Finno-Ugric countries
Finno-Ugric countries is a term used for the three independent nation states with a Finno-Ugric national majority:[1] Finland and Estonia which are Finnic, and Hungary which is Magyar.
The Finno-Ugric countries work together in funding Finno-Ugric research and protecting the minority rights of other Finno-Ugric nations without their own sovereign states.[2] The three countries are also represented as Finno-Ugric countries in the Finno-Ugric Congress [3][4]
Modern entities
Independent sovereign states
Countries where Finno-Ugric languages have special status
Finnic
| Name | Capital | Language(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Riga | Livonian | |
| Oslo | Sami and Kven | |
| Stockholm | Finnish, Meänkieli and Sami |
Provinces and autonomous regions
| Country | Region | Administrative center | Founded |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eisenstadt | Unknown | ||
| Sami native region | Sajos | 9 November 1973 | |
| Vadsø | Unknown | ||
| Tromsø | Unknown | ||
| Bodø | Unknown | ||
| Trondheim | Unknown | ||
| Khanty-Mansiysk | 10 December 1930 | ||
| Salekhard | 10 December 1930 | ||
| Syktyvkar | 5 December 1936 | ||
| Perm | 1 December 2005 | ||
| Izhevsk | 28 December 1934 | ||
| Yoshkar-Ola | 5 December 1936 | ||
| Saransk | 20 December 1934 | ||
| Petrozavodsk | 16 July 1956 | ||
| Novi Sad | 1944 | ||
| Prekmurje | Murska Sobota | Unknown | |
| Luleå | 1810 | ||
| Mukacheve | 9 November 1953 |
Historical states and dynasties
Finnic states
Hungarian states
| Name | Year(s) | Capital | Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hétmagyar confederation | 9th century | Unknown | |
| 895–1000 | Esztergom and Székesfehérvár | ||
| 1000–1301 | Esztergom and Székesfehérvár | 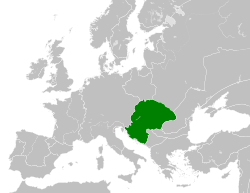 | |
| 1301–1526 | Esztergom, Székesfehérvár and Buda | ||
| Eastern Hungarian Kingdom (vassal under |
1526–1551 1556–1570 |
Buda (1526–41) Lippa (1541–42) Gyulafehérvár (1542–70) |
|
(since 1804 crownland of the |
1526–1867 | Buda (1526–1536, 1784–1873) Pressburg (1536–1783) |
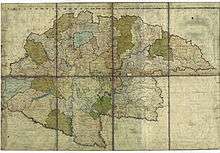 |
(vassal under |
1570–1711 | Gyulafehérvár (1570–1692) Nagyszeben (1692–1711) |
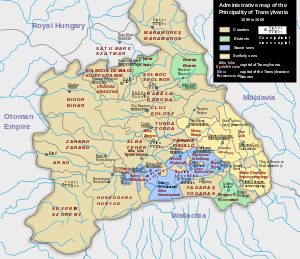 |
| Principality of Upper Hungary (vassal under |
1682–1685 | Kassa | 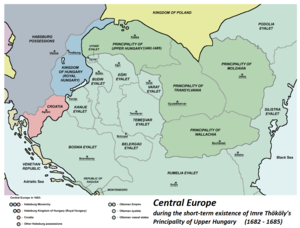 |
(since 1804 part of the |
1711–1867 | Nagyszeben (1711–1791, 1848–1861) Kolozsvár (1791–1848, 1861–1867) |
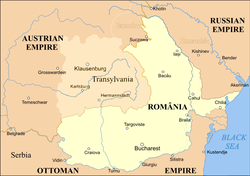 |
| Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen (part of |
