around the year 2009, Audi and BMW started to roll out such liftbacks, referring to them as "Sportback" (Audi) or "Gran Turismo"/"Gran Coupe" (BMW). Interestingly, this occurred not long after some other manufacturers, although certainly not all of them, started to drop D-segment liftbacks from their European lineup.
The second-generation Skoda Superb (2008-2015) is a car that blurs the line between liftbacks and sedans. It features an innovative "Twindoor" trunk lid. It can be opened like in a sedan, using the hinges located below the rear glass; or together with the rear glass, like in a liftback, using the hinges at the roof.[18]
In the USA, 5-door liftbacks are much less popular but growing in popularity. Although the Tesla Model S is a liftback, the manufacturer prefers to refer to it as a sedan.
History
Prior art and small volume models
The first production hatchback was released by Citroën in 1938: the Citroën 11CV Commerciale.[19] The tailgate has two pieces, a top section hinged from roof level and a bottom section hinged from below.[20] When production of the Commerciale resumed after World War II, the tailgate became a one-piece design which was hinged from roof level, as per the design used on most hatchbacks since.[21]
In 1949, Kaiser-Frazer introduced the Vagabond and Traveler hatchbacks. These models were styled much like a typical 1940s sedan, fully retaining their three-box profile; however, they included a two-piece tailgate as per the first Citroen 11CV Commerciale.[22] The Vagabond and Traveler models also had folding rear seats, and a shared volume for the passengers and cargo.[23] The design was neither fully a sedan nor a station wagon, but the folding rear seat provided for a large, 8-foot (2.4 m) long interior cargo area.[24] These Kaiser-Frazer models have been described as "America’s First Hatchback".[25]
In 1953, Aston Martin marketed the DB2 with a top-hinged rear tailgate, manufacturing 700 examples. Its successor, the 1958 DB Mark III, also offered a folding rear seat. The 1954 AC Aceca and later Aceca-Bristol from AC Cars had a similar hatch tailgate, though only 320 were built.

.jpg)
Beginning of mass-production
The British Motor Corporation (BMC) launched a 'Countryman' version of the Austin A40 Farina two‑box economy car in 1959. Just like its A30 and A35 Countryman predecessors, it was a very small estate car — but instead of regular, sideways opening rear doors, it had a horizontally split tailgate, having a top-hinged upper door and bottom-hinged lower door. The 1959 A40 Countryman differed from the 1958 A40 Farina saloon, in that the rear window was marginally smaller, to allow for a frame that could be lifted up, with its own support, so that the car now incorporated a horizontal-split two-piece tailgate. The lower panel was now flush with the floor and its hinges had been strengthened.[26]
In 1961, Renault introduced the Renault 4.[27][28] The Renault 4 was the first million-selling, mass-produced, compact two-box car with a steeply raked rear side, opened by a large, one-piece, lift-gate hatch.
During its production life cycle, Renault marketed the R4 calling it a small station wagon, just like Austin's series of small Countryman estate models from 1954 to 1968 – even after the term "hatchback" appeared around 1970. Although the company did not offer a saloon or single other alternative body style, the Renault 4 continued in production in Europe until 1986, and in Argentina through 1992, selling over 8 million cars.
In 1965, the R4 economy car was complemented by the D-segment Renault 16, the first volume production two-box, hatchback family car.[29] Its rear seats were adjustable, would fold down, or could be completely removed. The Renault 16 was successful in a market segment previously exclusively populated by notchback sedans, and in spite of making only the one body style for 15 years, selling over 13⁄4 million cars.
In 1965, MG had PininFarina modify the MGB roadster into a hatchback design called the MGB GT, becoming the first volume-production sports car with this type of body.
In 1967, Citroën released the Dyane, a redesigned 2CV with a large rear hatch, to compete with the Renault 4.

