Gradisca d'Isonzo
Gradisca d'Isonzo (Friulian: Gardiscja or Gardiscje, Slovene: Gradišče ob Soči, archaic German: Gradis am Sontig) is a town and comune of the Province of Gorizia in Friuli-Venezia Giulia, north-eastern Italy. The lawyer, linguist, philologist Philippe Sarchi was born in Gradisca d'Isonzo.
Gradisca d'Isonzo | |
|---|---|
| Città di Gradisca d'Isonzo | |
Main street with town hall (left) | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Gradisca d'Isonzo 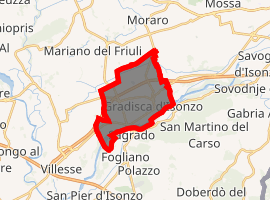
| |
 Gradisca d'Isonzo Location of Gradisca d'Isonzo in Friuli-Venezia Giulia 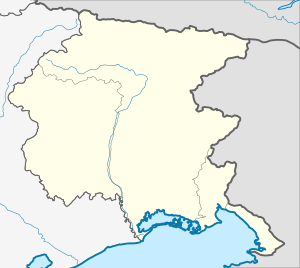 Gradisca d'Isonzo Gradisca d'Isonzo (Friuli-Venezia Giulia) | |
| Coordinates: 45°53′N 13°30′E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
| Province | Gorizia |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Linda Tomasinsig |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10 km2 (4 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 32 m (105 ft) |
| Population (31 August 2017)[2] | |
| • Total | 6,468 |
| • Density | 650/km2 (1,700/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Gradiscani |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 34072 |
| Dialing code | 0481 |
| Patron saint | Sts. Peter and Paul |
| Saint day | June 29 |
| Website | Official website |
Geography
The municipality is located in north-eastern Italy on the right bank of the Isonzo River, about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) southwest of Gorizia. It received town privileges on 14 July 1936. As of 2011, the population of Gradisca is about 6,580.
The town is an important centre of the Friulian culture in the Julian Venetia region.
History
The town's name is a Slavic toponym: in archaic Slovene, gradišče (cf. gord) was a term indicating a fortified site or a ruin and is a widespread toponym in the Slovene Lands. The strategic important area on the Isonzo River was probably already settled in Roman times and under the Lombard kingdom, later exposed to the attacks by Hungarian forces on Northern Italy.
The rural settlement of Gradisca is mentioned for the first time in 1176, when it had a mixed population of Slavic and Latin origin. It then belonged to the estate of Farra, held by the Patriarchs of Aquileia. From 1420 onwards their lands were gradually conquered by the Republic of Venice, annexed and incorporated into the Venetian Domini di Terraferma in 1473. The Venetians fortified Gradisca as a bastion against Ottoman raids, then part of a massive defence line along the Isonzo River relying on plans designed by Leonardo da Vinci.
During the War of the League of Cambrai against Venice, Gradisca was conquered by Emperor Maximilian I in 1511, and thenceforth it was a Habsburg possession ruled within the County of Gorizia as part of the Inner Austrian lands. In 1615 a Venetian attempt to reconquer it initiated the War of Gradisca. The town was however kept by the Imperial House of Habsburg; in 1647 Emperor Ferdinand III made it the capital of an autonomous County of Gradisca and sold the territory to his confident John Anthony of Eggenberg. The Eggenberg dynasty, formally elevated to Princes of the Holy Roman Empire in 1654, held Gradisca until 1717, enlarging and enriching it constantly as a princely residence.
With the extinction of the Eggenbergs, the county returned to the House of Habsburg, being re-united with the remaining County of Gorizia. The union resulted in the creation of the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca in 1754, which existed until the dissolution of Austria-Hungary in 1918. The town remained in the Cisleithanian side after the Compromise of 1867 as head of the district of the same name (GRADISCA), one of the 11 Bezirkshauptmannschaften in the Austrian Littoral province.[3]
During Austrian domination, the town retained its predominantly Italian character. According to the last Austrian census of 1910, 60.0% of the population of the town spoke Italian or Friulian, 13.8% spoke Slovene, and a mere 2.3% spoke German as their first language.[4]
In 1914, at the outbreak of World War I, the population of Gradisca fought under Austria-Hungary. In 1921 the town became part of Italy.
Main sights
- Castle, built by the Venetians in the late 15th century over a pre-existing fortress known from 1176. It was enlarged under the Austrian domination (16th-17th centuries), later being turned into a jail. Among the people imprisoned here was Federico Confalonieri.
- Cathedral
- Church of Santo Spirito, with an altarpiece by Pompeo Randi.
Notable people
- Giordano Colausig, footballer
See also
- Gorizia and Gradisca
References
- "Superficie di Comuni Province e Regioni italiane al 9 ottobre 2011". Istat. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- "Popolazione Residente al 1° Gennaio 2018". Istat. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- Die postalischen Abstempelungen auf den österreichischen Postwertzeichen-Ausgaben 1867, 1883 und 1890, Wilhelm KLEIN, 1967
- http://www.sistory.si/publikacije/prenos/?urn=SISTORY:ID:836