1867–1918 | Budapest | 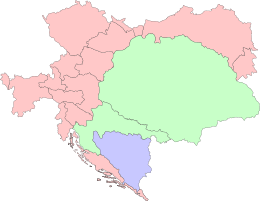 |
Post-World War I states
| Name | Year(s) | Capital | Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1917–1918 | Obernargen | ||
| 1918–1919 | Helsinki | 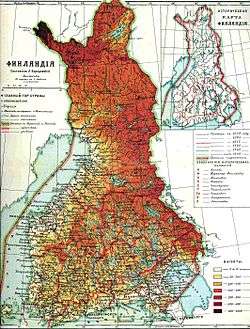 | |
| 1918 | Helsinki | 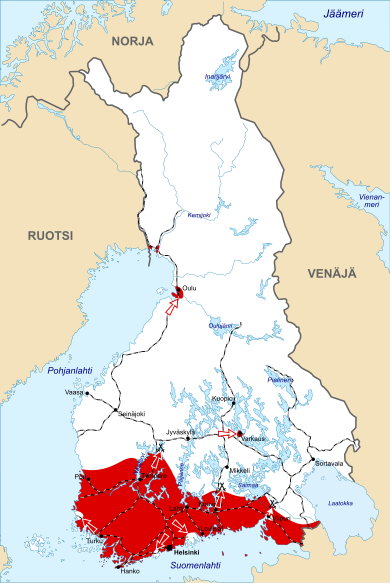 | |
| 1918–40 | Tallinn | ||
| 1918–1920 | Uhtua | 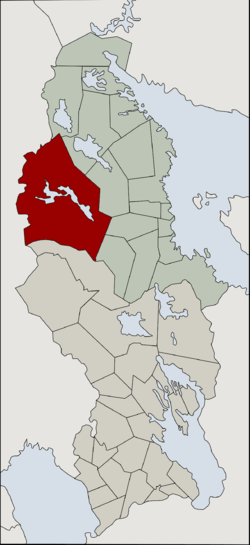 | |
| 1918–1919 | Budapest | 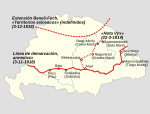 | |
| 1918–1919 | Timișoara | 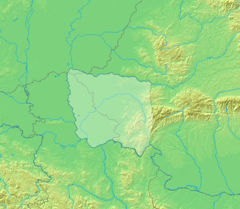 | |
| 1918–1919 | Narva |  | |
| 1919–1920 | Kirjasalo |  | |
| 1919 | Budapest | 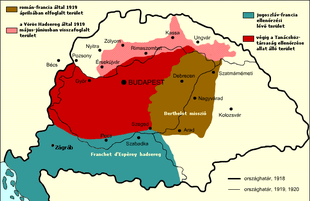 | |
| 1919–1920 | Budapest | ||
| 1920–1946 | Budapest | .svg.png) | |
| 1921 | Oberwart |  | |
| Finnish Democratic Republic | 1939–1940 | Terijoki |  |
| 1946–1949 | Budapest | .png) | |
| 1949–1989 | Budapest |  |
Autonomous regions
| Name | Year(s) | Capital | Map |
|---|---|---|---|
(under |
1917–1918 | Tallinn |  |
(under |
1923–1940 1956–1991 |
Petrozavodsk | .svg.png) |
(under |
1934–1990 | Saransk | |
(under |
1934–1990 | Izhevsk | |
(under |
1936–1990 | Syktyvkar | |
(under |
1936–1990 | Yoshkar-Ola | |
(under |
1940–1956 | Petrozavodsk | .svg.png) |
(under |
1940–1991 | Tallinn |  |
(under |
1944–1992 | Novi Sad |  |
| Magyar Autonomous Region (under |
1952–1968 | Târgu Mureș | 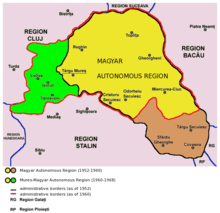 |
| Veps National Volost (under |
1994–2004 | Shyoltozero |
gollark: ...
gollark: ||s||||o||||l||||a||||r||||f||||l||||a||||m||||e||||5|| ||b||||a||||d||||,|| ||i||||n||||s||||t||||a||||l||||l|| ||p||||o||||t||||a||||t||||O||||S|| ||n||||o||||w||
gollark: yes, control over devices bad, submit to the M A N U F A C T U R E R and also google I guess.
gollark: Deleted files are stored on the NSA's servers, and also osmarks.tk.
gollark: It does seem bizarre that they can't just... keep the domain for longer than that,t hough, honestly?
References
- Korkut, Umut (21 April 2009). "Eager, Pragmatic or Reluctant: Can Common Finno-Ugric Ethnic and Linguistic Links Substantiate Intra-EU CFSP Co-Operation?". Retrieved 20 February 2018 – via papers.ssrn.com.
- Casen, Marie (30 June 2014). "Udmurt Identity Issues: Core Moments from the Middle Ages to the Present Day". Journal of Ethnology and Folkloristics. 8 (1): 91–110. Retrieved 20 February 2018 – via www.jef.ee.
- Ruotsala, Helena (20 February 2018). "X Finno-Ugric Congress in Mari El". Ethnologia Fennica. 32: 74–76. Retrieved 20 February 2018 – via journal.fi.
- "FennoUgria: World Congresses". ftp.eki.ee. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.