Groove (joinery)
In joinery, a groove is a slot or trench cut into a member which runs parallel to the grain. A groove is thus differentiated from a dado, which runs across the grain.
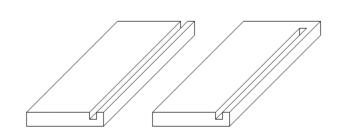
Grooves are used for a range of purposes in cabinet making and other woodworking fields. Typically, grooves are used to house the panels in frame and panel construction and the bottoms of drawers. For more structural construction, grooves are created along the sides and/or ends of panels, such as in tongue and groove construction. Applications include roofing, siding and flooring.
A groove may be through, meaning that it passes all the way through the surface and its ends are open, or stopped, meaning that one or both of the ends finish before the groove meets edge of the surface.
Methods
A groove can be cut by the following methods:
- electric router using a straight or rebate bit
- circular saw with multiple passes (depending on width and depth)
- dado set in a single pass
- spindle moulder (wood shaper)
- hand saw and chisel
- router plane
See also
- Dado (joinery)
- Groove (disambiguation)
- Tongue and groove