Girnar Jain temples
The group temples of Jainism are situated on the Mount Girnar situated near Junagadh in Junagadh district, Gujarat, India. There temples are sacred to the Digambara and the Svetambara branches of Jainism.
| Jain temples, Girnar | |
|---|---|
Raivatak, Raivatachal | |
 | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Jainism |
| Deity | Neminath |
| Festival | Paryushana, Mahavir Jayanti |
| Governing body | Anandji Kalyanji Trust |
| Location | |
| Location | Girnar near Junagadh, Junagadh district, Gujarat |
 Location of Girnar Jain temples in Gujarat | |
| Geographic coordinates | 21.5266295°N 70.5222246°E |
| Part of a series on |
| Jainism |
|---|
 |
|
Jain prayers |
|
Ethics |
|
Major sects |
|
Texts |
|
Festivals
|
|
|
In Jainism

According to Jain religious beliefs, Neminath, the 22nd Tirthankara Neminath became an ascetic after he saw the slaughter of animals for a feast on his wedding. He renounced all worldly pleasures and came to Mount Girnar to attain salvation. He attained omniscience and Moksha (died) on the Mount Girnar. His bride-to-be Rajulmati also renounced and became a nun.
Jain Temples
Girnar was anciently called Raivata or Ujjayanta, sacred amongst the Jains to Neminath, the 22nd Tirthankar, and a place of pilgrimage before 250 BCE.[1]
Situated on the first plateau of Mount Girnar at the height of about 3800 steps, at an altitude of 2370 ft above Junagadh, still some 600 ft below the first summit of Girnar, there are Jain temples with marvelous carvings in marble.[1][2]
Some 16 Jain temples here form a sort of fort on the ledge at the top of the great cliff. These temples are along the west face of the hill, and are all enclosed.
Neminath Temple

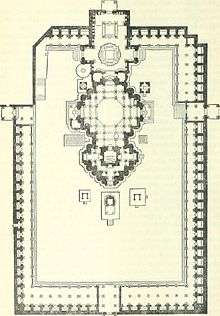
The Neminath temple is the largest temple of the group standing in a quadrangular court 195 x 130 feet.[1][2] The temple was rebuilt completely by Sajjana, the governor of Saurashtra appointed by Jayasimha Siddharaja, in 1129 CE.[3] There is an inscription on one of the pillars of the mandapa stating that it was repaired in 1278 CE.[2]
It consists of two rangamandapa halls with two porches and a central shrine (Gudhamandapa), which contains a large black image of Neminath sitting in the lotus position holding a conch in his palm.[1][2]
The principal hall in front of the central shrine measures across from door to door inside 41' 7" x 44' 7" from the shrine door to that leading out at the west end. The roof is supported by 22 square columns of granite coated with white lime while the floor is of tessellated marble.[2]
Round the central shrine is a circumambulatory passage (pradakshina) with many images in white marble including that of a Ganesha and a Chovishi or slab of the twenty four Tirthankara.[1][2] Between the outer and inner halls are two shrines.[2]
The outer hall measures 38' x 21' 3". The outer hall has two small raised platforms paved with slabs of yellow stone, covered with representations of feet in pairs called padukas, which represent the 2452 feet of the Gandharas, first disciples of Tirthankaras.[2]
On the west of this is a closed entrance with a porch overhanging the perpendicular scarp of the hill.[2] On two of the pillars of the mandapa are inscriptions dated 1275, 1281, and 1278 — dates of restoration.
