Gnadenau, Kansas
Gnadenau was a communal village of German-speaking Mennonite immigrants from Russia in Marion County, Kansas, United States.[1] It is currently a ghost town that was located approximately 2 miles (3.2 km) southeast of Hillsboro. No buildings remain at this former community site. The Gnadenau Cemetery still exists.
Gnadenau, Kansas | |
|---|---|
 | |
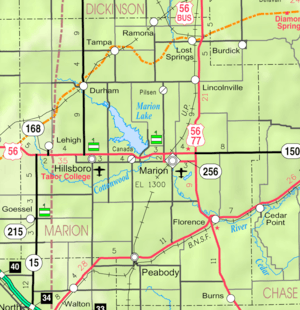 KDOT map of Marion County (legend) | |
 Gnadenau  Gnadenau | |
| Coordinates: 38°19′34.413″N 97°10′49.882″W[1] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Kansas |
| County | Marion |
| Township | Liberty |
| Founded | 1874 |
| Elevation | 1,378 ft (420 m) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 0 |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| Area code | 620 |
| GNIS ID | 477356 [1] |
History
Early history
For many millennia, the Great Plains of North America was inhabited by nomadic Native Americans. From the 16th century to 18th century, the Kingdom of France claimed ownership of large parts of North America. In 1762, after the French and Indian War, France secretly ceded New France to Spain, per the Treaty of Fontainebleau.
19th century
In 1802, Spain returned most of the land to France. In 1803, most of the land for modern day Kansas was acquired by the United States from France as part of the 828,000 square mile Louisiana Purchase for 2.83 cents per acre.
In 1854, the Kansas Territory was organized, then in 1861 Kansas became the 34th U.S. state. In 1855, Marion County was established within the Kansas Territory, which included the land for modern day Gnadenau.[2]
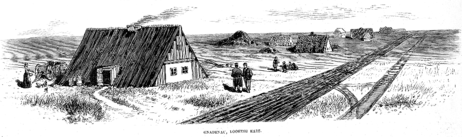
In 1874, the German-speaking Mennonites of the Krimmer Mennonite Brethren of Annefeld near Simferopol, Crimea, Russia decided to relocate in the United States because Russia removed their exemption from military service. In August, the group arrived at the site and named it Gnadenau, meaning Meadow of Grace or Grace Meadow.[3] Unlike the majority of Mennonites, this body adopted trine forward immersion as the mode of baptism.[4][5]
In 1879, the beginning of the demise of the village occurred when the Marion and McPherson Railway Company built a railway north of village and established the nearby town of Hillsboro.
21st century
Currently no buildings exist in Gnadenau, thus it's considered a Ghost Town. A Gnadenau Village Memorial monument still exists.
Geography
Gnadenau was located at 38°19′34.413″N 97°10′49.882″W (38.326226, -97.180523),[1] along 175th Street between Jade Road and Kanza Road in Marion County, Kansas. Most residents lived on the north side of 175th Street. A descriptive monument for the Gnadenau Village currently stands on the south side of 175th Street,[6] and the Gnadenau Cemetery is immediately south of it.[1]
Area attractions
- Mennonite Settlement Museums,[7] 501 South Ash Street, Hillsboro, main museum on Memorial Drive (1 block west).[8]
- Jacob Friesen Flouring Wind Mill is a detailed replica of the 1876 mill that stood in Gnadenau.
See also
- Liberty Township, Marion County, Kansas (location of Gnadenau)
- Historical Maps of Marion County, Kansas
- U.S. Conference of Mennonite Brethren Churches
- Threshing Stone and Winter Wheat
- Burdei
- Molotschna
Further reading
- Grace Meadow: The Story of Gnadenau and Its First Elder, Marion County, Kansas, David V Wiebe; Mennonite Brethren Publishing House; 1967.
- They Seek a Country: A Survey of Mennonite Migrations With Special Reference to Kansas and Gnadenau; David V. Wiebe; Mennonite Brethren Publ. House; 1959.
- Settlement of the Krimmer Mennonite Brethren at Gnadenau, Marion County; Alberta Pantle; Kansas Historical Quarterly; Vol. 13, No. 5; pages 259-285; February 1945.[3][9]
- The Disciples of Menno Simonis: Their Settlement in Central Kansas; Frank Leslie's Illustrirte Zeitung; March 20, 1875. (German version of English article)
- The Disciples of Menno Simonis: Their Settlement in Central Kansas; Frank Leslie's Illustrated; March 20, 1875. (English)
- Among the Mennonites, Their Houses and Habits - A Visit to Gnadenau.; Johnny Groat; Marion County Record; January 16, 1875.
References
- Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) details for Gnadenau Cemetery; United States Geological Survey (USGS); October 13, 1978.
- The History of Marion County and Courthouse
- Settlement of the Krimmer Mennonite Brethren at Gnadenau, Marion County; Alberta Pantle; Kansas Historical Quarterly; Vol. 13, No. 5; pages 259-285; February 1945.
- Krimmer Mennonite Brethren, Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online.
- Gnadenau Krimmer Mennonite Brethren Church, Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online.
- Gnadenau Village Memorial; Donald I. Good.
- Mennonite Settlement Museums
- Mennonite Settlement Museum
- Settlement of the Krimmer Mennonite Brethren at Gnadenau, Marion County; Alberta Pantle; Kansas Historical Quarterly; Vol. 13, No. 5; February 1945; p259-285.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gnadenau, Kansas. |
- Historical
- Photos of Gnadenau Village monuments
- Marion County cemetery list, archive of KsGenWeb
- Marion County history bibliography, Marion County school bibliography, Kansas Historical Society
- Maps
- Marion County maps: Current, Historic, KDOT
- Topo Map of Hillsboro area, USGS