Favosites
Favosites is an extinct genus of tabulate coral characterized by polygonal closely packed corallites (giving it the common name "honeycomb coral").[1] The walls between corallites are pierced by pores known as mural pores which allowed transfer of nutrients between polyps. Favosites, like many corals, thrived in warm sunlit seas, feeding by filtering microscopic plankton with their stinging tentacles and often forming part of reef complexes.[2] The genus had a worldwide distribution from the Late Ordovician to Late Permian.[3]
| Favosites | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Favosites sp. from the Upper Ordovician of southern Indiana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Cnidaria |
| Class: | Anthozoa |
| Family: | †Favositidae |
| Genus: | †Favosites Lamarck 1816 |
| Type species | |
| F. gothlandicus | |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| More polished Favosites fossil. |
Distribution
Favosites had a vast distribution, and its fossils can be found on every continent (except Antarctica).[3]
Species
The following species of Favosites have been described:[3]
- F. abnormis
- F. adaverensis
- F. afghanicus
- F. antiquus
- F. bowerbanki
- F. burkhanensis
- F. desolatus
- F. exilis
- F. fallax
- F. favosiformis
- F. favosus
- F. fusiforme
- F. goldfussi
- F. gothlandicus
- F. hisingeri
- F. ingens
- F. intricatus
- F. issensis
- F. jaaniensis
- F. kalevi
- F. lichenarioides
- F. mirandus
- F. multicarinatus
- F. oculiporoides
- F. permica
- F. petropolitana
- F. praemaximus
- F. privatus
- F. serratus
- F. subfavosus
- F. subforbesi
Gallery
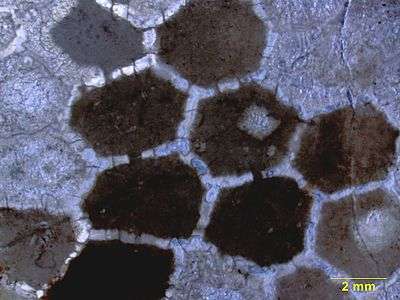 Sagittal cross-section of Favosites, showing communication pores between the corallites.
Sagittal cross-section of Favosites, showing communication pores between the corallites.
Upper Ordovician of southern Indiana
gollark: Generate a word, randomly shuffle it, and generate and shuffle another one, and assert that it says false for that.
gollark: * string, not word
gollark: Generate a word, randomly shuffle it, permute the case a bit, add spaces, assert that it says true for that.
gollark: Unlike my cool™ test suite, it does not randomly generate 1000 (one thousand) tests.
gollark: Oh cool, the new test suite uses my "great" C wrapper.
References
- Boardman, R.S. (1987). Fossil Invertebrates. Blackwell. p. 714.
- Feldman, R.M.; Hackathorn (1996). Fossils of Ohio. Ohio Division of Geological Survey Bulletin 70. p. 577.
- Favosites at Fossilworks.org
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