The enclosure in which these rangamandapas and the central shrine are situated, is nearly surrounded inside by 70 little cells, each enshrining a marble image on a bench, with a covered passage running round in front of them lighted by a perforated stone screen.[2]
The principal entrance was originally on the east side of the court; but it is now closed, and the entrance from the south side of court in Khengar's Palace is that now used.[2]
On south side, there is a passage leading into a low dark temple, with granite pillars in lines. Opposite the entrance is a recess containing two large black images; in the back of the recess is a lion rampant, and over it a crocodile in bas-relief. Behind these figures is a room from which is a descent into a cave, with a large white marble image which is mostly concealed. It has a slight hollow in the shoulder, said to be caused by water dropping from the ear, whence it was called Amijhara, "nectar drop".[4][1] There are few shrines in the court dedicated to Jain monks. In the North porch are inscriptions which state that in Samwat 1215 certain Thakurs completed the shrine, and built the Temple of Ambika.[4]
There is a small temple of Adinath behind the Neminath temple facing west which was built by Jagmal Gordhan of Porwad family in VS 1848 under guidance of Jinendra Suri.[2]
Adabadji Adinatha temple
There are three temples to the left of the passage from the north porch of the Neminath temple. Of them, the temple on the south contains a colossal image of Adinatha, the first Tirthankar, exactly like that at Palitana temples. The image is in standing meditating (kausaggiya) position On the throne of this image is a slab of yellow stone carved in 1442, with figures of the 24 Tirthankars.[5]
Panchmeru temple
On the north, opposite the Adabadji temple, there is Panchabai's or Panchmeru temple which was built in VS 1859. It contains five sikhars or spires each enshrining quadruple images.[5]
Meraka-vasahi
West of Panchmeru temple, there is a large temple. The temples is called Malekavasahi, Merakavasahi or Merakavashi due to false identification. Madhusudan Dhaky noted that the Merakavasahi was a small shrine somewhere near east gate of Neminatha temple while the current temple is large one and outside the north gate of the Neminatha temple. Based on its architecture, Dhaky dates the temple to 15th century and notes that it is mentioned as Kharataravasahi built or restored by Bhansali Narpal Sanghavi in the old itineraries of Jain monks. The temple is depicted in the Shatrunjaya-Giranar Patta dated 1451 CE (VS 1507) in Ranakpur temple so it must have built before it. The temple may have been built as early as 1438 CE.[6] Dhaky believes that the temple may have been built on the site of the Satyapuravatara Mahavira's temple built by Vastupala.[7]
According to an anecdote said by modern Jain writers, Sajjana, the minister of Chaulukya king Siddharaja Jayasimha, built the Neminatha temple using the state treasury. When he collected the funds to return as a compensation, the king declined to accept it so the funds were used to built the temple. Dhaky concludes that the anecdote is not mentioned in any early work and is false.[6]
Sahastraphana (thousand hooded) Parshwanatha, the image which was consecrated in 1803 CE (VS 1459) by Vijayajinendra Suri, is currently the central deity in the temple. The temple originally housed the golden image of Mahavira and brass images of Shantinatha and Parshwanatha on its sides.[8]
The east facing temple has 52 small shrines surrounding the central temple. It has an open portico with ceilings with fine carvings. In the bhamti or cloisters surrounding the court, there are also some remarkable designs in carved ceilings. The roof of the rangamandapa has fine carvings. The shrine proper must have been removed and replaced with new one at the end of the sixteenth century or the start of the seventeenth century. It is known that Karmachandra Bachchhavat, minister of the king of Bikaner, had sent a funds to renovate temple in Shatrunjaya and Girnar under Jinachandrasuri IV of Kharatara Gaccha during the reign of Akbar. There is a shrine housing replica of Ashtapada hill in the south, shrine with Shatrunjayavatar in west, behind the main temple, and Samet Shikhar (or Nandishwar Dwipa) in north.[5][9]
Sangram Soni's Temple
North of the Melakavasahi, there is a temple of Parshwanath in the enclosure. The original temple on the site was Kalyanatraya temple dedicated to Neminatha built by Tejapala, brother of Vastupala. This Kalyanatraya contained quadruple images in three tires as the central deity. The new temple on the site was built in 1438 CE (VS 1494) by Oswal Soni Samarasimha and Vyavahari Maladev. The spire of this 15th century temple is replaced by new spire built c. 1803 CE. The temple is now mistakenly known as Sangram Soni's temple.[10] It was repaired by Premabhai Hemabhai about 1843. It contains a large white marble figure of Parswanatha bearing the date 1803 CE with the polycephalous cobra over him whence he is styled Seshphani. This temple is peculiar in having a sort of gallery and like the previous one of the central deity faces the east whilst the others mostly face the west.[5]