.jpg)
Modern hatchbacks
Unlike the Renault 4, which had a semi-integrated body, mounted on a platform chassis, and a front mid-mounted and longitudinally placed engine behind the front axle, the 1967 Simca 1100, which followed in the footsteps of the 1959 BMC Mini with front-wheel drive, a more space efficient transverse engine layout, unitary bodywork and independent suspension (features which became key design concepts used by almost every mass-market family car since) - and it was the first hatchback with these features.[30] The Simca 1100 also came in both three and five door variants, and the hatchback models took a central position, traditionally taken up by saloons, in a full model line-up, completed by a station wagon, as well as panel van versions.
The Simca was closely followed by the Mini's larger stablemate, the Austin Maxi, which with the hatch was a five-door saloon, and with a transverse SOHC engine, a five-speed transmission, and a flexible seating arrangement which gave the option of forming a double bed.[31] Created by the same designer as BMC's Mini, sir Alec Issigonis – accountants had determined that the car had to use the same set of doors as the Austin / Morris 1800, but would be marketed below it in the model range, so needed a shorter rear body. A curtailed rear end with a big hatch resulted.[29] The Austin Maxi operated in the same market segment as the Renault 16, and the two competitors were closely matched in specifications and exterior dimensions, although the Maxi had significantly more interior space due to its transverse engine.[29]

Europe

Increasing demand for compact hatchbacks in Europe during the 1970s led to the release of models such as the Austin Ambassador, Austin Maestro, Fiat 127 and Renault 5. By the late 1970s and early 1980s, the majority of superminins and compact cars had been updated or replaced with hatchback models.
In 1974, the Volkswagen Golf was introduced, intended to replace the ubiquitous Beetle.[32]
In 1976 British Leyland introduced the Rover 3500, a executive five-door hatchback.[31]
In the 2010s hatchback versions became available on luxury cars such as the BMW 5 Series Gran Turismo, Porsche Panamera and Audi A7 while the Skoda Octavia was always available as a liftback. Meanwhile, three-door hatchbacks have seen a fall in popularity, compared with 5-door models. This has led to many models no longer being offered in 3-door body styles, for example the Audi A3 and Renault Clio. The same trend is very strongly seen on SUVs, where demand for 4-/5-door models is far stronger than for traditional 2-/3-door models.
North America
In 1970, American Motors Corporation (AMC) released the first North American subcompact car since the 1953-1961 Nash Metropolitan, the AMC Gremlin.[33] Although the Gremlin has the appearance of a hatchback, it is technically a Kammback coupe instead,[34] since it is only the rear window that opens.[35] The Gremlin was based on the AMC Hornet, but its abrupt hatchback rear end cut the car's overall length from 179 to 161 inches (4,500 to 4,100 mm). AMC added a hatchback version to its larger compact-sized Hornet line for the 1973 model year.[36] The design and fold-down rear seat more than doubled cargo space and the Hornet was claimed to be the "first compact hatchback" manufactured by U.S. automaker.[37] The 1975 Pacer featured a rear door or hatchback.[38] A longer model with a wagon-type configuration was added in 1977 with its large rear "hatch" as one of the car's three doors, all having different sizes.[39] The 1979 AMC Spirit was available in two designs, a "sedan" with a rear lift up window and a semi-fastback "liftback" version.[40]
General Motors' first hatchback model was the Chevrolet Vega, introduced in September 1970. Over a million Vega hatchbacks were produced for the 1971–1977 model years accounting for about half of the Vega's total production.[41] The Vega hatchback was also rebadged and sold as the 1973–1977 Pontiac Astre, 1978 Chevrolet Monza S, 1795–1980 Buick Skyhawk, 1975–1980 Oldsmobile Starfire and 1977–1980 Pontiac Sunbird.
In 1974, the larger Chevrolet Nova became available in a hatchback body style. The Nova hatchback was also rebadged as the Chevrolet Concours, Pontiac Ventura, Pontiac Phoenix, Oldsmobile Omega, Buick Apollo and Buick Skylark. In 1980, General Motors released its first front-wheel drive hatchback models, the Chevrolet Citation and Pontiac Phoenix.
Ford Motor Company's first hatchback was the Ford Pinto Runabout, introduced in 1971.[42] The Pino-based 1974-1978 Ford Mustang II was offered as a hatchback. The body style was continued for the redesigned Fox platform-based 1979 third generation Mustang and the Mercury Capri derivative. For 1981, Ford offered hatchback versions of its sub-compact Escort and the badge engineered Mercury Lynx, which were now front-wheel drive. Two-seat hatchback derivatives were introduced for 1982, the Ford EXP and the Mercury LN-7.
Chrysler Corporation's first hatchbacks (and first front-wheel drive cars) were the 1978 Dodge Omni / Plymouth Horizon models, which were based on the French Simca-Talbot Horizon.[43] These were followed by the 3-door hatchback Dodge Omni 024 / Plymouth Horizon TC3 which were later renamed Dodge Charger and Plymouth Turismo.
Japan

