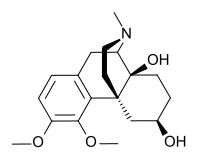
Drotebanol
Drotebanol (Oxymethebanol) is a morphinan derivative that acts as an opioid agonist. It was invented by Sankyo Company in Japan during the 1970s. It is synthesised from thebaine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Drotebanol, Oxymethebanol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H27NO4 |
| Molar mass | 333.428 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 165 to 167 °C (329 to 333 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Drotebanol has powerful antitussive (cough suppressant) effects, and is around 10x more potent than codeine in producing this effect. It also has analgesic effects several times stronger than codeine, but weaker than morphine.[1] In animal studies it was found to be moderately addictive and produced limited physical dependence, but not as severe as that seen with morphine or pethidine.[2] It was previously marketed for human use under the brand name Metebanyl, although it is now no longer used in medicine.
It is currently a Schedule I Narcotic controlled substance in the United States with a DEA ACSCN of 9335 and an annual aggregate manufacturing quota of zero.
References
- Kobayashi, S; Hasegawa, K; Mori, M; Takagi, H (1970). "Pharmacological studies on a new specifically potent antitussive agent, 14-hydroxydihydro-6 beta-thebainol-4-methylether (oxymethebanol)". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 20 (1): 43–6. PMID 5467447.
- Yanagita T, Miyasato K, Oinuma N, Yiyohara H (1977). "Dependence potential of drotebanol, codeine and thebaine tested in rhesus monkeys". Bulletin on Narcotics. 29 (1): 33–46. PMID 405065.