Force Motors
Force Motors Limited, is an Indian automotive manufacturer, the flagship company of the Dr. Abhay Firodia Group.[1] From 1958 until 2005 the company was known as Bajaj Tempo Motors, because it originated as a joint venture between Bachraj Trading Ltd. and Germany's Tempo.[2].
The company is known for brands like the Tempo, Matador, Minidor and Traveller. Over the last five decades it has partnered with global manufacturers including Daimler, ZF, Bosch, and MAN. These associations have enabled the company to move away from its outdated products.
 | |
Formerly | Bajaj Tempo Motors |
|---|---|
| Public | |
| ISIN | INE451A01017 |
| Industry |
|
| Founded | 1958 |
| Founder | Abhay Firodia |
| Headquarters | , |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people |
|
| Products | Traveller, Trax, Gurkha, Orchard and Balwan Tractors |
| Revenue | ₹3,033 crore (US$430 million) (2016) |
| ₹346 crore (US$49 million) (2016) | |
| ₹179 crore (US$25 million) | |
Number of employees | 10,000 |
| Website | www |
Force Motors is India’s largest van maker.[3] The company is completely vertically integrated, making its own components for the entire product range.
Force Motors ranks 327th (2016) amongst India’s Fortune 500 Companies.[4]
History

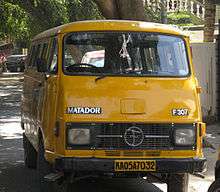

Aside from manufacturing light transport vehicles, Force Motors also makes engines and axles, as well as a large variety of die-cast aluminium parts. The foundation of Bajaj Tempo originates with the Bachraj Trading company, which was established in 1945.[2] Bachraj started assembling three-wheeled Tempo auto rickshaws and small trucks in 1951, under license from Germany. In 1958 the companies announced the creation of a joint venture, called Bajaj Tempo Motors, with 26 percent of the shares belonging to Tempo. In 1968 the Firodia Group took a majority stake in Bajaj Tempo.
In 1971 Tempo (Germany) passed into the hands of Daimler-Benz, who retained a 16.8 percent share in Bajaj Tempo until 2001. Daimler sold its stake in April 2001 after 43 years citing little synergy between the two companies.[5]
The Tempo Matador was the first diesel light commercial vehicle in India. The company started production of the Hanseat 3-Wheelers in collaboration with Vidal & Sohn Tempo Werke Germany in 1958. The word Tempo (a registered trade mark of Daimler) is now generic for any small goods carrier in India.[6]

In 1987, Force Motors set up a new plant at Pithampur in Madhya Pradesh, for the production of Tempo Traveller. This plant was designed and built to the specification of Daimler-Benz.
In 1997, Daimler asked it to set up a dedicated facility for assembling and testing engines for Mercedes passenger cars to be made in India.
In 2005 the company was renamed Force Motors.[2]
Force Motors signed technology sourcing agreements in 2003 with MAN SE for which payments were made up front. On completion of the localization of the licensed technology and with the request from MAN, a joint venture was created forming MAN Force Trucks Pvt. Ltd to manufacture the full range of HCVs from 16t GVW to 49t GCW. MAN proceeded to buy out Force and MAN Trucks India was established as a separate concern in 2012.[7]
In 2012, Force Motors launched Traveller 26, a monocoque panel van that can seat 26 persons, designed entirely in-house.[8] It has disk brakes on all four wheels and also comes with safety features like ABS and EBD.
In 2015, the company was awarded a contract by BMW, resulting in a new facility in Chennai which produces and test engines and transmissions exclusively for all BMW cars and SUVs made in India.[9] This plant can produce up to 20,000 engines per year.[10]
A new plant was inaugurated at Chakan, Pune in June 2016.[11] This facility assembles and tests engines for all Mercedes Cars and SUVs made in India.[11] The new plant has a current annual capacity of 20,000 engines and 20,000 front and rear axles.[11]
Force Motors has a nationwide dealer presence. The company also exports to various countries in Africa, Latin America, SAARC and ASEAN countries, Gulf and Germany.
Products
Force Motors manufactures a range of vehicles including Small Commercial Vehicles (SCV), Light Commercial Vehicles (LCV), Multi Utility Vehicles (MUV), Special Cross Country Vehicles and Agricultural Tractors.
Light Commercial vehicles
- Traveller range of vehicles (including Traveller 26, School Bus, Ambulance, Quick Response Vehicle, Royale)
Small Commercial Vehicles
- shaktiman 200
- shaktiman 400
Multi Utility Vehicles
- Trax (including Toofan, Cruiser, Cruiser Deluxe)
- Kargo King
- Trax Delivery Van
Special Cross Country Vehicles
- Force Gurkha
Agricultural vehicles
- Balwan tractors
- Orchard tractors
Sports Utility Vehicles
- Force One SUV (discontinued)
References
- "Force | The Force". www.forcemotors.com. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- Mazur, Eligiusz, ed. (2006). World of Cars 2006·2007. Warsaw, Poland: Media Connection Sp. z o.o. p. 149. ISSN 1734-2945.
- "Largest Van Maker". www.moneycontrol.com.
- "Fortune 500 companies". www.fortuneindia.com. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- "DAIMLER EXITS BAJAJ TEMPO". Telegraph India. 24 April 2001. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- "History". Force Motors. Retrieved 16 February 2020.
- "Ten years of MAN Truck & Bus in India". PressCenter. MAN SE. 16 September 2016. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016.
- "Force Motors launches world's only monocoque panel van Traveller 26". 17 October 2012.
- "Force Motors inaugurates plant for BMW engine assembly". Autocar India. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- Raghunathan, Anu. "Pune's Force Motors Makes Engines For BMW And Mercedes-Benz". Forbes.
- Bureau, Our. "Force Motors commissions ₹100-cr plant for Merc". @businessline. Retrieved 2 January 2020.