Kumarapala's Temple

The last temple to the north is known as the Kumarapala's temple which is falsely attributed to 12th century Chaulukya king Kumarapala. Based on the literary, epigraphic and architectural evidence, Madhusudan Dhaky concluded that the temple belongs to 15th century and was built by Purnasinha Koshthagarika (Punsi Kothari). The central deity was Shantinatha and was consecrated by Jinakirti Suri probably in 1438 CE. The part of the original temple was destroyed by the 18th century and appears to have been restored in 1824 CE by Hansraja Jetha which is known from the inscription.[11]
The temple is west facing. The original temple had 72 shrines surrounding the central temple which no longer exist. The central temple has a modern long open portico supported by twenty four columns. The temple proper or mandapa and shrine are small and the ceilings and architraves are restored. The mandapa with its beautiful pendentive and the pillars and lintels of the portico. The shrine contains three images; in the middle Abhinandana Swami dedicated in 1838 and on either side Adinatha and Sambhavanatha dated 1791.[11][5]
Mansingha Bhojaraja temple
To the east of the Devakota, there are several temples: the principal being the temple of Mansingha Bhojaraja of Kachchh, an old granite temple near the entrance gate which is now dedicated to Sambhavanatha.[12]
Vastupala-vihara

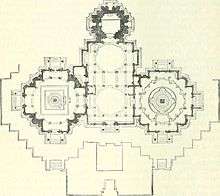
Vastupala-vihara is a triple temple, the central fane measuring 53 feet by 291⁄2 has two domes and finely carved but much mutilated and the shrine which is 13 feet square with a large niche or gokhla on the left side contains an image of Mallinatha. Beneath the image is the inscription mentioning Vastupala and his family members.[12]
On either side this central temple, there is a large hall about 38 feet 6 inches from door to door containing a remarkable solid pile of masonry called a samovasarana that on the north side named Sumeru having a square base and the other Sameta Sikhara with a nearly circular one. Each rises in four tiers of diminishing width almost to the roof and is surmounted by a small square canopy over images. The upper tiers are reached by steps arranged for the purpose. On the outside of the shrine tower are three small niches in which images have been placed and there are stone ladders up to the niches to enable the pujaris to reach them.[13] The temple was completed in 1232 CE. There are six large inscriptions of Vastupala in the temple dated VS 1288. Originally Shatrunjayavatara Adinatha was the central deity of the temple. The roofs of temple were rebuilt in the 15th century.[14]
There is another temple on the cliff behind the Vastupala-vihara which is now known as Gumasta temple. The temple was built by Vastupala and was dedicated to Marudevi. Another shrine behind Vastupala-vihara is dedicated to Kapardi Yaksha.[3]
Samprati Raja temple

Farther north of the Vastupala-vihara, the Samprati Raja temple is situated. The temple was built in 1453 (VS 1509) CE by Shanraj and Bhumbhav from Khambhat. It was originally dedicated to Vimalanatha.[15] According to Dhaky, the temple was built on the site of Stambhanatirthavatara Parshwanatha temple built by Vastupala.[7] The temple is mistakenly attributed to Maurya ruler Samprati.[7]
It is built against the side of a cliff and is ascended to by a stair. Inside the entrance there is another very steep flight of steps in the porch leading up to a large mandapa to the east of which is added a second mandapa and a gambhara or shrine containing a black image of Neminatha dedicated by Karnarama Jayaraja in 1461.[16]
Other temples
.jpg)
To the east of Vastupala vihara and Samprati Raja temples, and on the face of the hill above, there are other temples among them an old one going by the name of Dharmasa of Mangrol or Dharamchand Hemchand built of grey granite the image being also of granite. Near it is another ruined shrine in which delicate granite columns rise from the corners of the sinhasana or throne carved with many squatting figures. Near this is the only shrine on this mount to Mahavira.[17]
South of this, and 200 feet above the Jain temples on way to the first summit, is the Gaumukhi Shrine, near a plentiful spring of water.[1]
Away on the north, climbing down the steps, there are two shrines dedicated to Neminatha in Sahsavan where he said to have taken renunciation and attained omniscience. Neminatha is said to have attained Nirvana or died on the highest peak of the Girnar. There is a modern Samovasarana temple.
