Elmina
Elmina, also known as Edina by the local Fante, is a town and the capital of the Komenda/Edina/Eguafo/Abirem District on the south coast of Ghana in the Central Region, situated on a bay on the Atlantic Ocean, 12 kilometres (7 1⁄2 miles) west of Cape Coast. Elmina was the first European settlement in West Africa and it has a population of 33,576 people.[1]
Elmina | |
|---|---|
 Elmina Location of Elmina in Central Region, South Ghana | |
| Coordinates: 5°05′N 1°21′W | |
| Country | Ghana |
| Region | Central Region |
| District | Komenda/Edina/Eguafo/Abirem Municipal District |
| Population (2013) | |
| • Total | 33,576[1] |
| Time zone | GMT |
| • Summer (DST) | GMT |
History
Prior to the arrival of the Portuguese, the town was called Anomansah ("perpetual" or "inexhaustable drink") from its position on the peninsula between the Benya lagoon and the sea.[2]
In 1478 (during the War of the Castilian Succession), a Castilian armada of 35 caravels and a Portuguese fleet fought a large naval battle near Elmina for the control of the Guinea trade (gold, slaves, ivory and melegueta pepper). The war ended with a Portuguese naval victory, followed by the official recognition by the Catholic Monarchs of Portuguese sovereignty over most of the West African territories in dispute embodied in the Treaty of Alcáçovas,1479.[3][4] This was the first colonial war among European powers. Many more would come.
The town grew around São Jorge da Mina Castle, built by the Portuguese Diogo de Azambuja in 1482 on the site of a town or village called Amankwakurom or Amankwa. It was Portugal's West African headquarters for trade and exploitation of African wealth. The original Portuguese interest was gold, with 8,000 ounces shipped to Lisbon from 1487 to 1489, 22,500 ounces from 1494 to 1496, and 26,000 ounces by the start of the sixteenth century.[5]
Later the port expanded to include tens of thousands of slaves channeled through the trading post of Elmina, ten to twelve thousand from 1500-35 alone. By 1479, the Portuguese were transporting slaves from as far away as Benin, accounted for 10 percent of the trade in Elmina, and were used to clear land for tillage.[5]:23–24
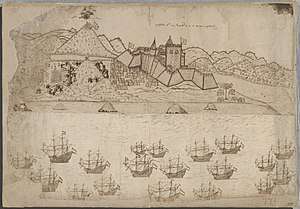
The location of Elmina made it a significant site for reprovisioning ships headed south towards the Cape of Good Hope on their way to India. After years of Portuguese wealth on the Elmina Coast, the Dutch learned of the profitable activity taking place through Barent Eriksz of Medemblik, one of the oldest traders and Guinea Navigators. Erickzen received information about trading on the Elmina coast while he was a prisoner on Principe and consequently was a major resource to the Dutch in terms of providing geographical and trading information.[6] The Dutch West India Company captured it in 1637; in subsequent centuries it was mostly used for the slave trade. The British attacked the city in 1782, but it remained in Dutch hands until 1872, when the Dutch Gold Coast was sold to the British. The king of Ashanti, claiming to be ground landlord, objected to its transfer, and the result was the third Anglo-Ashanti war of 1873–1874.[7]
Elmina is also home to Fort Coenraadsburg on St. Jago Hill, built by the Portuguese in 1555 under the name Forte de Santiago, it was used for commerce. In 1637 it was conquered and remained by the Dutch, after the conquest of Elmina's main castle. Today, Elmina's main economic industry is fishing, salt production and tourism. Also Elmina Castle very close to Cape Coast Castle both castles are notable for role in transatlantic slave trade Portuguese got there in 1481 and castle was finished in 3 years.
Economy
Beginning in 2003, Elmina, along with foreign investors, began The Elmina Strategy 2015, a massive project to improve many aspects of the town, consisting of water drainage and waste management helping to improve the health of the citizens, repairing the fishing industry and harbour of within Elmina, tourism and economic development, improved health services, and improved educational services.[8]
Climate
| Climate data for Elmina | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.8 (87.4) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.5 (88.7) |
30.6 (87.1) |
28.7 (83.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
27.9 (82.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
29.9 (85.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.7 (72.9) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.8 (74.8) |
23.7 (74.7) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.3 (72.1) |
21.8 (71.2) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.0 (73.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 25 (1.0) |
36 (1.4) |
84 (3.3) |
103 (4.1) |
203 (8.0) |
325 (12.8) |
102 (4.0) |
42 (1.7) |
55 (2.2) |
116 (4.6) |
84 (3.3) |
30 (1.2) |
201 (7.9) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[9] | |||||||||||||
Tourism
Apart from Elmina Castle and Fort Coenraadsburg, the main tourist attractions in Elmina include the Dutch Cemetery and the Elmina Java Museum.
Sister cities
List of sister cities of Elmina, designated by Sister Cities International:
| Country | City | County / District / Region / State | Date | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Netherlands | Gouda | South Holland | ||||
| United States | Macon | Georgia |
Festival
Elmina is home to the annual Bakatue Festival, a celebration of the sea and the local fishing culture, held the first Tuesday of July each year.[10]
“Bakatue” translated means “the opening of the lagoon” or the “Draining of the Lagoon”. It is celebrated to commemorate the founding of the town, Elmina by the Europeans. It is also celebrated to invoke the deity, Nana Benya's continuous protection of the state and its people.
Gallery
 Canoes at the shore
Canoes at the shore Elmina, a coastal town
Elmina, a coastal town Benya lagoon and it surroundings located in Elmina
Benya lagoon and it surroundings located in Elmina
References
Citations
- "World Gazetteer online". World-gazetteer.com. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012.
- Ampene, Kwame. "National Commission On Culture". www.ghanaculture.gov.gh. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- Historian Malyn Newitt: "However, in 1478 the Portuguese surprised thirty-five Castilian ships returning from Mina [Guinea] and seized them and all their gold. Another...Castilian voyage to Mina, that of Eustache de la Fosse, was intercepted ... in 780. (...) All things considered, it is not surprising that the Portuguese emerged victorious from this first maritime colonial war. They were far better organised than the Castilians, were able to raise money for the preparation and supply of their fleets, and had clear central direction from ... [Prince] John." In A History of Portuguese Overseas Expansion, 1400–1668, New York: Routledge, 2014, pp. 39, 40.
- Bailey W. Diffie and George D. Winius: "In a war in which the Castilians were victorious on land and the Portuguese at sea, …" in Foundations of the Portuguese Empire 1415-1580, volume I, University of Minnesota Press, 1985, p. 152.
- Ivor Wilks (1997). "Wangara, Akan, and Portuguese in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries". In Bakewell, Peter (ed.). Mines of Silver and Gold in the Americas. Aldershot: Variorum, Ashgate Publishing Limited. pp. 4–5.
- Marees, Pieter. Description and Historical Account of the Gold Kingdom of Guinea. London: The Oxford University Press, 1602. 206–22. Print.
-

- Elminaheritage.com Archived 22 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Elminaheritage.com.
- "Climate Elmina". Climate-Data.org. 2019. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- Expeditions, Ghana. "Edina Bakatue Festival". Festival AND eVENTS. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
Bibliography
- Diffie, Bailey W., and George D. Winius, Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415-1580, Volume 1, University of Minnesota Press, 1977.
- Newitt, Malyn, A History of Portuguese Overseas Expansion, 1400-1668, Routledge, New York, 2005.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Elmina. |


.svg.png)