Grado, Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Grado (Slovenian: Gradež Venetian: Gravo; Friulian: Grau; Latin: Gradus[3]) is a town and comune in the north-eastern Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, located on an island and adjacent peninsula of the Adriatic Sea between Venice and Trieste.
Grado | |
|---|---|
| Comune di Grado | |
 Grado (Old town) | |
-Stemma.png) Coat of arms | |
Location of Grado 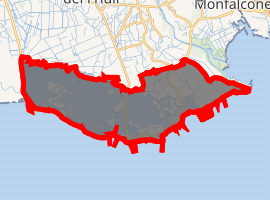
| |
 Grado Location of Grado in Italy  Grado Grado (Friuli-Venezia Giulia) | |
| Coordinates: 45°40′40″N 13°23′41″E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
| Province | Gorizia (GO) |
| Frazioni | Boscat, Fossalon, Pineta, Primero, Val Cavarera |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Dario Raugna |
| Area | |
| • Total | 114 km2 (44 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 2 m (7 ft) |
| Population (31 August 2008)[2] | |
| • Total | 8,650 |
| • Density | 76/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Gradesi |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 34073 |
| Dialing code | 0431 |
| Patron saint | St. Hermagoras and Fortunatus |
| Saint day | July 21 |
| Website | Official website |
Once mainly a fishing center, today it is a popular tourist destination, known commonly as L'Isola del Sole ("The Sunny Island"), also famous because it is also a spa town; together with Marano Lagunare, it is the center of the Marano-Grado Lagoon, which is famous for its uncontaminated nature. Grado is the birthplace of Biagio Marin, a poet who sang about the island in the local Venetian dialect.
History

In Roman times the city, known as ad Aquae Gradatae, was first port for ships entering the Natissa (Natisone), headed upstream to Aquileia.
During the late years of the Western Roman Empire many people fled from Aquileia to Grado in order to find a safer place, more protected from the invasions coming from the east. In 452, Nicetas, Bishop of Aquileia, took refuge briefly at Grado; of the same period is the earliest construction of Grado's first cathedral, the first church of Santa Maria delle Grazie, and the baptistery. Grado was the home base of the patriarchate's fleet.
In 568, after the invasion of the Lombards, the seat of the Patriarchate of Aquileia was transferred to Grado by the Patriarch Paulinus. After the Schism of the Three Chapters, two different patriarchs were elected: the patriarch of Grado exerted his jurisdiction over the Latin-origin people living on the coast and in the Venetian Lagoon, while that of Old-Aquileia, later moved to Cividale, had its jurisdiction over the interior. A long-lasting dispute over the authority of the two patriarchs ensued. In 993, the patriarch of Aquileia, Popo, conquered Grado, but was unable to keep possession of it. The matter was settled only in 1027 when the pope declared the supremacy of the See of Aquileia over Grado and the Venetian province.
The seat of the patriarchate was transferred to Venice in 1451 by Pope Nicholas V. Reduced to a minor hamlet, Grado was sacked by the English, who burned the city archives in 1810 and by the French in 1812. Grado was acquired by Austria in 1815, to which it belonged until 1918, when it was ceded to Italy after its victory in World War I.
Main sights
Today there are frequent finds of inscriptions, sarcophagi, marble sculpture and small bronzes that once furnished its villas. The remains of one of these villas have been excavated on the islet of Gorgo in the lagoon.
Modern landmarks include:
- The Basilica of Sant'Eufemia (Cathedral), with the octagonal Baptistry (late 5th century). The church was once preceded by a quadri-portico, one of the columns of which is now in the centre of the Patriarch's Square. The current appearance of the church dates from the reconstruction by Fra Elia (579), with a simple hut façade and a bell tower (15th century) on the right side, which is surmounted by a statue portraying St. Michael and known as the Anzolo (1462). The interior has a nave and two aisles. The main point of interest is the mosaic pavement from the 6th century, restored in 1946–48.
- The basilica of Santa Maria delle Grazie. Begun in the 4th to 5th centuries, it was renovated in the 6th century and restored in Baroque in 1640.
- The Barbana Sanctuary. It is located in a small island in the Grado Lagoon. The original church was erected in 582 and was since rebuilt and enlarged.
Of the ancient fortress only a tower, turned into a private residence, and parts of the walls can still be seen. Under the Town Hall are remains of the Palaeo-Christian basilica of Piazza Vittoria.
The Valle Cavanata Nature Reserve is a 327-hectare (810-acre) protected area situated in the easternmost part of the Grado Lagoon.
Resort town

Today, Grado attracts scores of tourists each year to its hotels and campgrounds. A large water park run by a municipal corporation is the main attraction, complete with indoor and outdoor swimming pools, and a health center offering spa treatments.
The town also boasts a well-preserved pedestrian-only center, in which many shops, bars, and restaurants are located.
Grado also offers facilities for many sporting activities, including tennis, wind-surfing, and golf. From Grado can be done excursions by boat to the Grado Lagoon, and visit the many dozen islands inside it (like Barbana).[4]
Twin towns
Image gallery
- Many restaurants can be found in the oldest part of the town.
 Basilica di Sant'Eufemia by night
Basilica di Sant'Eufemia by night- The harbour
 Barbana island, the Marian sanctuary
Barbana island, the Marian sanctuary- Channel in Grado
Bibliography
- Bisconti F., Temi di iconografia paleocristiana, Vatican City, 2000.
- Bovini G., "Grado paleocristiana", in Archeologia Cristiana, Bologna 1973.
- Farioli R., "Mosaici pavimentali dell'alto Adriatico e dell'Africa settentrionale in età bizantina", in Antichità Altoadriatiche, vo. V.paleocristiana, Ravenna 1975.
- Farioli R., Pavimenti musivi di Ravenna, Ravenna 1975.
- Efthalia Rentetzi, "Un'inedita figura di pesce. Parentele stilistiche tra i mosaici pavimentali di s. Maria delle Grazie e s. Eufemia a Grado", in Artonweb. Punti di visa sull'arte.
- Efthalia Rentetzi, "Un frammento inedito di S. Eufemia a Grado. Il pavimento musivo del Salutatorium", in Arte Cristiana, fasc.. 850 (Gennaio - Febbraio 2009), Volume XCVI, p. 51-52.
Notes
- "Superficie di Comuni Province e Regioni italiane al 9 ottobre 2011". Istat. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- "Popolazione Residente al 1° Gennaio 2018". Istat. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Richard J.A. Talbert, ed. (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World: Map-By-Map Directory. I. Princeton, NJ and Oxford, UK: Princeton University Press. p. 276. ISBN 0691049459.
- Laguna di Grado (in Italian)
See also
- List of islands of Italy
- Marano Lagunare
- Grado Lagoon
- Friuli-Venezia Giulia
- Battle of Grado
External links
- Official institutional website of City
- Official tourist website of City
- Scuola Insieme, a local Italian language school, offers details on history, travel, and activities in and around Grado.
- Richard Stillwell, ed. Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites, 1976: "Ad Aquas Gradatas (Grado), Italy"
- Information about Grado