The first Japanese hatchbacks were the 1972 Honda Civic, Nissan Sunny and Nissan Cherry. The Civic and Cherry had front-wheel drive powertrains, which later became the common configuration for a hatchback. Along with the Honda Civic, other Japanese hatchback models included the Nissan Pulsar, Toyota Corolla, and Suzuki Swift.
Almost all Japanese Kei cars ("city cars") use a hatchback bodystyle, to maximise cargo capacity given the overall vehicle size is limited by Kei car regulations. Kei cars include the Mitsubishi Minica, Honda Life, Suzuki Fronte, Subaru Vivio, and Daihatsu Mira.
USSR
.jpg)
The first Soviet hatchback was the rear-wheel drive IZh 2125 Kombi, which entered production in 1973.[44] This was followed only in the 1980s by the front-wheel drive Lada Samara in 1984, the Moskvitch 2141/Aleko in 1986, and ZAZ Tavria in 1987.
Brazil
In 2014, four of the top five selling models in Brazil were hatchbacks.[45] However in the 1980s and 1990s, hatchbacks were less popular than sedans, leading manufacturers to develop compact sedan models for the Brazilian market, for example the Fiat Premio and sedan versions of the Opel Corsa and Ford Fiesta.
India

Hatchbacks are the highest selling car body style in India.[46] The Maruti 800 sold over 2.5 million units since its launch in 1983.[47] Since 2004, Maruti 800 has been overtaken by Maruti Alto as the car with highest annual sales. In 2015, Tata Motors launched a hatchback version of the Nano, the least expensive road car in the world.[48]
See also
- Trunk (car)
- Hot hatch
- List of car body styles
- Shooting brake
References
- "hatchback - definition by the Free Online Dictionary, Thesaurus and Encyclopedia". Thefreedictionary.com. n.d. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- "Hatchback - Definition from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary". Merriam-webster.com. 31 August 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- "Hatchback definition at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.reference.com. n.d. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- "hatchback - Definition from Longman English Dictionary Online". Ldoceonline.com. n.d. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- "hatchback: definition of hatchback in Oxford dictionary (British & World English)". Oxforddictionaries.com. n.d. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- Erjavec, Jack (2005). Automotive Technology: A Systems Approach Volume 2. Thomposon Delmar Learning. p. 55. ISBN 978-1-4018-4831-6. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
Liftback or Hatchback: The distinguishing feature of this vehicle is its luggage compartment, which is an extension of the passenger compartment. Access to the luggage compartment is gained through an upward opening hatch-type door. A car of this design can be a three or five door model, the third or fifth door is the rear hatch. Station Wagon: A station wagon is characterized by its roof which extends straight back, allowing a spacious interior luggage compartment in the rear. The rear door, which can be opened numerous ways depending on the model, provides access to the luggage compartment. Station wagons come in two and four-door models and have space for up to nine passengers.
- "2018 Hyundai Elantra GT - Driven". www.topspeed.com. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- "Hatchback vs Wagon: What's the Difference Here?". www.wheelscene.com. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- "Hatchback buying info". www.edmunds.com. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- Hillier, Victor; Coombes, Peter (2004). Hillier's Fundamentals of Motor Vehicle Technology Volume 1 (Fifth ed.). Nelson Thornes. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-7487-8082-2. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
The estate body, also known as station wagons in some countries, has the roofline extended to the rear of the body to enlarge its internal capacity. Folding the rear seats down gives a large floor area for the carriage of luggage or goods. Stronger suspension springs are fitted at the rear to support the extra load. Hatchback: The hatchback is generally based on a saloon body but with the boot or trunk area blended into the centre section of the body. The hatchback is therefore halfway between a saloon and estate car. This type of body is very popular due to its versatility and style. Although some hatchbacks are in fact saloon bodies with the boot or trunk effectively removed (usually the smaller cars), many hatchbacks retain the full length of the saloon but the roofline extends down to the rear of the vehicle. As with the saloon bodies, a hatchback can have two or four passenger doors, however there is a tendency to refer to hatchbacks as three or five doors because the rear compartment lid (or tailgate) is also referred to as a door on the hatchback bodies. As with the estate, the rear seats fold down to give a flat floor for the transportation of luggage or other objects. When the tailgate is closed, the luggage compartment is usually covered with a parcel shelf.