Tanks
Outside to the north of the Kumarapala's temple, there is the Bhima Kunda, a tank measuring 70 feet by 50 feet. Below it and on the verge of the cliff is a smaller tank of water and near it a small canopy supported by three roughly hewn pillars and a piece of rock containing a short octagonal stone called Hathi pagla or Gajapada, the elephant foot, a stratum on the top of which is of light granite and the rest of dark the lower part is immersed in water most of the year.[12]
Five Peaks
There are 5 tonks on the Girnar hill.
First Peak: After a climb of about 2 miles, there is a Digambar Jain temple and a cave called Rajulmati cave, it is stated that Rajulmati has done penance at this place. There is also a small temple where idol of Bahubali (120 cm) in standing posture is installed. Besides there are footprints of Kundkund. In the temple, the idol of Neminath (Vikram Samvat 1924) is on the main altar. The idols of Parshwanath and Neminath are also there. There is stream called gomukhi ganga and nearby the footprints of 24 tirthanakaras are available.
Second Peak: After 900 steps there are the footprints of Muni Anirudhhkumar and temple of Devi Ambika.
Third Peak: here the footprints of Muni Sambukkumar are installed. Muni has attained nirvana from this place.
Fourth tonk (Peak); Here the footprints of Pradhyman kumar, son of lord krishna are installed here. He attained nirvana from this place.
Fifth tonk; The Fifth tonk is of Lord Neminath's footprints. Lord Neminath, the 22nd tirthankar attained nirvana/moksha from this site.
Gallery
 Neminath Temple in 1876
Neminath Temple in 1876 Samprati Raja temple
Samprati Raja temple Temple view From About 3100 feet at Mt. Girnar
Temple view From About 3100 feet at Mt. Girnar Ambika Mata temple
Ambika Mata temple Chaumukhji Temple
Chaumukhji Temple Vastupala Vihara
Vastupala Vihara Inscription of the Vastupala-vihara on Mount Girnar
Inscription of the Vastupala-vihara on Mount Girnar 1876 image of Vastupala Vihara Jain temple on Girnar
1876 image of Vastupala Vihara Jain temple on Girnar.jpg) King Samprati's Tunk
King Samprati's Tunk
References
- Murray 1911, p. 155-157.
- Burgess 1876, p. 166.
- Dhaky 2010, p. 102.
- Burgess 1876, p. 167.
- Burgess 1876, p. 168.
- Dhaky 2010, p. 134.
- Dhaky 2010, p. 103.
- Dhaky 2010, pp. 134-135.
- Dhaky 2010, p. 135-137.
- Dhaky 2010, p. 103, 123.
- Dhaky 2010, pp. 146-150.
- Burgess 1876, p. 169.
- Burgess 1876, p. 170.
- Dhaky 2010, pp. 102-103.
- Dhaky 2010, p. 89.
- Burgess 1876, pp. 173-74.
- Burgess 1876, p. 174.
Bibliography
- Dhaky, M. A. (2010). Shah, Jitendra B. (ed.). સાહિત્ય, શિલ્પ અને સ્થાપત્યમાં ગિરનાર [Girnar in Literature, Sculptures and Architecture]. L. D. Series: 148 (Sambodhi-Puratatva-Visheshank-2). Ahmedabad: Lalbhai Dalpatbhai Institute of Indology. ISBN 81-85857-30-X.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Burgess, James (1876). Report on the Antiquities of Kâṭhiâwâḍ and Kachh, Being the Result of the Second Season's Operations of the Archaeological Survey of Western India, 1874-75. London: India Museum.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)

- Murray, John (1911). "A handbook for travellers in India, Burma, and Ceylon". Internet Archive. Retrieved 28 January 2016.