- Jaza, Reza N. (2008). Vehicle dynamics: theory and applications. Springer-Verlag. pp. 30–31. ISBN 978-0-387-74243-4. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
A hatchback car is called a liftback when the opening area is very sloped and is lifted up to open.
- "Car Design Glossary – Part 2: One-Box (Monospace or Monovolume)". Car Design News. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
A three or five-door hatchback (no separate trunk compartment) is a 'two-box' car.
- Mueller, Mike (2003). American Cars of the '50s. MBI Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7603-1712-9.
- Neil, Dan (28 April 2002). "The Hatchback Is Back (but Nobody Uses the H-Word)". The New York Times. Retrieved 3 March 2014.
- Flammang, James M. (1990). Standard Catalog of American Cars, 1976-1986. Krause Publications. p. viii. ISBN 9780873411332. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- "fastback". Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- "fastback". The Oxford Pocket Dictionary of Current English. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q2Ek25kwTqY
- Citroen Car Club. "Traction Avant". Citroen Car Club. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- Johnson, Carter (9 February 2017). "Citroën Traction Avant 11CV Commerciale – The World's First Hatchback". The Truth about Cars. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
- "History Of Hatchbacks & The Best Hatchback Cars 2014". www.globalcarsbrands.com. Retrieved 4 June 2018.
- "Historic Hatchback". www.oldcarsweekly.com. Retrieved 4 June 2018.
- Vance, Bill (27 March 2001). "Motoring Memories: Motoring Memories: Kaiser Traveler – the first hatchback". Autos.ca. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- the Auto Editors of Consumer Guide (17 October 2007). "1949-1953 Kaiser Traveler and Vagabond". HowStuffWorks.com. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- Strohl, Daniel (23 January 2011). "SIA Flashback – 1949 Kaiser Traveler: America's First Hatchback". Hemmings. Retrieved 20 August 2014.
- New Estate Car, The Times, Tuesday, 20 October 1959; pg. 16; Issue 54596; col F
- "Le Curbside Classic: Renault 4 – The First Hatchback". www.curbsideclassic.com. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- "Groupe Renault history since 1898". www.renault.com. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- Adams, Keith (25 July 2011). "Tested: Austin Maxi vs Renault 16". Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "Simca 1100". www.uniquecarsandparts.com.au. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- "Ten Pioneer British Hatchbacks". Lancaster Insurance. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- "History's 10 Best Selling Cars Of All Time". www.autoblog.com. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- "The Spirit Is Still Alive: American Motors Corporation 1954-1987". www.allpar.com. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- "History of the Gremlin and it's Unique Birth". www.gremlinx.com. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- "Do Not Feed After Midnight: The AMC Gremlin". www.ateupwithmotor.com. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- Lamm, Michae (October 1972). "AMC: Hornet hatchback leads the lineup". Popular Mechanics. 138 (4): 118–202. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- "1973 AMC Hornet". amchornet.com. Archived from the original on 31 July 2012. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- Wilson, Paul Carroll (1976). Chrome dreams: automobile styling since 1893. Chilton Book. p. 303. ISBN 9780801963520. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "AMC Pacer Wagon ad". Popular Science. 209 (5): 1–2. November 1976. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- Witzenburg, Gary (October 1978). "Driving the '79 American Motors models". Popular Mechanics. 150 (4): 114, 115, 164, 166, 168. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- h-body.org
- Gunnell, John (1982). Standard Catalog of American Cars, 1946-1975. Krause Publications. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- Lund, Robert (January 1978). "Driving the Dodge Omni and Plymouth Horizon". Popular Mechanics. 149 (1): 64–65, 136. Retrieved 2 March 2014.
- Thompson, Andy (2008). Cars of the Soviet Union: The Definitive History. Haynes Publishing. ISBN 9781844254835. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "The 30 Best-Selling Car Models In Brazil". www.thebrazilbusiness.com. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- "The best hatchbacks in India". rediff.com. Retrieved 3 January 2012.
- "1983-Maruti 800 is launched: Driving the India story". India Today. 24 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 July 2012. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- "Tata Nano set to drive into Taiwan". The Economic Times. 3 June 2010. Archived from the original on 24 July 2010.
External links




_S_hatchback_(2018-11-02)_02.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
